16S rRNA gene metabarcoding and TEM reveals different ecological strategies within the genus Neogloboquadrina (planktonic foraminifer)
- PMID: 29377905
- PMCID: PMC5788372
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191653
16S rRNA gene metabarcoding and TEM reveals different ecological strategies within the genus Neogloboquadrina (planktonic foraminifer)
Abstract
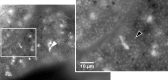
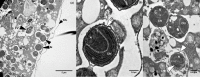
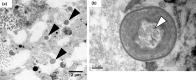
Uncovering the complexities of trophic and metabolic interactions among microorganisms is essential for the understanding of marine biogeochemical cycling and modelling climate-driven ecosystem shifts. High-throughput DNA sequencing methods provide valuable tools for examining these complex interactions, although this remains challenging, as many microorganisms are difficult to isolate, identify and culture. We use two species of planktonic foraminifera from the climatically susceptible, palaeoceanographically important genus Neogloboquadrina, as ideal test microorganisms for the application of 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding. Neogloboquadrina dutertrei and Neogloboquadrina incompta were collected from the California Current and subjected to either 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding, fluorescence microscopy, or transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to investigate their species-specific trophic interactions and potential symbiotic associations. 53-99% of 16S rRNA gene sequences recovered from two specimens of N. dutertrei were assigned to a single operational taxonomic unit (OTU) from a chloroplast of the phylum Stramenopile. TEM observations confirmed the presence of numerous intact coccoid algae within the host cell, consistent with algal symbionts. Based on sequence data and observed ultrastructure, we taxonomically assign the putative algal symbionts to Pelagophyceae and not Chrysophyceae, as previously reported in this species. In addition, our data shows that N. dutertrei feeds on protists within particulate organic matter (POM), but not on bacteria as a major food source. In total contrast, of OTUs recovered from three N. incompta specimens, 83-95% were assigned to bacterial classes Alteromonadales and Vibrionales of the order Gammaproteobacteria. TEM demonstrates that these bacteria are a food source, not putative symbionts. Contrary to the current view that non-spinose foraminifera are predominantly herbivorous, neither N. dutertrei nor N. incompta contained significant numbers of phytoplankton OTUs. We present an alternative view of their trophic interactions and discuss these results within the context of modelling global planktonic foraminiferal abundances in response to high-latitude climate change.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Leal M, Ferrier-Pagès C. Molecular trophic markers in marine food webs and their potential use for coral ecology. Mar Genomics. 2016; 29:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2016.02.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pompanon F, Deagle BE, Symondson WOC, Brown DS, Jarman SN, Taberlet P. Who is eating what: diet assessment using next generation sequencing. Mol Ecol. 2012; 21:1931–1950. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05403.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ray JL, Althammer J, Skaar KS, Simonelli P, Larsen A, Stoecker D, et al. Metabarcoding and metabolome analyses of copepod grazing reveal feeding preference and linkage to metabolite classes in dynamic microbial plankton communities. Mol Ecol. 2016; 25:5585–5602. doi: 10.1111/mec.13844 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, Xu Q, Zhao Y, Yang H. Sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) eukaryotic food source composition determined by 18s rDNA barcoding. Mar Biol. 2016; 163:153 doi: 10.1007/s00227-016-2931-x - DOI
-
- Azam F, Smith DC, Steward GF, Hagstrӧm Å. Bacteria-organic matter coupling and its significance for oceanic carbon cycling. Microb Ecol. 1994; 28:167–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00166806 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

