Effect of Nanoparticle Surface Coating on Cell Toxicity and Mitochondria Uptake
- PMID: 29377103
- PMCID: PMC6800125
- DOI: 10.1166/jbn.2017.2337
Effect of Nanoparticle Surface Coating on Cell Toxicity and Mitochondria Uptake
Abstract
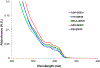
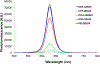
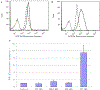
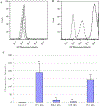
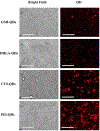
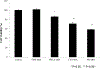
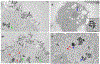
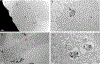
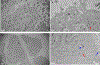
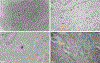
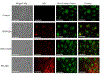
We report on the effect of surface charge and the ligand coating composition of CdSe/ZnS core/shell quantum dot (QD) nanoparticles on human keratinocyte toxicity using fluorescent microscopy, flow cytometry, transmission electron microscopy. Two commonly reported positive charged (cysteamine, polyethylenimine) and two negative charged (glutathione, dihydrolipoic acid) ligands were studied. The QDs were fully characterized by UV-vis absorption spectroscopy, fluorescence emission spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering and zeta potential. Differences in surface coatings and charges were evaluated against cellular uptake, ROS generation, cytotoxicity, and mitochondrial targeting. Results show that the negative charged QDs coated with GSH exhibit excellent water solubility, high quantum yield and low cytotoxicity. Ligand composition is more important in ROS generation than surface charge whereas surface charge is an important driver of cytotoxicity. Most importantly we observe the selective accumulation of glutathione coated QDs in vesicles in the mitochondria matrix. This observation suggests a new strategy for developing mitochondria-targeted nanomaterials for drug/gene delivery.
Keywords: Quantum Dots; Keratinoyctes; Endocytosis; Inracellular Localization; Mitochondria.
Figures
References
-
- Chan WC, Maxwell DJ, Gao X, Bailey RE, Han M, Nie S, Luminescent Quantum Dots for Multiplexed Biological Detection and Imaging. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 13, 40–46 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Chen L, Quantum Dots, Lighting up the Research and Development of Nanomedicine. Nanomedicine 7, 385–402 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Hutter E, Maysinger D, Gold Nanoparticles and Quantum Dots for Bioimaging. Microsc Res Tech. 2011, 74, 592–604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
