Physical activity for women with breast cancer after adjuvant therapy
- PMID: 29376559
- PMCID: PMC6491330
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011292.pub2
Physical activity for women with breast cancer after adjuvant therapy
Abstract
Background: Women with a diagnosis of breast cancer may experience short- and long-term disease and treatment-related adverse physiological and psychosocial outcomes. These outcomes can negatively impact prognosis, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and psychosocial and physical function. Physical activity may help to improve prognosis and may alleviate the adverse effects of adjuvant therapy.
Objectives: To assess effects of physical activity interventions after adjuvant therapy for women with breast cancer.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Breast Cancer Group (CBCG) Specialised Registry, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Embase, the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro), SPORTDiscus, PsycINFO, ClinicalTrials.gov, and the World Health Organization (WHO) International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, on 18 September 2015. We also searched OpenGrey and Healthcare Management Information Consortium databases.
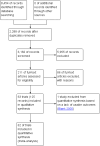
Selection criteria: We searched for randomised and quasi-randomised trials comparing physical activity interventions versus control (e.g. usual or standard care, no physical activity, no exercise, attention control, placebo) after adjuvant therapy (i.e. after completion of chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy, but not hormone therapy) in women with breast cancer.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently selected studies, assessed risk of bias, and extracted data. We contacted trial authors to ask for additional information when needed. We calculated an overall effect size with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for each outcome and used GRADE to assess the quality of evidence for the most important outcomes.
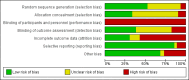
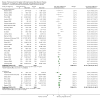
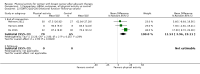
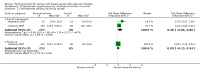
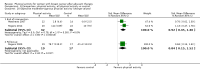
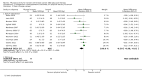
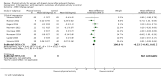
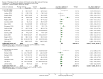
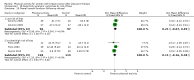
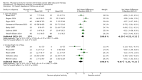
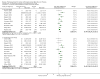
Main results: We included 63 trials that randomised 5761 women to a physical activity intervention (n = 3239) or to a control (n = 2524). The duration of interventions ranged from 4 to 24 months, with most lasting 8 or 12 weeks (37 studies). Twenty-eight studies included aerobic exercise only, 21 involved aerobic exercise and resistance training, and seven used resistance training only. Thirty studies described the comparison group as usual or standard care, no intervention, or control. One-fifth of studies reported at least 20% intervention attrition and the average physical activity adherence was approximately 77%.No data were available on effects of physical activity on breast cancer-related and all-cause mortality, or on breast cancer recurrence. Analysis of immediately postintervention follow-up values and change from baseline to end of intervention scores revealed that physical activity interventions resulted in significant small-to-moderate improvements in HRQoL (standardised mean difference (SMD) 0.39, 95% CI 0.21 to 0.57, 22 studies, 1996 women; SMD 0.78, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.17, 14 studies, 1459 women, respectively; low-quality evidence), emotional function (SMD 0.21, 95% CI 0.10 to 0.32, 26 studies, 2102 women, moderate-quality evidence; SMD 0.31, 95% CI 0.09 to 0.53, 15 studies, 1579 women, respectively; low-quality evidence), perceived physical function (SMD 0.33, 95% CI 0.18 to 0.49, 25 studies, 2129 women; SMD 0.60, 95% CI 0.23 to 0.97, 13 studies, 1433 women, respectively; moderate-quality evidence), anxiety (SMD -0.57, 95% CI -0.95 to -0.19, 7 studies, 326 women; SMD -0.37, 95% CI -0.63 to -0.12, 4 studies, 235 women, respectively; low-quality evidence), and cardiorespiratory fitness (SMD 0.44, 95% CI 0.30 to 0.58, 23 studies, 1265 women, moderate-quality evidence; SMD 0.83, 95% CI 0.40 to 1.27, 9 studies, 863 women, respectively; very low-quality evidence).Investigators reported few minor adverse events.Small improvements in physical activity interventions were sustained for three months or longer postintervention in fatigue (SMD -0.43, 95% CI -0.60 to -0.26; SMD -0.47, 95% CI -0.84 to -0.11, respectively), cardiorespiratory fitness (SMD 0.36, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.69; SMD 0.42, 95% CI 0.05 to 0.79, respectively), and self-reported physical activity (SMD 0.44, 95% CI 0.17 to 0.72; SMD 0.51, 95% CI 0.08 to 0.93, respectively) for both follow-up values and change from baseline scores.However, evidence of heterogeneity across trials was due to variation in intervention components (i.e. mode, frequency, intensity, duration of intervention and sessions) and measures used to assess outcomes. All trials reviewed were at high risk of performance bias, and most were also at high risk of detection, attrition, and selection bias. In light of the aforementioned issues, we determined that the evidence was of very low, low, or moderate quality.
Authors' conclusions: No conclusions regarding breast cancer-related and all-cause mortality or breast cancer recurrence were possible. However, physical activity interventions may have small-to-moderate beneficial effects on HRQoL, and on emotional or perceived physical and social function, anxiety, cardiorespiratory fitness, and self-reported and objectively measured physical activity. The positive results reported in the current review must be interpreted cautiously owing to very low-to-moderate quality of evidence, heterogeneity of interventions and outcome measures, imprecision of some estimates, and risk of bias in many trials. Future studies with low risk of bias are required to determine the optimal combination of physical activity modes, frequencies, intensities, and durations needed to improve specific outcomes among women who have undergone adjuvant therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures



























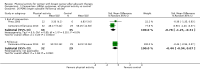


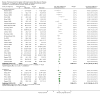







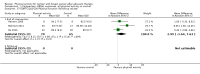
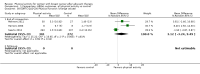
















