Global synonymous mutagenesis identifies cis-acting RNA elements that regulate HIV-1 splicing and replication
- PMID: 29377940
- PMCID: PMC5805364
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006824
Global synonymous mutagenesis identifies cis-acting RNA elements that regulate HIV-1 splicing and replication
Abstract
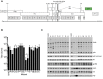
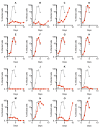
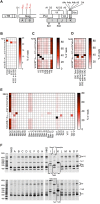
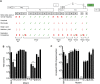
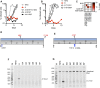
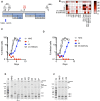
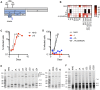
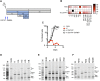
The ~9.5 kilobase HIV-1 genome contains RNA sequences and structures that control many aspects of viral replication, including transcription, splicing, nuclear export, translation, packaging and reverse transcription. Nonetheless, chemical probing and other approaches suggest that the HIV-1 genome may contain many more RNA secondary structures of unknown importance and function. To determine whether there are additional, undiscovered cis-acting RNA elements in the HIV-1 genome that are important for viral replication, we undertook a global silent mutagenesis experiment. Sixteen mutant proviruses containing clusters of ~50 to ~200 synonymous mutations covering nearly the entire HIV-1 protein coding sequence were designed and synthesized. Analyses of these mutant viruses resulted in their division into three phenotypic groups. Group 1 mutants exhibited near wild-type replication, Group 2 mutants exhibited replication defects accompanied by perturbed RNA splicing, and Group 3 mutants had replication defects in the absence of obvious splicing perturbation. The three phenotypes were caused by mutations that exhibited a clear regional bias in their distribution along the viral genome, and those that caused replication defects all caused reductions in the level of unspliced RNA. We characterized in detail the underlying defects for Group 2 mutants. Second-site revertants that enabled viral replication could be derived for Group 2 mutants, and generally contained point mutations that reduced the utilization of proximal splice sites. Mapping of the changes responsible for splicing perturbations in Group 2 viruses revealed the presence of several RNA sequences that apparently suppressed the use of cryptic or canonical splice sites. Some sequences that affected splicing were diffusely distributed, while others could be mapped to discrete elements, proximal or distal to the affected splice site(s). Overall, our data indicate complex negative regulation of HIV-1 splicing by RNA elements in various regions of the HIV-1 genome that enable balanced splicing and viral replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist
Figures
References
-
- Frankel AD, Young JA. HIV-1: fifteen proteins and an RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:1–25. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.1 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cullen BR. RNA-sequence-mediated gene regulation in HIV-1. Infect Agents Dis. 1994;3(2–3):68–76. . - PubMed
-
- Stoltzfus CM, Madsen JM. Role of viral splicing elements and cellular RNA binding proteins in regulation of HIV-1 alternative RNA splicing. Curr HIV Res. 2006;4(1):43–55. . - PubMed
-
- Malim MH, Tiley LS, McCarn DF, Rusche JR, Hauber J, Cullen BR. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires binding of the Rev trans-activator to its RNA target sequence. Cell. 1990;60(4):675–83. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

