Effects of Omegaven®, EPA, DHA and oxaliplatin on oesophageal adenocarcinoma cell lines growth, cytokine and cell signal biomarkers expression
- PMID: 29378575
- PMCID: PMC5789622
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-018-0664-1
Effects of Omegaven®, EPA, DHA and oxaliplatin on oesophageal adenocarcinoma cell lines growth, cytokine and cell signal biomarkers expression
Abstract
Background: There is limited evidence assessing the effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) on oesophageal adenocarcinoma, both in vitro and in vivo. We evaluated the effects of the omega-3 PUFA and oxaliplatin on OE33 and OE19 cells.
Method: The two oesophageal cells were treated with Omegaven® (fish oil emulsion), EPA, DHA and oxaliplatin and incubated for up to 144 h.
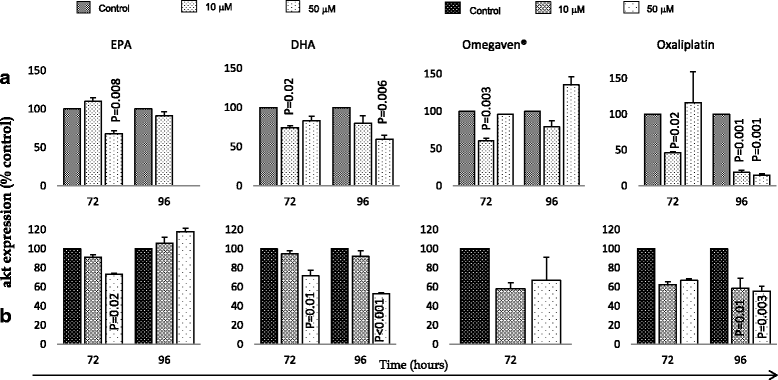
Results: The following inhibitory effects were observed on OE33 cells: EPA reduced cell growth by 39% (p = 0.001), DHA by 59% (p < 0.000) and Oxaliplatin by 77% (p < 0.000). For OE19 cells, the EPA reduced growth by 1% (p = 0.992), DHA by 26% (p = 0.019) and oxaliplatin by 76% (p < 0.000). For both cells, Omegaven® resulted in reduced cell growth at intermediate concentrations (20-40 μM) and increased cell growth at low (10 μM) and high (50 μM) concentrations. DHA, Omegaven® and oxaliplatin were associated with significant downregulation of VEGF and p53 protein, and upregulation of p21 protein. DHA, Omegaven® and Oxaliplatin also led to significant downregulation of the total ERK1/2 and Akt proteins.
Conclusion: DHA, Omegaven® and oxaliplatin were associated with downregulation of p53 and VEGF in both cells. Of the PUFAs studied, DHA alone or in combination (Omegaven®) had greater in vitro anti-cancer effects than EPA alone.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
A M Eltweri, A R Dennison and D J Bowrey received departmental grant support from Fresenius Kabi for clinical trial investigating the effects of Omegaven® intravenous supplement in patients with advanced oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma receiving palliative chemotherapy. A R Dennison have received speaking honoraria from Fresenius Kabi. D J Bowrey has received departmental grant support for unrelated work from Nutricia. The other authors have no conflicts to declare.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- Eltweri AM, Thomas AL, Metcalfe M, Calder PC, Dennison AR, Bowrey DJ. Potential applications of fish oils rich in omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the management of gastrointestinal cancer. Clin Nutr. 2016; - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