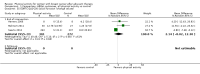










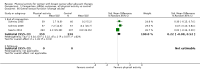








































































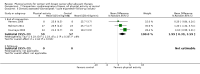

















































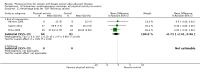

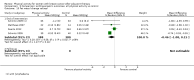




































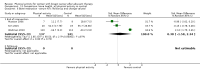



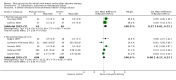







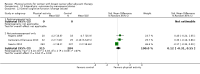










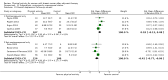


















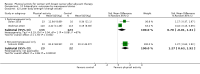




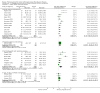

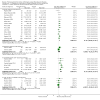













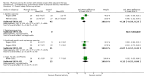





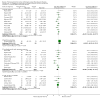


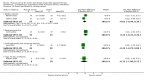












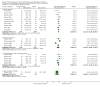


























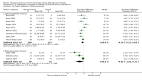




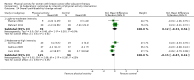











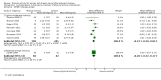

























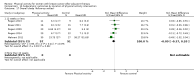



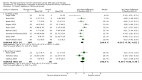












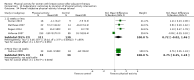





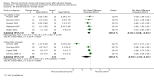










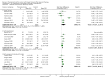

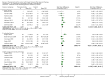











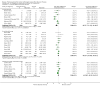


























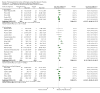

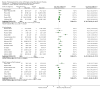

























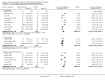





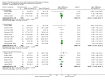

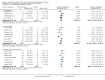





































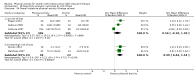

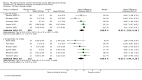










Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Banasik 2011 {published data only}
-
- Banasik J, Williams H, Haberman M, Blank SE, Bendel R. Effect of Iyengar yoga practice on fatigue and diurnal salivary cortisol concentration in breast cancer survivors. Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners 2011;23(3):135‐42. - PubMed
Baruth 2013 {published data only}
-
- Baruth M, Wilcox S, Der AC, Heiney S. Effects of home‐based walking on quality of life and fatigue outcomes in early stage breast cancer survivors: a 12‐week pilot study. Journal of Physical Activity and Health 2015;12 Suppl 1:S110‐S8. - PubMed
Basen‐Enquist 2006 {published data only}
-
- Basen‐Engquist K, Taylor CL, Rosenblum C, Smith MA, Shinn EH, Greisinger A, et al. Randomized pilot test of a lifestyle physical activity intervention for breast cancer survivors. Patient Education & Counseling 2006;64(1‐3):225‐34. - PubMed
Blank 2005 {published data only}
-
- Blank SE, Kittel J, Haberman MR. Active practice of Iyengar yoga as an intervention for breast cancer survivors. International Journal of Yoga Therapy 2003;13(1):51‐9.
Bower 2011 {published data only}
Cadmus 2009 {published data only}
-
- Irwin ML, Varma K, Alvarez‐Reeves M, Cadmus L, Wiley A, Chung GG, et al. Randomized controlled trial of aerobic exercise on insulin and insulin‐like growth factors in breast cancer survivors: the Yale Exercise and Survivorship Study. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention 2009;18(1):306‐13. - PMC - PubMed
Cantarero‐Villanueva 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cantarero‐Villanueva I, Fernandez‐Lao C, Cuesta‐Vargas AI, Moral‐Avila R, Fernandez‐De‐Las‐Penas C, Arroyo‐Morales M. The effectiveness of a deep water aquatic exercise program in cancer‐related fatigue in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2013;94(2):221‐30. - PubMed
Carson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Carson JW, Carson KM, Porter LS, Keefe FJ, Seewaldt VL. Yoga of Awareness program for menopausal symptoms in breast cancer survivors: results from a randomized trial. Supportive Care in Cancer 2009;17(10):1301‐9. - PubMed
Cerulli 2014 {published data only}
-
- Cerulli C, Minganti C, Santis C, Tranchita E, Quaranta F, Parisi A. Therapeutic horseback riding in breast cancer survivors: a pilot study. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine 2014;20(8):623‐9. - PubMed
Cormie 2014 {published data only}
-
- Cormie P, Pumpa K, Galvao DA, Turner E, Spry N, Saunders C, et al. Is it safe and efficacious for women with lymphedema secondary to breast cancer to lift heavy weights during exercise: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Cancer Survivorship 2013;7(3):413‐24. - PubMed
Courneya 2003 {published data only}
-
- Courneya KS, Jones LW, Mackey JR, Fairey AS. Exercise beliefs of breast cancer survivors before and after participation in a randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine 2006;13(3):259‐64. - PubMed
-
- Courneya KS, Mackey JR, Bell GJ, Jones LW, Field CJ, Fairey AS. Randomized controlled trial of exercise training in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors: cardiopulmonary and quality of life outcomes. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2003;21(9):1660‐8. - PubMed
-
- Fairey AS, Courneya KS, Field CJ, Bell GJ, Jones LW, Mackey JR. Effects of exercise training on fasting insulin, insulin resistance, insulin‐like growth factors, and insulin‐like growth factor binding proteins in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention 2003;12(8):721‐7. - PubMed
-
- Fairey AS, Courneya KS, Field CJ, Bell GJ, Jones LW, Mackey JR. Randomized controlled trial of exercise and blood immune function in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors. Journal of Applied Physiology 2005;98(4):1534‐40. - PubMed
-
- Fairey AS, Courneya KS, Field CJ, Bell GJ, Jones LW, Martin BS, et al. Effect of exercise training on C‐reactive protein in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. Brain, Behavior, & Immunity 2005;19(5):381‐8. - PubMed
Cuesta‐Vargas 2014 {published data only}
-
- Cuesta‐Vargas AI, Buchan J, Arroyo‐Morales M. A multimodal physiotherapy programme plus deep water running for improving cancer‐related fatigue and quality of life in breast cancer survivors. European Journal of Cancer Care 2014;23(1):15‐21. - PubMed
Daley 2007 {published data only}
-
- Daley AJ, Crank H, Mutrie N, Saxton JM, Coleman R. Determinants of adherence to exercise in women treated for breast cancer. European Journal of Oncology Nursing 2007;11(5):392‐9. - PubMed
-
- Daley AJ, Crank H, Mutrie N, Saxton JM, Coleman R. Patient recruitment into a randomised controlled trial of supervised exercise therapy in sedentary women treated for breast cancer. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2007;28(5):603‐13. - PubMed
-
- Daley AJ, Crank H, Saxton JM, Mutrie N, Coleman R, Roalfe A. Randomized trial of exercise therapy in women treated for breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2007;25(13):1713‐21. - PubMed
-
- Daley AJ, Mutrie N, Crank H, Coleman R, Saxton J. Exercise therapy in women who have had breast cancer: design of the Sheffield women's exercise and well‐being project. Health Education Research 2004;19(6):686‐97. - PubMed
DeNysschen 2011 {published data only}
-
- DeNysschen CA, Brown JK, Cho MH, Dodd MJ. Nutritional symptom and body composition outcomes of aerobic exercise in women with breast cancer. Clinical Nursing Research 2011;20(1):29‐46. - PubMed
Do 2015 {published data only}
Dolan 2016 {published data only}
-
- Dolan LB, Campbell K, Gelmon K, Neil‐Sztramko S, Holmes D, McKenzie DC. Interval versus continuous aerobic exercise training in breast cancer survivors ‐ a pilot RCT. Supportive Care in Cancer 2016;24(1):119‐27. - PubMed
Duijits 2012 {published data only}
-
- Duijts SFA, Beurden M, Oldenburg HSA, Hunter MS, Kieffer JM, Stuiver MM, et al. Efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy and physical exercise in alleviating treatment‐induced menopausal symptoms in patients with breast cancer: results of a randomized, controlled, multicenter trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2012;30(33):4124‐33. - PubMed
-
- Mewes JC, Steuten LM, Duijts SF, Oldenburg HS, Beurden M, Stuiver MM, et al. Cost‐effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy and physical exercise for alleviating treatment‐induced menopausal symptoms in breast cancer patients. Journal of Cancer Survivorship 2015;9(1):126‐35. - PubMed
Ergun 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ergun M, Eyigor S, Karaca B, Kisim A, Uslu R. Effects of exercise on angiogenesis and apoptosis‐related molecules, quality of life, fatigue and depression in breast cancer patients. European Journal of Cancer Care 2013;22(5):626‐37. - PubMed
Fillion 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fillion L, Gagnon P, Leblond F, Gelinas C, Savard J, Dupuis R, et al. A brief intervention for fatigue management in breast cancer survivors. Cancer Nursing 2008;31(2):145‐59. - PubMed
Guinan 2013 {published data only}
-
