Endothelial-dependent dilation following chronic hypoxia involves TRPV4-mediated activation of endothelial BK channels
- PMID: 29380056
- PMCID: PMC5854740
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-018-2112-5
Endothelial-dependent dilation following chronic hypoxia involves TRPV4-mediated activation of endothelial BK channels
Abstract
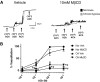
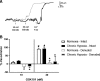
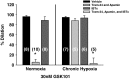
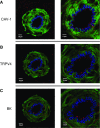
Following chronic hypoxia (CH), the systemic vasculature exhibits blunted vasoconstriction due to endothelial-dependent hyperpolarization (EDH). Previous data demonstrate that subsequent to CH, EDH-mediated vasodilation switches from a reliance on SKca and IKca channels to activation of the endothelial BKca channels (eBK). The mechanism by which endothelial cell stimulation activates eBK channels following CH is not known. We hypothesized that following CH, EDH-dependent vasodilation involves a TRPV4-dependent activation of eBK channels. ACh induced concentration-dependent dilation in pressurized gracilis arteries from both normoxic and CH rats. Inhibition of TRPV4 (RN-1734) attenuated the ACh response in arteries from CH rats but had no effect in normoxic animals. In the presence of L-NNA and indomethacin, TRPV4 blockade attenuated ACh-induced vasodilation in arteries from CH rats. ACh elicited endothelial TRPV4-mediated Ca2+ events in arteries from both groups. GSK1016790A (GSK101, TRPV4 agonist) elicited vasodilation in arteries from normoxic and CH rats. In arteries from normoxic animals, TRAM-34/apamin abolished the dilation to TRPV4 activation, whereas luminal iberiotoxin had no effect. In CH rats, only administration of all three Kca channel inhibitors abolished the dilation to TRPV4 activation. Using Duolink®, we observed co-localization between Cav-1, TRPV4, and BK channels in gracilis arteries and in RAECs. Disruption of endothelial caveolae with methyl-β-cyclodextrin significantly decreased ACh-induced vasodilation in arteries from both groups. In gracilis arteries, endothelial membrane cholesterol was significantly decreased following 48 h of CH. In conclusion, CH results in a functional coupling between muscarinic receptors, TRPV4 and Kca channels in gracilis arteries.
Keywords: BK channel; Chronic hypoxia; Endothelium; TRPV4.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Endothelial cell membrane cholesterol content regulates the contribution of TRPV4 channels in ACh-induced vasodilation in rat gracilis arteries.Microcirculation. 2022 Jul;29(4-5):e12774. doi: 10.1111/micc.12774. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Microcirculation. 2022. PMID: 35689491 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen sulfide-induced vasodilation mediated by endothelial TRPV4 channels.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):H1437-H1444. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00465.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27765747 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role of endothelial BKCa channels in altered vasoreactivity following hypoxia.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Nov;299(5):H1439-50. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00124.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20817829 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelium-dependent cerebral artery dilation mediated by transient receptor potential and Ca2+-activated K+ channels.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;57(2):148-53. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181f580d9. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20729757 Review.
-
Role of TRPV4 channel in vasodilation and neovascularization.Microcirculation. 2021 Aug;28(6):e12703. doi: 10.1111/micc.12703. Epub 2021 May 24. Microcirculation. 2021. PMID: 33971061 Review.
Cited by
-
TRPV4 channel activation induces the transition of venous and arterial endothelial cells toward a pro-inflammatory phenotype.Physiol Rep. 2021 Feb;9(3):e14613. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14613. Physiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33512067 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Channel Regulation in Caveolae and Its Pathological Implications.Cells. 2025 Apr 24;14(9):631. doi: 10.3390/cells14090631. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40358155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell transcriptomic heterogeneity between conduit and resistance mesenteric arteries in rats.Physiol Genomics. 2023 Apr 1;55(4):179-193. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00126.2022. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Physiol Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36912534 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cell membrane cholesterol content regulates the contribution of TRPV4 channels in ACh-induced vasodilation in rat gracilis arteries.Microcirculation. 2022 Jul;29(4-5):e12774. doi: 10.1111/micc.12774. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Microcirculation. 2022. PMID: 35689491 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial TRPV4 channels and vasodilator reactivity.Curr Top Membr. 2020;85:89-117. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2020.01.007. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Curr Top Membr. 2020. PMID: 32402646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Doyle MP, Walker BR. Attentuation of systemic vasoreactivity in chronically hypoxic rats. Am J Phys. 1991;260:R1114–R1122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

