Development a hyaluronic acid ion-pairing liposomal nanoparticle for enhancing anti-glioma efficacy by modulating glioma microenvironment
- PMID: 29378465
- PMCID: PMC6058578
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2018.1431979
Development a hyaluronic acid ion-pairing liposomal nanoparticle for enhancing anti-glioma efficacy by modulating glioma microenvironment
Abstract
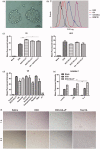
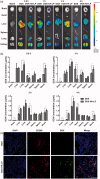
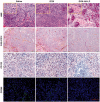
Glioma, one of the most common brain tumors, remains a challenge worldwide. Due to the specific biological barriers such as blood-brain barrier (BBB), cancer stem cells (CSCs), tumor associated macrophages (TAMs), and vasculogenic mimicry channels (VMs), a novel versatile targeting delivery for anti-glioma is in urgent need. Here, we designed a hyaluronic acid (HA) ion-pairing nanoparticle. Then, these nanoparticles were encapsulated in liposomes, termed as DOX-HA-LPs, which showed near-spherical morphology with an average size of 155.8 nm and uniform distribution (PDI = 0.155). HA was proven to specifically bind to CD44 receptor, which is over-expressed on the surface of tumor cells, other associated cells (such as CSCs and TAMs) and VMs. We systematically investigated anti-glioma efficacy and mechanisms in vivo and in vitro. The strong anti-glioma efficacy could attribute to the accumulation in glioma site and the regulation of tumor microenvironment with depletion of TAMs, inhibition of VMs, and elimination of CSCs.
Keywords: CD44; CSCs; Hyaluronic acid; TAMs; glioma.
Figures


References
-
- Allen TM. (1994). The use of glycolipids and hydrophilic polymers in avoiding rapid uptake of liposomes by the mononuclear phagocyte system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 13:285–309.
-
- Cohen ZR, Ramishetti S, Peshes-Yaloz N, et al. (2015). Localized RNAi therapeutics of chemoresistant grade iv glioma using hyaluronan-grafted lipid-based nanoparticles. ACS Nano 9:1581–91. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