- Guinan EM, Hussey JM, Walsh JM, Kennedy MJ, Connolly EM. The effect of aerobic exercise on the metabolic risk profile of breast cancer survivors 2‐6 months post chemotherapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2011;29(27):1983–92.
Hatchett 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hatchett A, Hallam JS, Ford MA. Evaluation of a social cognitive theory‐based email intervention designed to influence the physical activity of survivors of breast cancer. Psycho‐Oncology 2013;22:829–36. - PubMed
Heim 2007 {published data only}
-
- Heim ME, Malsburg ML, Niklas A. Randomized controlled trial of a structured training program in breast cancer patients with tumor‐related chronic fatigue. Onkologie 2007;30(8‐9):429‐34. - PubMed
Herrero 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gómez AM, Martinez C, Fiuza‐Luces C, Herrero F, Pérez M, Madero L, et al. Exercise training and cytokines in breast cancer survivors. International Journal of Sports Medicine 2011;32:461‐7. - PubMed
-
- Herrero F, San Juan AF, Fleck SJ, Balmer J, Pérez M, Cañete S, et al. Combined aerobic and resistance training in breast cancer survivors: a randomized, controlled pilot trial. International Journal of Sports Medicine 2006;27(7):573‐80. - PubMed
Irwin 2015 {published data only}
Kaltsatou 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kaltsatou A, Mameletzi D, Douka S. Physical and psychological benefits of a 24‐week traditional dance program in breast cancer survivors. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies 2011;15(2):162‐7. - PubMed
Kiecolt‐Glaser 2014 {published data only}
Kim 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kim SH, Cho YU, Kim SJ, Hong S, Han MS, Choi E. The effect on bone outcomes of adding exercise to supplements for osteopenic breast cancer survivors: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Cancer Nursing 2016;39(2):144‐52. - PubMed
Ligibel 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ligibel JA, Campbell N, Partridge A, Chen WY, Salinardi T, Chen H, et al. Impact of a mixed strength and endurance exercise intervention on insulin levels in breast cancer survivors. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2008;26(6):907‐12. - PubMed
-
- Ligibel JA, Giobbie‐Hurder A, Olenczuk D, Campbell N, Salinardi T, Winer EP, et al. Impact of a mixed strength and endurance exercise intervention on levels of adiponectin, high molecular weight adiponectin and leptin in breast cancer survivors. Cancer Causes & Control 2009;20(8):1523‐8. - PubMed
Littman 2012 {published data only}
Loh 2014 {published data only}
-
- Loh SY, Lee SY, Murray L. The Kuala Lumpur Qigong trial for women in the cancer survivorship phase‐efficacy of a three‐arm RCT to improve QOL. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention 2014;15(19):8127‐34. - PubMed
Loudon 2014 {published data only}
Malicka 2011 {published data only}
-
- Malicka I, Stefanska M, Rudziak M, Jarmoluk P, Pawlowska K, Szczepanska‐Gieracha J, et al. The influence of Nordic walking exercise on upper extremity strength and the volume of lymphoedema in women following breast cancer treatment. Isokinetics and Exercise Science 2011;19(4):295‐304.
Martin 2013 {published data only}
-
- Martin E, Battaglini C, Groff D, Naumann F. Improving muscular endurance with the MVe Fitness Chair™ in breast cancer survivors: a feasibility and efficacy study. Journal of Science & Medicine in Sport 2013;16(4):372‐6. - PubMed
Matthews 2007 {published data only}
-
- Matthews CE, Wilcox S, Hanby CL, Ananian C, Heiney SP, Gebretsadik T, et al. Evaluation of a 12‐week home‐based walking intervention for breast cancer survivors. Supportive Care in Cancer 2007;15(2):203‐11. - PubMed
McKenzie 2003 {published data only}
-
- McKenzie DC, Kalda AL. Effect of upper extremity exercise on secondary lymphedema in breast cancer patients: a pilot study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2003;21(3):463‐6. - PubMed
Mehnert 2011 {published data only}
-
- Mehnert A, Veers S, Howaldt D, Braumann KM, Koch U, Schulz KH. Effects of a physical exercise rehabilitation group program on anxiety, depression, body image, and health‐related quality of life among breast cancer patients. Onkologie 2011;34(5):248‐53. - PubMed
Milne 2008 {published data only}
-
- Milne HM, Wallman KE, Gordon S, Courneya KS. Effects of a combined aerobic and resistance exercise program in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2008;108(2):279‐88. - PubMed
-
- Milne HM, Wallman KE, Gordon S, Courneya KS. Impact of a combined resistance and aerobic exercise program on motivational variables in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2008;36(2):158‐66. - PubMed
Murtezani 2014 {published data only}
-
- Murtezani A, Ibraimi Z, Bakalli A, Krasniqi S, Disha ED, Kurtishi I. The effect of aerobic exercise on quality of life among breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics 2014;10(3):658‐64. - PubMed
Musanti 2012 {published data only}
-
- Musanti R. A study of exercise modality and physical self‐esteem in breast cancer survivors. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2012;44(2):352‐61. - PubMed
Mustian 2004 {published data only}
-
- Mustian KM, Katula JA, Gill DL, Roscoe JA, Lang D, Murphy K. Tai Chi Chuan, health‐related quality of life and self‐esteem: a randomized trial with breast cancer survivors. Supportive Care in Cancer 2004;12(12):871‐6. - PubMed
-
- Mustian KM, Katula JA, Zhao H. A pilot study to assess the influence of tai chi chuan on functional capacity among breast cancer survivors. Journal of Supportive Oncology 2006;4(3):139‐45. - PubMed
-
- Peppone LJ, Mustian K, Rosier RN, Piazza KM, Hicks DG, Palesh OG, et al. The effect of tai chi chuan on bone remodeling and cytokines among breast cancer survivors: a feasibility trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2009;27(15):9610.
Naumann 2012 {published data only}
-
- Naumann F, Martin E, Philpott M, Smith C, Groff D, Battaglini C. Can counselling add value to an exercise intervention for improving quality of life in breast cancer survivors? A feasibility study. Journal of Supportive Oncology 2012;10(5):188‐94. - PubMed
Nieman 1995 {published data only}
-
- Nieman DC, Cook VD, Henson DA, Suttles J, Rejeski WJ, Ribisl PM, et al. Moderate exercise training and natural killer cell cytotoxic activity in breast cancer patients. International Journal of Sports Medicine 1995;16(5):334‐7. - PubMed
Nikander 2007 {published data only}
-
- Nikander R, Sievänen H, Ojala K, Oivanen T, Kellokumpu‐Lehtinen P, Saarto T. Effect of a vigorous aerobic regimen on physical performance in breast cancer patients ‐ a randomized controlled pilot trial. Acta Oncologica 2007;46(2):181‐6. - PubMed
Payne 2008 {published data only}
-
- Payne JK, Held J, Thorpe J, Shaw H. Effect of exercise on biomarkers, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and depressive symptoms in older women with breast cancer receiving hormonal therapy. Oncology Nursing Forum 2008;35(4):635‐42. - PubMed
Peppone 2015 {published data only}
Pinto 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pinto BM, Clark MM, Maruyama NC, Feder SI. Psychological and fitness changes associated with exercise participation among women with breast cancer. Psycho‐Oncology 2003;12(2):118‐26. - PubMed
Pinto 2005 {published data only}
-
- Pinto BM, Frierson GM, Rabin C, Trunzo JJ, Marcus BH. Home‐based physical activity intervention for breast cancer patients. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(15):3577‐87. - PubMed
-
- Pinto BM, Trunzo JJ, Rabin C, Cady B, Fenton MA, Herman A, et al. Recruitment strategies for a home‐based physical activity intervention for breast cancer patients. Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings 2004;11(3):171‐8.
-
- Rabin C, Pinto BM, Frierson G. Mediators of a randomized controlled physical activity intervention for breast cancer survivors. Journal Sport Exercise Psychology 2006;28:269‐84.
Pinto 2015 {published data only}
Portela 2008 {published data only}
Rahnama 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nuri R, Kordi MR, Moghaddasi M, Rahnama N, Damirchi A, Rahmani‐Nia F, et al. Effect of combination exercise training on metabolic syndrome parameters in postmenopausal women with breast cancer. Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics 2012;8(2):238‐42. - PubMed
Rogers 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rogers LQ, Hopkins‐Price P, Vicari S, Markwell S, Pamenter R, Courneya KS, et al. Physical activity and health outcomes three months after completing a physical activity behavior change intervention: persistent and delayed effects. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention 2009;8(5):1410‐8. - PubMed
-
- Rogers LQ, Hopkins‐Price P, Vicari S, Pamenter R, Courneya KS, Markwell S, et al. A randomized trial to increase physical activity in breast cancer survivors. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2009;41(4):935‐46. - PubMed
Rogers 2013 {published data only}
