Celiac disease and hepatitis C relationships in transcriptional regulatory networks
- PMID: 29379596
- PMCID: PMC5758739
Celiac disease and hepatitis C relationships in transcriptional regulatory networks
Abstract
Aim: we mainly aimed to elucidate potential comorbidities between celiac disease and hepatitis c by means of data and network analysis approaches.
Background: understanding the association among the disorders evidently has important impact on the diagnosis and therapeutic approaches. Celiac disease is the most challenging, common types of autoimmune disorders. On the other hand, hepatitis c virus genome products like some proteins are supposed to be resemble to gliadin types that in turn activates gluten intolerance in people with inclined to gluten susceptibilities. Moreover, a firm support of association between chronic hepatitis and celiac disease remains largely unclear. Henceforth exploring cross-talk among these diseases will apparently lead to the promising discoveries concerning important genes and regulators.
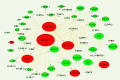
Methods: 321 and 1032 genes associated with celiac disease and hepatitis c retrieved from DisGeNET were subjected to build a gene regulatory network. Afterward a network-driven integrative analysis was performed to exploring prognosticates genes and related pathways.
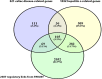
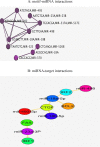
Results: 105 common genes between these diseases included 11 transcription factors were identified as hallmark molecules where by further screening enriched in biological GO terms and pathways chiefly in immune systems and signaling pathways such as chemokines, cytokines and interleukins.
Conclusion: in silico data analysis approaches indicated that the identified selected combinations of genes covered a wide range of known functions triggering the inflammation implicated in these diseases.
Keywords: celiac disease; hepatitis c; regulatory network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ehsani-Ardakani MJ, Rostami Nejad M, Villanacci V, Volta U, Manenti S, Caio G, et al. Gastrointestinal and non-gastrointestinal presentation in patients with celiac disease. Arch Iran Med. 2013;16:78–82. - PubMed
-
- Rostami-Nejad M, Villanacci V, Hogg-Kollars S, Volta U, Manenti S, Reza-Zali M, et al. Endoscopic and histological pitfalls in the diagnosis of celiac disease: A multicentre study assessing the current practice. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2013;105:326–33. - PubMed
-
- Lindenbach BD, Rice CM. Unravelling hepatitis C virus replication from genome to function. Nature. 2005;436:933–8. - PubMed
-
- Mengshol JA, Golden-Mason L, Rosen HR. Mechanisms of Disease: HCV-induced liver injury. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;4:622–34. - PubMed
-
- Gale M Jr, Foy EM. Evasion of intracellular host defence by hepatitis C virus. Nature. 2005;436:939–45. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
