HIV evolution and diversity in ART-treated patients
- PMID: 29378595
- PMCID: PMC5789667
- DOI: 10.1186/s12977-018-0395-4
HIV evolution and diversity in ART-treated patients
Abstract
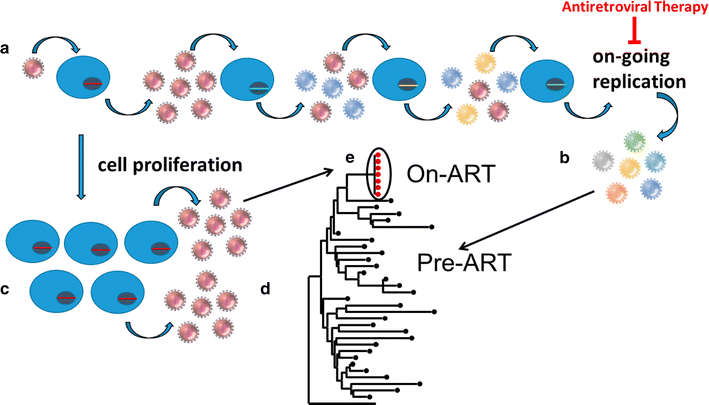
Characterizing HIV genetic diversity and evolution during antiretroviral therapy (ART) provides insights into the mechanisms that maintain the viral reservoir during ART. This review describes common methods used to obtain and analyze intra-patient HIV sequence data, the accumulation of diversity prior to ART and how it is affected by suppressive ART, the debate on viral replication and evolution in the presence of ART, HIV compartmentalization across various tissues, and mechanisms for the emergence of drug resistance. It also describes how CD4+ T cells that were likely infected with latent proviruses prior to initiating treatment can proliferate before and during ART, providing a renewable source of infected cells despite therapy. Some expanded cell clones carry intact and replication-competent proviruses with a small fraction of the clonal siblings being transcriptionally active and a source for residual viremia on ART. Such cells may also be the source for viral rebound after interrupting ART. The identical viral sequences observed for many years in both the plasma and infected cells of patients on long-term ART are likely due to the proliferation of infected cells both prior to and during treatment. Studies on HIV diversity may reveal targets that can be exploited in efforts to eradicate or control the infection without ART.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy (ART); Expanded clones; HIV diversity; HIV genetics; HIV persistence; HIV replication; HIV reservoir.
Figures
References
-
- Boltz VF, Ambrose Z, Kearney MF, Shao W, Kewalramani VN, Maldarelli F, Mellors JW, Coffin JM. Ultrasensitive allele-specific PCR reveals rare preexisting drug-resistant variants and a large replicating virus population in macaques infected with a simian immunodeficiency virus containing human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 2012;86:12525–12530. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