Rogers 2014 {published data only}
Rogers 2015 {published data only}
-
- Rogers LQ, Courneya KS, Anton PM, Hopkins‐Price P, Verhulst S, Vicari SK, et al. Effects of the BEAT Cancer physical activity behavior change intervention on physical activity, aerobic fitness, and quality of life in breast cancer survivors: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2015;149(1):109‐19. - PMC - PubMed
Saarto 2012 {published data only}
-
- Luoma ML, Hakamies‐Blomqvist L, Blomqvist C, Nikander R, Gustavsson‐Lilius M, Saarto T. Experiences of breast cancer survivors participating in a tailored exercise intervention ‐ a qualitative study. Anticancer Research 2014;34(3):1193‐9. - PubMed
-
- Nikander R, Sievanen H, Ojala K, Kellokumpu‐Lehtinen PL, Palva T, Blomqvist C, et al. Effect of exercise on bone structural traits, physical performance and body composition in breast cancer patients ‐ a 12‐month RCT. Journal of Musculoskeletal Neuronal Interactions 2012;12(3):127‐35. - PubMed
-
- Saarto T, Penttinen HM, Sievanen H, Kellokumpu‐Lehtinen PL, Hakamies‐Blomqvist L, Nikander R, et al. Effectiveness of a 12‐month exercise program on physical performance and quality of life of breast cancer survivors. Anticancer Research 2012;32(9):3875‐84. - PubMed
-
- Saarto T, Sievanen H, Kellokumpu‐Lehtinen P, Nikander R, Vehmanen L, Huovinen R, et al. Effect of supervised and home exercise training on bone mineral density among breast cancer patients. A 12‐month randomised controlled trial. Osteoporosis International 2012;23:1601–12. - PubMed
Schmitz 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ahmed RL, Thomas W, Yee D, Schmitz KH. Randomized controlled trial of weight training and lymphedema in breast cancer survivors. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006;24(18):2765‐72. - PubMed
-
- Ohira T, Schmitz KH, Ahmed RL, Yee D. Effects of weight training on quality of life in recent breast cancer survivors: the Weight Training for Breast Cancer Survivors (WTBS) study. Cancer 2006;106(9):2076‐83. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz KH, Ahmed RL, Hannan PJ, Yee D. Safety and efficacy of weight training in recent breast cancer survivors to alter body composition, insulin, and insulin‐like growth factor axis proteins. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention 2005;14(7):1672‐80. - PubMed
Schmitz 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hayes SC, Speck RM, Reimet E, Stark A, Schmitz KH. Does the effect of weight lifting on lymphedema following breast cancer differ by diagnostic method: results from a randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2011;130(1):227‐34. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz KH, Ahmed RL, Troxel A, Cheville A, Smith R, Lewis‐Grant L, et al. Weight lifting in women with breast‐cancer‐related lymphedema. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;361(7):664‐73. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz KH, Ahmed RL, Troxel AB, Cheville A, Lewis‐Grant L, Smith R, et al. Weight lifting for women at risk for breast cancer‐related lymphedema: a randomized trial. JAMA 2010;304(24):2699‐705. - PubMed
Segar 1998 {published data only}
-
- Segar ML, Katch VL, Roth RS, Garcia AW, Portner TI, Glickman SG, et al. The effect of aerobic exercise on self‐esteem and depressive and anxiety symptoms among breast cancer survivors. Oncology Nursing Forum 1998;25(1):107‐13. - PubMed
Short 2014 {published data only}
-
- Short CE, James EL, Girgis A, D’Souza MI, Plotnikoff RC. Main outcomes of the Move More for Life Trial: a randomised controlled trial examining the effects of tailored‐print and targeted‐print materials for promoting physical activity among post‐treatment breast cancer survivors. Psycho‐Oncology 2014;24(7):771‐8. - PubMed
-
- Short CE, James EL, Plotnikoff RC. Theory‐ and evidence‐based development and process evaluation of the Move More for Life program: a tailored‐print intervention designed to promote physical activity among post‐treatment breast cancer survivors. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2013;10:124. - PMC - PubMed
Taleghani 2012 {published data only}
Vallance 2007 {published data only}
-
- Vallance J, Plotnikoff RC, Karvinen KH, Mackey JR, Courneya KS. Understanding physical activity maintenance in breast cancer survivors. American Journal of Health Behavior 2010;34(2):225‐36. - PubMed
-
- Vallance JK, Courneya KS, Plotnikoff RC, Dinu I, MacKey JR. Maintenance of physical activity in breast cancer survivors after a randomized trial. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2008;40(1):173‐80. - PubMed
-
- Vallance JK, Courneya KS, Plotnikoff RC, Mackey JR. Analyzing theoretical mechanisms of physical activity behavior change in breast cancer survivors: results from the Activity Promotion (ACTION) trial. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2008;35(2):150‐8. - PubMed
-
- Vallance JK, Courneya KS, Plotnikoff RC, Yasui Y, Mackey JR. Randomized controlled trial of the effects of print materials and step pedometers on physical activity and quality of life in breast cancer survivors. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2007;25(17):2352‐9. - PubMed
-
- Vallance JKH. Promoting physical activity in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences [Internet] 2008;68(7):2877.
Waltman 2010 {published data only}
-
- McGuire R, Waltman N, Zimmerman L. Intervention components promoting adherence to strength training exercise in breast cancer survivors with bone loss. Western Journal of Nursing Research 2011;33(5):671‐89. - PubMed
-
- Ott C, Waltman N, Twiss J, Gross G, Lindsey A, Moore T. Predictors of adherence to strength training at six months in breast cancer survivors at risk for osteoporosis. Oncology Nursing Forum 2007;34(1):200‐1.
-
- Ott CD, Twiss JJ, Waltman NL, Gross GJ, Lindsey AM. Challenges of recruitment of breast cancer survivors to a randomized clinical trial for osteoporosis prevention. Cancer Nursing 2006;29(1):21‐33. - PubMed
-
- Twiss JJ, Waltman NL, Berg K, Ott CD, Gross GJ, Lindsey AM. An exercise intervention for breast cancer survivors with bone loss. Journal of Nursing Scholarship 2009;41(1):20‐7. - PubMed
-
- Waltman NL, Twiss JJ, Ott CD, Gross GJ, Lindsey AM, Moore TE, et al. The effect of weight training on bone mineral density and bone turnover in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors with bone loss: a 24‐month randomized controlled trial. Osteoporosis International 2010;21(8):1361‐9. - PubMed
Winters‐Stone 2011 {published data only}
-
- Dobek J, Winters‐Stone KM, Bennett JA, Nail L. Musculoskeletal changes after 1 year of exercise in older breast cancer survivors. Journal of Cancer Survivorship: Research and Practice 2014;8(2):304‐11. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Anderson 2012 {published data only}
Benton 2014 {published data only}
-
- Benton MJ, Schlairet MC, Gibson DR. Change in quality of life among breast cancer survivors after resistance training: is there an effect of age?. Journal of Aging and Physical Activity 2014;22(2):178‐85. - PubMed
Bloom 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bloom JR, Stewart SL, D'Onofrio CN, Luce J, Banks PJ. Addressing the needs of young breast cancer survivors at the 5 year milestone: can a short‐term, low intensity intervention produce change?. Journal of Cancer Survivorship: Research and Practice 2008;2(3):190‐204. - PubMed
Buffart 2012 {published data only}
-
- Buffart L, Ross W, Chinapaw M, Brug J, Knol D, Korstjens I, et al. How does exercise improve cancer survivors' quality of life?. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 2012;15:S333‐S4.
Burnham 2002 {published data only}
-
- Burnham TR, Wilcox A. Effects of exercise on physiological and psychological variables in cancer survivors. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2002;34(12):1863‐7. - PubMed
Cadmus‐Bertram 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cadmus Bertram LA, Pierce JP, Patterson RE, Ojeda‐Fournier H, Newman VA, Parker BA. Training overweight/obese older women at high risk for breast cancer to use web‐based weight loss tools: the HELP pilot study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2011;29(27):233.
Cantarero‐Villanueva 2012 {published data only}
-
- Cantarero‐Villanueva I, Fernandez‐Lao C, Fernandez‐de‐las‐Penas C, Lopez‐Barajas IB, Del‐Moral‐Avila R, la‐Llave‐Rincon AI, et al. Effectiveness of water physical therapy on pain, pressure pain sensitivity, and myofascial trigger points in breast cancer survivors: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Pain Medicine (United States) 2012;13(11):1509‐19. - PubMed
Cantarero‐Villanueva 2012a {published data only}
-
