Expert consensus document: Clinical and molecular diagnosis, screening and management of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: an international consensus statement
- PMID: 29377879
- PMCID: PMC6022848
- DOI: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.166
Expert consensus document: Clinical and molecular diagnosis, screening and management of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: an international consensus statement
Abstract
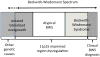
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS), a human genomic imprinting disorder, is characterized by phenotypic variability that might include overgrowth, macroglossia, abdominal wall defects, neonatal hypoglycaemia, lateralized overgrowth and predisposition to embryonal tumours. Delineation of the molecular defects within the imprinted 11p15.5 region can predict familial recurrence risks and the risk (and type) of embryonal tumour. Despite recent advances in knowledge, there is marked heterogeneity in clinical diagnostic criteria and care. As detailed in this Consensus Statement, an international consensus group agreed upon 72 recommendations for the clinical and molecular diagnosis and management of BWS, including comprehensive protocols for the molecular investigation, care and treatment of patients from the prenatal period to adulthood. The consensus recommendations apply to patients with Beckwith-Wiedemann spectrum (BWSp), covering classical BWS without a molecular diagnosis and BWS-related phenotypes with an 11p15.5 molecular anomaly. Although the consensus group recommends a tumour surveillance programme targeted by molecular subgroups, surveillance might differ according to the local health-care system (for example, in the United States), and the results of targeted and universal surveillance should be evaluated prospectively. International collaboration, including a prospective audit of the results of implementing these consensus recommendations, is required to expand the evidence base for the design of optimum care pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
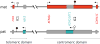

References
-
- Mussa A, et al. Prevalence of beckwith-wiedemann syndrome in North West of Italy. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2013;161:2481–2486. - PubMed
-
- de Villiers MR, de Villiers PJT, Kent AP. The Delphi technique in health sciences education research. Med Teach. 2005;27:639–643. - PubMed
-
- Beckwith JB. Extreme cytomegaly of the adrenal fetal cortex, omphalocele, hyperplasia of kidneys and pancreas, and Leydig-cell hyperplasia: Another syndrome. West Soc Pediatr Res. 1963;11
-
- Wiedemann HR. Familial malformation complex with umbilical hernia and macroglossia - a ‘new syndrome’? J Genet Hum. 1964;13:223–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

