Circadian rhythms in mitochondrial respiration
- PMID: 29378772
- PMCID: PMC5854864
- DOI: 10.1530/JME-17-0196
Circadian rhythms in mitochondrial respiration
Abstract
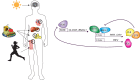
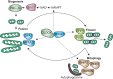
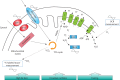
Many physiological processes are regulated with a 24-h periodicity to anticipate the environmental changes of daytime to nighttime and vice versa. These 24-h regulations, commonly termed circadian rhythms, among others control the sleep-wake cycle, locomotor activity and preparation for food availability during the active phase (daytime for humans and nighttime for nocturnal animals). Disturbing circadian rhythms at the organ or whole-body level by social jetlag or shift work, increases the risk to develop chronic metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes mellitus. The molecular basis of this risk is a topic of increasing interest. Mitochondria are essential organelles that produce the majority of energy in eukaryotes by converting lipids and carbohydrates into ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. To adapt to the ever-changing environment, mitochondria are highly dynamic in form and function and a loss of this flexibility is linked to metabolic diseases. Interestingly, recent studies have indicated that changes in mitochondrial morphology (i.e., fusion and fission) as well as generation of new mitochondria are dependent on a viable circadian clock. In addition, fission and fusion processes display diurnal changes that are aligned to the light/darkness cycle. Besides morphological changes, mitochondrial respiration also displays diurnal changes. Disturbing the molecular clock in animal models leads to abrogated mitochondrial rhythmicity and altered respiration. Moreover, mitochondrial-dependent production of reactive oxygen species, which plays a role in cellular signaling, has also been linked to the circadian clock. In this review, we will summarize recent advances in the study of circadian rhythms of mitochondria and how this is linked to the molecular circadian clock.
Keywords: circadian clock; circadian rhythm; mitochondria; mitochondrial functioning; respiration.
© 2018 The authors.
Figures
References
-
- Ammar A, Chtourou H, Hammouda O, Trabelsi K, Chiboub J, Turki M, AbdelKarim O, El Abed K, Ben Ali M, Hoekelmann A, et al 2015. Acute and delayed responses of C-reactive protein, malondialdehyde and antioxidant markers after resistance training session in elite weightlifters: effect of time of day. Chronobiology International 32 1211–1222. (10.3109/07420528.2015.1079215) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andrews JL, Zhang X, McCarthy JJ, McDearmon EL, Hornberger TA, Russell B, Campbell KS, Arbogast S, Reid MB, Walker JR, et al. 2010. CLOCK and BMAL1 regulate MyoD and are necessary for maintenance of skeletal muscle phenotype and function. PNAS 107 19090–19095. (10.1073/pnas.1014523107) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bray MS, Shaw CA, Moore MWS, Garcia RAP, Zanquetta MM, Durgan DJ, Jeong WJ, Tsai J-Y, Bugger H, Zhang D, et al. 2008. Disruption of the circadian clock within the cardiomyocyte influences myocardial contractile function, metabolism, and gene expression. American Journal of Physiology: Heart and Circulatory Physiology 294 H1036–H1047. - PubMed
-
- Cela O, Scrima R, Pazienza V, Merla G, Benegiamo G, Augello B, Fugetto S, Menga M, Rubino R, Fuhr L, et al. 2016. Clock genes-dependent acetylation of complex I sets rhythmic activity of mitochondrial OxPhos. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA): Molecular Cell Research 1863 596–606. (10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.12.018) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