- Cantarero‐Villanueva I, Fernandez‐Lao C, Moral‐Avila R, Fernandez‐de‐Las‐Penas C, Feriche‐Fernandez‐Castanys MB, Arroyo‐Morales M. Effectiveness of core stability exercises and recovery myofascial release massage on fatigue in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Evidence‐Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2012;2012:1‐9. [DOI: 10.1155/2012/620619] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cantarero‐Villanueva I, Fernandez‐Lao C, Diaz‐Rodriguez L, Fernandez‐de‐las‐Penas C, Moral‐Avila R, Arroyo‐Morales M. A multimodal exercise program and multimedia support reduce cancer‐related fatigue in breast cancer survivors: a randomised controlled clinical trial. European Journal of Integrative Medicine 2011;3(3):e189‐e200.
Cantarero‐Villanueva 2013a {published data only}
-
- Cantarero‐Villanueva I, Fernández‐Lao C, Caro‐Morán E, Morillas‐Ruiz J, Galiano‐Castillo N, Díaz‐Rodríguez L, et al. Aquatic exercise in a chest‐high pool for hormone therapy‐induced arthralgia in breast cancer survivors: a pragmatic controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2013;27(2):123‐32. - PubMed
Carter 2012 {published data only}
-
- Carter CL, Onicescu G, Cartmell KB, Sterba KR, Tomsic J, Alberg AJ. The comparative effectiveness of a team‐based versus group‐based physical activity intervention for cancer survivors. Supportive Care in Cancer 2012;20(8):1699‐707. - PubMed
Casla 2015 {published data only}
-
- Casla S, Lopez‐Tarruella S, Jerez Y, Marquez‐Rodas I, Galvao DA, Newton RU, et al. Supervised physical exercise improves VO2max, quality of life, and health in early stage breast cancer patients: a randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2015;153(2):371‐82. - PubMed
Cheema 2006 {published data only}
-
- Cheema BSB, Gaul CA. Full‐body exercise training improves fitness and quality of life in survivors of breast cancer. Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research 2006;20(1):14‐21. - PubMed
Cho 2006 {published data only}
-
- Cho OH, Yoo YS, Kim NC. Efficacy of comprehensive group rehabilitation for women with early breast cancer in South Korea. Nursing & Health Sciences 2006;8(3):140‐6. - PubMed
Cohen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Cohen L, Chen Z, Arun B, Shao Z, Dryden M, Xu L, et al. External Qigong therapy for women with breast cancer prior to surgery. Integrative Cancer Therapies 2010;9(4):348‐53. - PubMed
Culos‐Reed 2006 {published data only}
-
- Culos‐Reed S, Carlson LE, Daroux LM, Hately‐Aldous S. A pilot study of yoga for breast cancer survivors: physical and psychological benefits. Psycho‐Oncology 2006;15(10):891‐7. - PubMed
Cunningham 1998 {published data only}
-
- Cunningham AJ, Edmonds CV, Jenkins GP, Pollack H, Lockwood GA, Warr D. A randomized controlled trial of the effects of group psychological therapy on survival in women with metastatic breast cancer. Psycho‐Oncology 1998;7(6):508‐17. - PubMed
D'Atillio 2007 {published data only}
-
- D'Attilio MG, Angelillo A, Fochitto M, Sorrentino P, Capelli G, Federico B, et al. Adapted physical activity for breast cancer patients. Can the quality of life be enhanced?. Igiene Moderna 2007;128(5):167‐78.
Damush 2006 {published data only}
-
- Damush TM, Perkins A, Miller K. The implementation of an oncologist referred, exercise self‐management program for older breast cancer survivors. Psycho‐Oncology 2006;15(10):884‐90. - PubMed
Danhauer 2009 {published data only}
De Backer 2007 {published data only}
-
- Backer IC, Breda E, Vreugdenhil A, Nijziel MR, Kester AD, Schep G. High‐intensity strength training improves quality of life in cancer survivors. Acta Oncologica 2007;46(8):1143‐51. - PubMed
Demark 2006 {published data only}
Dimeo 2008 {published data only}
-
- Dimeo F, Schwartz S, Wesel N, Voigt, Thiel E. Effects of an endurance and resistance exercise program on persistent cancer‐related fatigue after treatment. Annals of Oncology 2008;19(8):1495‐9. - PubMed
Djuric 2002 {published data only}
-
- Djuric Z, DiLaura NM, Jenkins I, Darga L, Jen CK, Mood D, et al. Combining weight‐loss counseling with the weight watchers plan for obese breast cancer survivors. Obesity Research 2002;10(7):657‐65. - PubMed
Eyigor 2010 {published data only}
-
- Eyigor S, Karapolat H, Yesil H, Uslu R, Durmaz B. Effects of pilates exercises on functional capacity, flexibility, fatigue, depression and quality of life in female breast cancer patients: a randomized controlled study. European Journal of Physical & Rehabilitation Medicine 2010;46(4):481‐7. - PubMed
Fernandez‐Lao 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez‐Lao C, Cantarero‐Villanueva I, Fernandez‐De‐Las‐Penas C, Moral‐Avila R, Castro‐Sanchez AM, Arroyo‐Morales M. Effectiveness of a multidimensional physical therapy program on pain, pressure hypersensitivity, and trigger points in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clinical Journal of Pain 2012;28(2):113‐21. - PubMed
Fernandez‐Lao 2013 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez‐Lao C, Cantarero‐Villanueva I, Ariza‐Garcia A, Courtney C, Fernandez‐De‐Las‐Penas C, Arroyo‐Morales M. Water‐ versus land‐based multimodal exercise program effects on body composition in breast cancer survivors: a controlled clinical trial. Supportive Care in Cancer 2013;21(2):521‐30. - PubMed
Fong 2014 {published data only}
-
- Fong SSM, Ng SSM, Luk WS, Chung JWY, Ho JSC, Ying M, et al. Effects of qigong exercise on upper limb lymphedema and blood flow in survivors of breast cancer: a pilot study. Integrative Cancer Therapies 2014;13(1):54‐61. - PubMed
Galantino 2013 {published data only}
-
- Galantino ML, Callens ML, Cardena GJ, Piela NL, Mao JJ. Tai chi for well‐being of breast cancer survivors with aromatase inhibitor‐associated arthralgias: a feasibility study. Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine 2013;19(6):38‐44. - PubMed
Gordon 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gordon LG, Battistutta D, Scuffham P, Tweeddale M, Newman B. The impact of rehabilitation support services on health‐related quality of life for women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Research & Treatment 2005;93(3):217‐26. - PubMed
Hanna 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hanna LR, Avila PF, Meteer JD, Nicholas DR, Kaminsky LA. The effects of a comprehensive exercise program on physical function, fatigue, and mood in patients with various types of cancer. Oncology Nursing Forum 2008;35(3):461‐9.
Hayes 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hayes SC, Rye S, Disipio T, Yates P, Bashford J, Pyke C, et al. Exercise for health: a randomized, controlled trial evaluating the impact of a pragmatic, translational exercise intervention on the quality of life, function and treatment‐related side effects following breast cancer. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2013;137(1):175‐86. - PubMed
Headley 2004 {published data only}
-
- Headley JA, Ownby KK, John LD. The effect of seated exercise on fatigue and quality of life in women with advanced breast cancer. Oncology Nursing Forum 2004;31(5):977‐83. - PubMed
Hojan 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hojan K, Molinska‐Glura M, Milecki P. Physical activity and body composition, body physique, and quality of life in premenopausal breast cancer patients during endocrine therapy ‐ a feasibility study. Acta Oncologica (Stockholm, Sweden) 2013;52(2):319‐26. - PubMed
Hsiao‐Fang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hsiao‐Fang H, Tsai‐Chung L, Liang‐Chih L, Chien‐Teng W, Ya‐Jung W. Effects of a walking program on fatigue and exercise capacity in post‐surgery breast cancer women [Chinese]. Journal of Nursing 2013;60(5):53‐63. - PubMed
Hsieh 2008 {published data only}
Hunt‐Shanks 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hunt‐Shanks TT, Blanchard CM, Baker F, Hann D, Roberts CS, McDonald J, et al. Exercise use as complementary therapy among breast and prostate cancer survivors receiving active treatment: examination of exercise intention. Integrative Cancer Therapies 2006;5(2):109‐16. - PubMed
Husebo 2014 {published data only}
Hutnick 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hutnick NA, Williams NI, Kraemer WJ, Orsega‐Smith E, Dixon RH, Bleznak AD, et al. Exercise and lymphocyte activation following chemotherapy for breast cancer. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2005;37(11):1827‐35. - PubMed
Ibfelt 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ibfelt E, Rottmann N, Kjaer T, Hoybye MT, Ross L, Frederiksen K. No change in health behavior, BMI or self‐rated health after a psychosocial cancer rehabilitation: results of a randomized trial. Acta Oncologica 2011;50(2):289‐98. - PubMed
Isabell 2010 {published data only}
-
- Isabell UB, Maja R. Yoga supports physical and mental well‐being after breast cancer surgery. Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics and Gynecology 2010;31:125.
Jeff 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jeffs E, Wiseman T. Randomised controlled trial to determine the benefit of daily home‐based exercise in addition to self‐care in the management of breast cancer‐related lymphoedema: a feasibility study. Supportive Care in Cancer 2012;21(4):1013‐23. - PubMed
