Therapeutic Inertia and Treatment Intensification
- PMID: 29380142
- PMCID: PMC6452867
- DOI: 10.1007/s11906-018-0802-1
Therapeutic Inertia and Treatment Intensification
Abstract
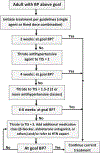
Purpose of review: This review aims to emphasize how therapeutic inertia, the failure of clinicians to intensify treatment when blood pressure rises or remains above therapeutic goals, contributes to suboptimal blood pressure control in hypertensive populations.
Recent findings: Studies reveal that the therapeutic inertia is quite common and contributes to suboptimal blood pressure control. Quality improvement programs and standardized approaches to support antihypertensive treatment intensification are ways to combat therapeutic inertia. Furthermore, programs that utilize non-physician medical professionals such as pharmacists and nurses demonstrate promise in mitigating the effects of this important problem. Therapeutic inertia impedes antihypertensive management and requires a broad effort to reduce its effects. There is an ongoing need for renewed focus and research in this area to improve hypertension control.
Keywords: Antihypertensive therapy; HTN management; Hypertension control; Therapeutic inertia; Treatment intensification.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest relevant to this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
-
Berlowitz DR, Ash AS, Hickey EC, Friedman RH, Glickman M, Kader B, et al. Inadequate management of blood pressure in a hypertensive population. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(27):1957–63. 10.1056/NEJM199812313392701.
•This article is an excellent introduction to the concept of therapeutic inertia.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

