The degree of enhancer or promoter activity is reflected by the levels and directionality of eRNA transcription
- PMID: 29378788
- PMCID: PMC5828394
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.308619.117
The degree of enhancer or promoter activity is reflected by the levels and directionality of eRNA transcription
Abstract
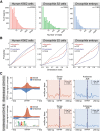
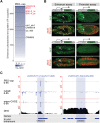
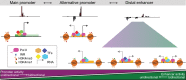
Gene expression is regulated by promoters, which initiate transcription, and enhancers, which control their temporal and spatial activity. However, the discovery that mammalian enhancers also initiate transcription questions the inherent differences between enhancers and promoters. Here, we investigate the transcriptional properties of enhancers during Drosophila embryogenesis using characterized developmental enhancers. We show that while the timing of enhancer transcription is generally correlated with enhancer activity, the levels and directionality of transcription are highly varied among active enhancers. To assess how this impacts function, we developed a dual transgenic assay to simultaneously measure enhancer and promoter activities from a single element in the same embryo. Extensive transgenic analysis revealed a relationship between the direction of endogenous transcription and the ability to function as an enhancer or promoter in vivo, although enhancer RNA (eRNA) production and activity are not always strictly coupled. Some enhancers (mainly bidirectional) can act as weak promoters, producing overlapping spatio-temporal expression. Conversely, bidirectional promoters often act as strong enhancers, while unidirectional promoters generally cannot. The balance between enhancer and promoter activity is generally reflected in the levels and directionality of eRNA transcription and is likely an inherent sequence property of the elements themselves.
Keywords: developmental enhancers; eRNA; embryonic development; ncRNA; promoters; spatio–temporal expression.
© 2018 Mikhaylichenko et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



Comment in
-
Enhancer transcription: what, where, when, and why?Genes Dev. 2018 Jan 1;32(1):1-3. doi: 10.1101/gad.311605.118. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 29440223 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression: Developmental enhancers in action.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;19(4):210. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2018.15. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29463930 No abstract available.
-
Gene expression: Developmental enhancers in action.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Apr;19(4):187. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2018.13. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 29479083 No abstract available.
References
-
- Andersson R, Refsing Andersen P, Valen E, Core LJ, Bornholdt J, Boyd M, Heick Jensen T, Sandelin A. 2014b. Nuclear stability and transcriptional directionality separate functionally distinct RNA species. Nat Commun 5: 5336. - PubMed
-
- Andersson R, Sandelin A, Danko CG. 2015. A unified architecture of transcriptional regulatory elements. Trends Genet 31: 426–433. - PubMed
-
- Archer TK, Lefebvre P, Wolford RG, Hager GL. 1992. Transcription factor loading on the MMTV promoter: a bimodal mechanism for promoter activation. Science 255: 1573–1576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