Johansson 2005 {published data only}
-
- Johansson K, Tibe K, Weibull A, Newton RU. Low intensity resistance exercise for breast cancer patients with arm lymphedema with or without compression sleeve. Lymphology 2005;38(4):167‐80. - PubMed
Johnsson 2013 {published data only}
-
- Johnsson A, Johnsson A, Johansson K. Physical activity during and after adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Physiotherapy 2013;99(3):221‐7. - PubMed
Kilbreath 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kilbreath S, Refshauge K, Beith J, Lee M. Resistance and stretching shoulder exercises early following axillary surgery for breast cancer. Rehabilitation Oncology 2006;24(2):9‐14.
Kilbreath 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kilbreath SL, Refshauge KM, Beith JM, Ward LC, Lee M, Simpson JM, et al. Upper limb progressive resistance training and stretching exercises following surgery for early breast cancer: a randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2012;133(2):667‐76. - PubMed
Kilgour 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kilgour RD, Jones DH, Keyserlingk JR. Effectiveness of a self‐administered, home‐based exercise rehabilitation program for women following a modified radical mastectomy and axillary node dissection: a preliminary study. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2008;109(2):285‐95. - PubMed
Kim Soo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kim SH, Shin MS, Lee HS, Lee ES, Ro JS, Kang HS, et al. Randomized pilot test of a simultaneous stage‐matched exercise and diet intervention for breast cancer survivors. Oncology Nursing Forum 2011;38(2):E97‐E106. - PubMed
Kovacic 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kovacic T, Kovacic M. Impact of relaxation training according to Yoga in Daily Life system on perceived stress after breast cancer surgery. Integrative Cancer Therapies 2011;10(1):16‐26. - PubMed
LaStayo 2011 {published data only}
Lee 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lee SA, Kang J, Kim YD, An AR, Kim S, Kim Y, et al. Effects of a scapula‐oriented shoulder exercise programme on upper limb dysfunction in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled pilot trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2010;24(7):600‐13. - PubMed
Ligibel 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ligibel JA, Meyerhardt J, Pierce JP, Najita J, Shockro L, Campbell N, et al. Impact of a telephone‐based physical activity intervention upon exercise behaviors and fitness in cancer survivors enrolled in a cooperative group setting. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2012;132(1):205‐13. - PMC - PubMed
May 2008 {published data only}
-
- May AM, Weert E, Korstjens I, Hoekstra‐Weebers JEHM, Schans CP, Zonderland ML, et al. Improved physical fitness of cancer survivors: a randomised controlled trial comparing physical training with physical and cognitive‐behavioural training. Acta Oncologica 2008;47(5):825‐34. - PubMed
McClure 2010 {published data only}
-
- McClure MK, McClure RJ, Day R, Brufsky AM. Randomized controlled trial of the Breast Cancer Recovery Program for women with breast cancer‐related lymphedema. American Journal of Occupational Therapy 2010;64(1):59‐72. - PubMed
Mefferd 2007 {published data only}
-
- Mefferd K, Nichols JF, Pakiz B, Rock CL. A cognitive behavioral therapy intervention to promote weight loss improves body composition and blood lipid profiles among overweight breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2007;104(2):145‐52. - PubMed
Moadel 2007 {published data only}
-
- Moadel AB, Shah C, Wylie‐Rosett J, Harris MS, Patel SR, Hall CB, et al. Randomized controlled trial of yoga among a multiethnic sample of breast cancer patients: effects on quality of life. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2007;25(28):4387‐95. - PubMed
Naraphong 2015 {published data only}
-
- Naraphong W, Lane A, Schafer J, Whitmer K, Wilson BR. Exercise intervention for fatigue‐related symptoms in Thai women with breast cancer: a pilot study. Nursing Health Science 2015;17(1):33–41. - PubMed
Naumann 2012a {published data only}
-
- Naumann F, Munro A, Martin E, Magrani P, Buchan J, Smith C, et al. An individual‐based versus group‐based exercise and counselling intervention for improving quality of life in breast cancer survivors: a feasibility and efficacy study. Psycho‐Oncology 2012;21(10):1136‐9. - PubMed
Noble 2012 {published data only}
-
- Noble M, Russell C, Kraemer L, Sharratt M. UW WELL‐FIT: the impact of supervised exercise programs on physical capacity and quality of life in individuals receiving treatment for cancer. Supportive Care in Cancer 2012;20(4):865‐73. - PubMed
Oh 2010 {published data only}
Oldervoll 2011 {published data only}
Pinto 2008 {published data only}
-
- Pinto BM, Rabin C, Abdow S, Papandonatos GD. A pilot study on disseminating physical activity promotion among cancer survivors: a brief report. Psycho‐Oncology 2008;17(5):517‐21. - PubMed
Pinto 2013 {published data only}
-
- Pinto BM, Dunsiger S, Waldemore M. Physical activity and psychosocial benefits among breast cancer patients. Psycho‐Oncology 2013;22(10):2193‐9. - PubMed
-
- Pinto BM, Papandonatos GD, Goldstein MG. A randomized trial to promote physical activity among breast cancer patients. Health Psychology 2013;32(6):616‐26. - PubMed
Rabin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Rabin CS, Pinto BM, Trunzo JJ, Frierson GM, Bucknam LM. Physical activity among breast cancer survivors: regular exercisers vs participants in a physical activity intervention. Psycho‐Oncology 2006;15(4):344‐54. - PubMed
Rabin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rabin C, Pinto B, Dunsiger S, Nash J, Trask P. Exercise and relaxation intervention for breast cancer survivors: feasibility, acceptability and effects. Psycho‐oncology 2009;18(3):258‐66. - PubMed
Sandel 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sandel SL, Judge JO, Landry N, Faria L, Ouellette R, Majczak M. Dance and movement program improves quality‐of‐life measures in breast cancer survivors. Cancer Nursing 2005;28(4):301‐9. - PubMed
Schmidt 2012 {published data only}
-
- Schmidt T, Weisser B, Jonat W, Baumann FT, Mundhenke C. Gentle strength training in rehabilitation of breast cancer patients compared to conventional therapy. Anticancer Research 2012;32(8):3229‐33. - PubMed
Schneider 2007 {published data only}
-
- Schneider CM, Hsieh CC, Sprod LK, Carter SD, Hayward R. Effects of supervised exercise training on cardiopulmonary function and fatigue in breast cancer survivors during and after treatment. Cancer 2007;110(4):918‐25. - PubMed
Schwartz 1999 {published data only}
-
- Schwartz AL. Fatigue mediates the effects of exercise on quality of life. Quality of Life Research 1999;8(6):529‐38. - PubMed
Segal 2001 {published data only}
-
- Segal R, Evans W, Johnson D, Smith J, Colletta S, Gayton J, et al. Structured exercises improves physical functioning in women with stages I and II breast cancer: results of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2001;19(3):657‐65. - PubMed
Sherman 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sherman KA, Heard G, Cavanagh KL. Psychological effects and mediators of a group multi‐component program for breast cancer survivors. Journal of Behavioral Medicine 2010;33(5):378‐91. - PubMed
Speed‐Andrews 2010 {published data only}
-
- Speed‐Andrews AE, Stevinson C, Belanger LJ, Mirus JJ, Courneya KS. Pilot evaluation of an Iyengar yoga program for breast cancer survivors. Cancer Nursing 2010;33(5):369‐81. - PubMed
Sprod 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sprod LK, Drum SN, Bentz AT, Carter SD, Schneider CM. The effects of walking poles on shoulder function in breast cancer survivors. Integrative Cancer Therapies 2005;4(4):287‐93. - PubMed
Sprod 2010 {published data only}
Stan 2012 {published data only}
-
- Stan DL, Rausch SM, Sundt K, Cheville AL, Youdas JW, Krause DA, et al. Pilates for breast cancer survivors: Impact on physical parameters and quality of life after mastectomy. Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing 2012;16(2):131‐41. - PubMed
Stan 2013 {published data only}
-
- Stan D, Cheville A, Croghan I, Pruthi S. Randomized controlled study of yoga versus strengthening exercises in breast cancer survivors with persistent fatigue. Supportive Care in Cancer 2013;21:S261‐S2. - PubMed
Stevinson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Stevinson C. Exercise programme improves functional outcomes during breast cancer therapy. Focus on Alternative & Complementary Therapies 2007;12(3):202‐3.
Szczwpanska‐Gieracha 2010 {published data only}
-
- Szczepanska‐Gieracha J, Malicka I, Figula M, Rymaszewska J, Wozniewski M. The influence of eight‐week Nordic walking exercise on life quality of women after mastectomy. Onkologia Polska 2010;13(2):90‐5.
