Validity of the CR-POSSUM model in surgery for colorectal cancer in Spain (CCR-CARESS study) and comparison with other models to predict operative mortality
- PMID: 29378647
- PMCID: PMC5789585
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-018-2839-x
Validity of the CR-POSSUM model in surgery for colorectal cancer in Spain (CCR-CARESS study) and comparison with other models to predict operative mortality
Abstract
Background: To validate and recalibrate the CR- POSSUM model and compared its discriminatory capacity with other European models such as POSSUM, P-POSSUM, AFC or IRCS to predict operative mortality in surgery for colorectal cancer.
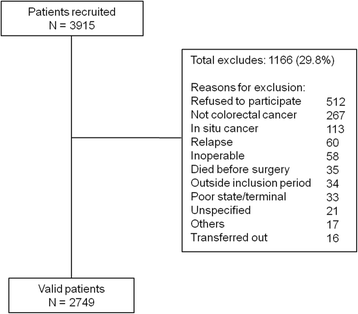
Methods: Prospective multicenter cohort study from 22 hospitals in Spain. We included patients undergoing planned or urgent surgery for primary invasive colorectal cancers between June 2010 and December 2012 (N = 2749). Clinical data were gathered through medical chart review. We validated and recalibrated the predictive models using logistic regression techniques. To calculate the discriminatory power of each model, we estimated the areas under the curve - AUC (95% CI). We also assessed the calibration of the models by applying the Hosmer-Lemeshow test.
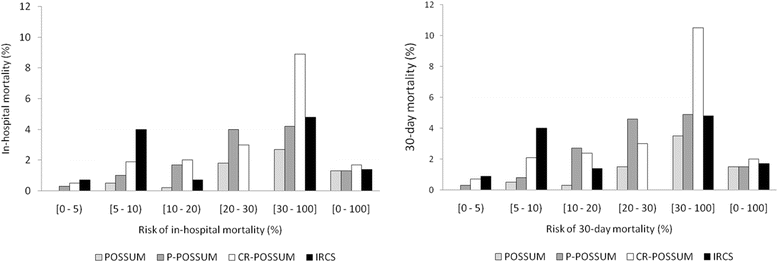
Results: In-hospital mortality was 1.5% and 30-day mortality, 1.7%. In the validation process, the discriminatory power of the CR-POSSUM for predicting in-hospital mortality was 73.6%. However, in the recalibration process, the AUCs improved slightly: the CR-POSSUM reached 75.5% (95% CI: 67.3-83.7). The discriminatory power of the CR-POSSUM for predicting 30-day mortality was 74.2% (95% CI: 67.1-81.2) after recalibration; among the other models the POSSUM had the greatest discriminatory power, with an AUC of 77.0% (95% CI: 68.9-85.2). The Hosmer-Lemeshow test showed good fit for all the recalibrated models.
Conclusion: The CR-POSSUM and the other models showed moderate capacity to discriminate the risk of operative mortality in our context, where the actual operative mortality is low. Nevertheless the IRCS might better predict in-hospital mortality, with fewer variables, while the CR-POSSUM could be slightly better for predicting 30-day mortality.
Trail registration: Registered at: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02488161.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Cr-possum; Operative mortality; Predictive model.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Clinical Research Ethics Committees of the Parc Taulí Sabadell-University Hospital; Hospital del Mar; Fundació Unió Catalana d’Hospitals; Gipuzkoa Health Area; Basque Country (CEIC-E); Hospital Galdakao-Usansolo; Hospital Txagorritxu; Hospital Basurto; La Paz University Hospital; Fundación Alcorcón University Hospital; Hospital Universitario Clínico San Carlos (formerly Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Area 7 – Hospital Clínico San Carlos); Costa del Sol Health Agency and the Regional Committee of Clinical Trials of Andalusia approved the study, and all patients provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. GLOBOCAN. Estimated Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide in. 2012:2012. Available at: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Default.aspx. Accessed 8 June 2015
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- PS09/00805, PI09/90441, PS09/00314, PS09/00910, PS09/00746, PI09/90460, PI09/90490, PI09/90397, PI09/90453/Instituto de Salud Carlos III/International
- 2010111098/The Department of Health of the Basque Country/International
- KRONIK 11/006/KRONIKGUNE -Centro de Investigación en Cronicidad/International
- thematic networks - REDISSEC (Health Services Research on Chronic Diseases Network (RD12/0001/0007)/Istituto de Salud Carlos III/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical