Combined and Alternating Topical Steroids and Food Elimination Diet for the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- PMID: 29380175
- PMCID: PMC7063535
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-018-4931-9
Combined and Alternating Topical Steroids and Food Elimination Diet for the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Abstract
Background: Few studies have examined combined or alternating treatment algorithms in eosinophilic esophagitis.
Aims: We conducted a retrospective cohort study to ascertain the efficacy and adherence to a combined and alternating treatment approach with topical corticosteroids and 2-food elimination diet for pediatric EoE.
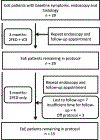
Methods: Patients were prescribed a 2-food elimination diet (milk and soy) and topical corticosteroid (fluticasone or oral viscous budesonide) for 3 months, after which the steroid was discontinued and 2-food elimination diet continued for 3 months. An EGD was performed at baseline, 3 and 6 months. Clinical, endoscopic, and histologic data were extracted from electronic medical records. Nonparametric tests assessed adherence and outcomes.
Results: Twenty-nine eosinophilic esophagitis cases were included (mean age 11.5 years, 61% male). Complete adherence to combined therapy and 2-food elimination diet alone was 75 and 79%, respectively. Median eosinophil counts decreased from 51 to 2 eosinophils/hpf (p < 0.001) after combined treatment and rebounded to 31 (p = 0.07) after 2FED alone. Dysphagia improved after both the combined and 2-food elimination diet alone treatment approaches (52 vs. 11% and 10%; p = 0.001, 0.005). Nonsignificant improvements in endoscopic findings were documented across the length of follow-up.
Conclusions: An initial combined treatment approach resulted in significant improvements in symptoms and histologic findings. While symptomatic improvements continued with 2-food elimination diet alone, the histologic improvement was not maintained. While loss to follow-up may obscure the efficacy of 2-food elimination diet alone, a combined/alternating treatment approach merits assessment in a larger prospective study.
Keywords: Dysphagia; Eosinophilic esophagitis, topical corticosteroids; Food bolus impaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
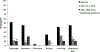
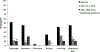

Comment in
-
Topical Steroids and Elimination Diets for EoE: Happier Together?Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Sep;63(9):2163-2164. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5055-y. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29675661 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Katzka DA. ACG clinical guideline: Evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(5):679–92; quiz 693. doi:10.1038/ajg.2013.71. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