Tang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tang M, Liou T, Lin C. Improving sleep quality for cancer patients: benefits of a home‐based exercise intervention. Supportive Care in Cancer 2010;18(10):1329‐39. - PubMed
Taso 2014 {published data only}
-
- Taso CJ, Lin HS, Lin WL, Chen SM, Huang WT, Chen SW. The effect of yoga exercise on improving depression, anxiety, and fatigue in women with breast cancer: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Nursing Research 2014;22(3):155‐64. - PubMed
Thorsen 2005 {published data only}
-
- Thorsen L, Skovlund E, Stromme SB, Hornslien K, Dahl AA, Fossa SD. Effectiveness of physical activity on cardiorespiratory fitness and health‐related quality of life in young and middle‐aged cancer patients shortly after chemotherapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(10):2378‐88. - PubMed
Tidhar 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tidhar D, Katz‐Leurer M. Aqua lymphatic therapy in women who suffer from breast cancer treatment‐related lymphedema: a randomized controlled study. Supportive Care in Cancer 2010;18(3):383‐92. - PubMed
Turner 2004 {published data only}
-
- Turner J, Hayes S, Reul‐Hirche H. Improving the physical status and quality of life of women treated for breast cancer: a pilot study of a structured exercise intervention. Journal of Surgical Oncology 2004;86(3):141‐6. - PubMed
Ulger 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ulger O, Yagli NV. Effects of yoga on the quality of life in cancer patients. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice 2010;16(2):60‐3. - PubMed
Van Puymbroeck 2011 {published data only}
-
- Puymbroeck M, Schmid A, Shinew KJ, Hsieh PC. Influence of Hatha yoga on physical activity constraints, physical fitness, and body image of breast cancer survivors: a pilot study. International Journal of Yoga Therapy 2011;21:49‐60. - PubMed
Van Weert 2005 {published data only}
-
- Weert E, Hoekstra‐Weebers J, Grol B, Otter R, Arendzen H, Postema K, et al. A multidimensional cancer rehabilitation program for cancer survivors ‐ effectiveness on health‐related quality of life. Journal of Psychosomatic Research 2005;58(6):485‐96. - PubMed
Wong 2012 {published data only}
Wu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wu H, Dodd MJ, Cho MH. Patterns of fatigue and effect of exercise in patients receiving chemotherapy for breast cancer. Oncology Nursing Forum 2008;35(5):E90‐E9.
Yuen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Yuen HK, Sword D. Home‐based exercise to alleviate fatigue and improve functional capacity among breast cancer survivors. Journal of Allied Health 2007;36:e257‐e75. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Lahart 2016 {published data only}
Lohrisch 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lohrisch CA, McKenzie D, Truong P, Jesperson D, Gelmon KA, Premji S. Randomized trial of exercise versus control for musculoskeletal symptoms from adjuvant anastrozole for postmenopausal early breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2011;29(S15):636.
Luu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Luu X, Rifkind K, Dhage S, Castaneda M, Zeng X, Joseph KAP. The effects of yoga on urban underserved breast cancer patients. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014;32:e17557.
References to ongoing studies
Deli‐Conwright 2014 {published data only}
-
- Dieli‐Conwright CM, Mortimer JE, Schroeder ET, Courneya K, Demark‐Wahnefried W, Buchanan TA. Randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effects of combined progressive exercise on metabolic syndrome in breast cancer survivors: rationale, design, and methods. BMC Cancer 2014;14(1):238. - PMC - PubMed
Galiano‐Castillo 2013 {published data only}
-
- Galiano‐Castillo N, Ariza‐Garcia A, Cantarero‐Villanueva I, Fernandez‐Lao C, Diaz‐Rodriguez L, Legeren‐Alvarez M. Telehealth system (e‐CUIDATE) to improve quality of life in breast cancer survivors: rationale and study protocol for a randomized clinical trial. Trials 2013;14(1):187. [NCT01801527] - PMC - PubMed
IRCT2014042117379N1 {published data only}
-
- IRCT2014042117379N1. Comparing self‐efficacy, outcome expectations for promoting the physical activity of the women with breast cancer in two groups with and without educational program. http://apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=IRCT2014042117379N1 (accessed 16 July 2016).
KIlbreath 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kilbreath S, Refshauge KM, Beith J, Ward L, Sawkins K, Paterson R, et al. Prevention of osteoporosis as a consequence of aromatase inhibitor therapy in postmenopausal women with early breast cancer: rationale and design of a randomized controlled trial. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2011;32(5):704‐9. [ACTRN12608000220369] - PubMed
NCT02057536 {published data only}
-
- NCT02057536. The Effect of an Exercise Program in Breast Cancer Patients With Joint Pain While Taking Aromatase Inhibitors. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02057536 (accessed 16 July 2016).
NCT02235051 {published data only}
-
- NCT02235051. Exercise Intervention in Preventing Breast Cancer Recurrence in Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Survivors. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02235051 (accessed 16 July 2016).
NCT02332876 {published data only}
-
- NCT02332876. Physical Activity and Neuropsychological Outcomes in a Cancer Population. https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02332876 (accessed 16 July 2016).
NCT02420249 {published data only}
-
- NCT02420249. Qigong for Breast Cancer Survivors. https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02420249 (accessed 16 July 2016).
NCT02433067 {published data only}
-
- NCT02433067. Physical Activity Intervention on Myocardial Function in Patients With HER2 + Breast Cancer (CARDAPAC). https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02433067 (accessed 16 July 2016).
NCT02527889 {published data only}
-
- NCT02527889. The Effect of Resistive Exercise on Forearm Blood Flow and Tissue Oxygenation Among Breast Cancer Survivors With or at Risk for Breast Cancer‐related Lymphoedema (BCRL). https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02527889 (accessed 16 July 2016).
Additional references
Azim 2011
-
- Azim HA Jr, Azambuja E, Colozza M, Bines J, Piccart MJ. Long‐term toxic effects of adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Annals of Oncology 2011;22(9):1939‐47. - PubMed
Ballard‐Barbash 2012
Battaglini 2014
Beasley 2012
Beisecker 1997
-
- Beisecker A, Cook MR, Ashworth J, Hayes J, Brecheisen M, Helmig L, et al. Side effects of adjuvant chemotherapy: perceptions of node‐negative breast cancer patients. Psycho‐Oncology 1997;6(2):85‐93. - PubMed
Bluethmann 2015
-
- Bluethmann SM, Vernon SW, Gabriel KP, Murphy CC, Bartholomew LK. Taking the next step: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of physical activity and behavior change interventions in recent post‐treatment breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2015;149(2):331‐42. - PMC - PubMed
Bluethmann 2016
-
- Bluethmann SM, Bartholomew LK, Murphy CC, Vernon SW. Use of theory in behavior change interventions: an analysis of programs to increase physical activity in posttreatment breast cancer survivors. Health Education & Behavior 2016;May 25:[Epub ahead of print]. [DOI: 10.1177/1090198116647712] - DOI
Bourke 2013
Bourke 2014
Bovelli 2010
-
- Bovelli D, Plataniotis G, Roila F, ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Cardiotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents and radiotherapy‐related heart disease: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Annals of Oncology 2010;21(Suppl 5):277‐82. - PubMed
Bradt 2011
Bray 2013
-
- Bray F, Ren J‐S, Masuyer E, Ferlay J. Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult population in 2008. International Journal of Cancer 2013;132:1133‐45. - PubMed
Brown 2011
-
- Brown JC, Huedo‐Medina TB, Pescatello LS, Pescatello SM, Ferrer RA, Johnson BT. Efficacy of exercise interventions in modulating cancer‐related fatigue among adult cancer survivors: a meta‐analysis. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention 2011;20(1):123‐33. - PubMed
Brown 2012
Buffart 2012a
Button 2015
Camoriano 1990
-
- Camoriano JK, Loprinzi CL, Ingle JN, Therneau TM, Krook JE, Veeder MH. Weight change in women treated with adjuvant therapy or observed following mastectomy for node‐positive breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 1990;8(8):1327‐34. - PubMed
Candy 2016
Carayol 2013
-
- Carayol M, Bernard P, Boiché J, Riou F, Mercier B, Cousson‐Gélie F, et al. Psychological effect of exercise in women with breast cancer receiving adjuvant therapy: what is the optimal dose needed?. Annals of Oncology 2013;24:291‐300. - PubMed
Caspersen 1985
Cella 2002
-
- Cella D, Eton DT, Lai JS, Peterman AH, Merkel DE. Combining anchor and distribution‐based methods to derive minimal clinically important differences on the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy (FACT) anemia and fatigue scales. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2002;24(6):547‐61. - PubMed
