Effect of body mass index on diabetogenesis factors at a fixed fasting plasma glucose level
- PMID: 29377927
- PMCID: PMC5788342
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189115
Effect of body mass index on diabetogenesis factors at a fixed fasting plasma glucose level
Erratum in
-
Correction: Effect of body mass index on diabetogenesis factors at a fixed fasting plasma glucose level.PLoS One. 2018 May 7;13(5):e0197212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197212. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29734369 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Aim: The present study evaluated the relative influence of body mass index (BMI) on insulin resistance (IR), first-phase insulin secretion (FPIS), second-phase insulin secretion (SPIS), and glucose effectiveness (GE) at a fixed fasting plasma glucose level in an older ethnic Chinese population.
Methods: In total, 265 individuals aged 60 years with a fasting plasma glucose level of 5.56 mmol/L were enrolled. Participants had BMIs of 20.0-34.2 kg/m2. IR, FPIS, SPIS, and GE were estimated using our previously developed equations. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to assess the correlations between the four diabetogenesis factors and BMI. A general linear model was used to determine the differences in the percentage of change among the four factor slopes against BMI.
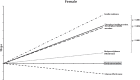
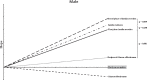
Results: Significant correlations were observed between BMI and FPIS, SPIS, IR, and GE in both women and men, which were higher than those reported previously. In men, BMI had the most profound effect on SPIS, followed by IR, FPIS, and GE, whereas in women, the order was slightly different: IR, followed by FPIS, SPIS, and GE. Significant differences were observed among all these slopes, except for the slopes between FPIS and SPIS in women (p = 0.856) and IR and FPIS in men (p = 0.258).
Conclusions: The contribution of obesity to all diabetes factors, except GE, was higher than that reported previously. BMI had the most profound effect on insulin secretion in men and on IR in women in this 60-year-old cohort, suggesting that lifestyle modifications for obesity reduction in women remain the most important method for improving glucose metabolism and preventing future type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R (1979) Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. American Journal of Physiology 237: E214–223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kahn SE (2003) The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of Type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 46: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/s00125-002-1009-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Polonsky KS, Sturis J, Bell GI (1996) Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus—a genetically programmed failure of the beta cell to compensate for insulin resistance. The New England Journal of Medicine 334: 777–783. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199603213341207 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Caumo A, Luzi L (2004) First-phase insulin secretion: does it exist in real life? Considerations on shape and function. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287: E371–385. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00139.2003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pratley RE, Weyer C (2001) The role of impaired early insulin secretion in the pathogenesis of Type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 44: 929–945. doi: 10.1007/s001250100580 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