Cella 2002a
-
- Cella D, Hahn EA, Dineen K. Meaningful change in cancer‐specific quality of life scores: differences between improvement and worsening. Quality of Life Research 2002;11(3):207‐21. - PubMed
Chan 2015
-
- Chan RJ, McCarthy AL, Devenish J, Sullivan KA, Chan A. Systematic review of pharmacologic and non‐pharmacologic interventions to manage cognitive alterations after chemotherapy for breast cancer. European Journal of Cancer 2015;51(4):437‐50. - PubMed
Cheema 2008
-
- Cheema B, Gaul CA, Lane K, Fiatarone Singh MA. Progressive resistance training in breast cancer: a systematic review of clinical trials. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2008;109(1):9‐26. - PubMed
Cheema 2014
-
- Cheema BS, Kilbreath SL, Fahey PP, Delaney GP, Atlantis E. Safety and efficacy of progressive resistance training in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2014;148(2):249‐68. - PubMed
Chiu 2015
-
- Chiu HY, Huang HC, Chen PY, Hou WH, Tsai PS. Walking improves sleep in individuals with cancer: a meta‐analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Oncology Nursing Forum 2015;42(2):E54‐E62. - PubMed
Chung 2013
-
- Chung C, Lee S, Hwang S, Park E. Systematic review of exercise effects on health outcomes in women with breast cancer. Asian Nursing Research 2013;7(3):149‐59. - PubMed
Cochran 1954
-
- Cochran WG. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 1954;10(1):101‐29.
Craft 2012
Cramer 2013
Cramp 2010
-
- Cramp F, James A, Lambert J. The effects of resistance training on quality of life in cancer: a systematic literature review and meta‐analysis. Supportive Care in Cancer 2010;18(11):1367‐76. - PubMed
Cramp 2012
de Jong 2002
-
- Jong N, Courtens AM, Abu‐Saad HH, Schouten HC. Fatigue in patients with breast cancer receiving adjuvant chemotherapy: a review of the literature. Cancer Nursing 2002;25(4):283‐97. - PubMed
Demark‐Wahnefried 2005
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7:177‐88. - PubMed
Duijts 2011
-
- Duijts SF, Faber MM, Oldenburg HS, Beurden M, Aaronson NK. Effectiveness of behavioral techniques and physical exercise on psychosocial functioning and health‐related quality of life in breast cancer patients and survivors ‐ a meta‐analysis. Psycho‐Oncology 2011;20(2):115‐26. - PubMed
Eastell 1993
-
- Eastell R, Robins SP, Colwell T. Evaluation of bone turnover in type I osteoporosis using biochemical markers specific for both bone formation and bone resorption. Osteoporosis International 1993;3:255‐260. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Eton 2004
-
- Eton DT, Cella D, Yost KJ, Yount SE, Peterman AH, Neuberg DS, et al. A combination of distribution‐ and anchor‐based approaches determined minimally important differences (MIDs) for four endpoints in a breast cancer scale. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2004;57(9):898‐910. - PubMed
Ferlay 2013
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, et al. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 [Internet]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013. Available from http://globocan.iarc.fr (accessed April 2014).
Ferrer 2011
Fong 2012
Galvao 2005
-
- Galvao DA, Newton RU. Review of exercise intervention studies in cancer patients. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(4):899‐909. - PubMed
Greenland 1985
-
- Greenland S, Robins JM. Estimation of common effect parameter from sparse follow up data. Biometrics 1985;41:55‐68. - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Holmes 2005
-
- Holmes MD, Chen WY, Feskanich D, Kroenke CH, Colditz GA. Physical activity and survival after breast cancer diagnosis. JAMA 2005;293(20):2479‐86. - PubMed
IARC 2012
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Latest World Cancer Statistics. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013; Vol. Press release no. 223.
Ibrahim 2011
-
- Ibrahim EM, Al‐Homaidh A. Physical activity and survival after breast cancer diagnosis: meta‐analysis of published studies. Medical Oncology 2011;28(3):753‐65. - PubMed
Ingram 2007
-
- Ingram C, Visovsky C. Exercise intervention to modify physiologic risk factors in cancer survivors. Seminars in Oncology Nursing 2007;23(4):275‐84. - PubMed
Jemal 2011
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Statistics 2011;61(2):69‐90. - PubMed
Keilani 2016
-
- Keilani M, Hasenoehrl T, Neubauer M, Crevenna R. Resistance exercise and secondary lymphedema in breast cancer survivors ‐ a systematic review. Supportive Care in Cancer 2016;24(4):1907‐16. - PubMed
Knols 2005
-
- Knols R, Aaronson NK, Uebelhart D, Fransen J, Aufdemkampe G. Physical exercise in cancer patients during and after medical treatment: a systematic review of randomized and controlled clinical trials. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(16):3830‐42. - PubMed
Knols 2010
Kodama 2009
-
- Kodama S, Saito K, Tanaka S, Maki M, Yachi Y, Asumi M, et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness as a quantitative predictor of all‐cause mortality and cardiovascular events in healthy men and women: a meta‐analysis. JAMA 2009;301(19):2024‐35. - PubMed
Kriska 1990
-
- Kriska AM, Knowler WC, LaPorte RE. Development of a questionnaire to examine relationship of physical activity and diabetes in Pima Indians. Diabetes Care 1990;13:401‐11. - PubMed
Kroenke 2005
-
- Kroenke CH, Chen WY, Rosner B, Holmes MD. Weight, weight gain, and survival after breast cancer diagnosis. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(7):1370‐8. - PubMed
Lahmann 2005
Lee 2010a
-
- Lee MS, Choi TY, Ernst E. Tai chi for breast cancer patients: a systematic review. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2010;120(2):309‐16. - PubMed
Lynch 2011
-
- Lynch BM, Neilson HK, Friedenreich CM. Physical activity and breast cancer prevention. Recent Results in Cancer Research 2011;186:13‐42. - PubMed
Mantel 1959
-
- Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 1959;22:719‐48. - PubMed
Markes 2009
McAuley 2000
-
- McAuley L, Pham B, Tugwell P, Moher D. Does the inclusion of grey literature influence estimates of intervention effectiveness reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 2000;356:1228–31. - PubMed
McNeely 2006
McNeely 2010
Meneses‐Echavez 2015
Mishra 2012a
Mishra 2012b
Moher 2010
Nelson 2016
Pan 2015
Paramanandam 2014
-
- Paramanandam VS, Roberts D. Weight training is not harmful for women with breast cancer‐related lymphoedema: a systematic review. Journal of Physiotherapy 2014;60(3):136‐43. - PubMed
Physical Activity Guidelines 2008
-
- Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee. Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee Report, 2008. Washington: US Department of Health and Human Services. Available at http://www.health.gov/paguidelines/Report/pdf/CommitteeReport.pdf (accessed 09 January 2018) 2008.
RevMan [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Schmitz 2010
-
- Schmitz KH, Courneya KS, Matthews C, Demark‐Wahnefried W, Galvão D, Pinto BM, et al. American College of Sports Medicine roundtable on exercise guidelines for cancer survivors. Medicine and Science in Sport and Exercise Science 2010;42(7):1409‐26. - PubMed
Shoemaker 2013
Spark 2013
-
- Spark LC, Reeves MM, Fjeldsoe BS, Eakin EG. Physical activity and/or dietary interventions in breast cancer survivors: a systematic review of the maintenance of outcomes. Journal of Cancer Survivorship: Research and Practice 2013;7(1):74‐82. - PubMed
Speck 2010
-
- Speck RM, Courneya KS, Masse LC, Duval S, Schmitz KH. An update of controlled physical activity trials in cancer survivors: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Cancer Survivorship: Research and Practice 2010;4(2):87‐100. - PubMed
Vallance 2008
-
- Vallance JK, Courneya KS, Plotnikoff RC, Yasui Y, Mackey JR. Randomized controlled trial of the effects of print materials and step pedometers on physical activity and quality of life in breast cancer survivors. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2007;25(17):2352‐9. - PubMed
Winters‐Stone 2010
-
- Winters‐Stone KM, Schwartz A, Nail LM. A review of exercise interventions to improve bone health in adult cancer survivors. Journal of Cancer Survivorship: Research and Practice 2010;4(3):187‐201. - PubMed
Yang 2016
-
- Yang GS, Kim HJ, Griffith KA, Zhu S, Dorsey SG, Renn CL. Interventions for the treatment of aromatase inhibitor‐associated arthralgia in breast cancer survivors: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Cancer Nursing 2016;Jun 21:[Epub ahead of print]. [DOI: 10.1097/NCC.0000000000000409] - DOI - PubMed
Yost 2011
Zeng 2014
-
- Zeng Y, Huang M, Cheng AS, Zhou Y, So WK. Meta‐analysis of the effects of exercise intervention on quality of life in breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer (Tokyo, Japan) 2014;21(3):262‐74. - PubMed
Zhu 2016
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

