Riedel's thyroiditis: clinical presentation, treatment and outcomes
- PMID: 29380231
- PMCID: PMC5845586
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-018-1526-3
Riedel's thyroiditis: clinical presentation, treatment and outcomes
Abstract
Background: Riedel´s thyroiditis (RT) is a rare inflammatory disease of the thyroid gland, causing compression and fibrosis of adjacent tissues. Typically the goiter is hard and firm. Hoarseness, dyspnea, and dysphagia may be present.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all patients known by us with RT in addition to all patients with appropriate ICD-10 codes evaluated at the Karolinska University Hospital 2003-2015. Clinical, biochemical, and histological data of patients with RT were recorded in detail. Histological preparations were re-examined when available.
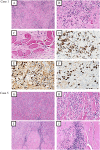
Results: RT was diagnosed in six patients. Five were females and the median age at first presentation was 50 years (25-81 years). Median follow-up time was 3.75 years (1-22 years). At diagnosis five had hypothyroidism. Four had extrathyroidal manifestations, and one of these had also distant fibrosis. One patient had a clear IgG4/IgG ratio over 40%. One patient was treated with tracheostomy, one with isthmectomy and one with total thyroidectomy. Four had been treated with glucocorticoids, four with tamoxifen, and two with both drugs. One had also been treated with mycophenolate mofetil combined with Rituximab. At the end of follow-up four was doing fine, one had recurrent episodes of inflammation and one had died of possible complications to RT.
Conclusion: It is important to recognize RT and give adequate treatment. Steroids are still the mainstay of therapy but other medications against fibrosclerosis can be considered. Wakefulness of other fibrosing manifestations is essential. Immunohistochemistry can show whether IgG-4 plasma cells are increased which could lead to fibrosis in other organs.
Keywords: Diagnose; Glucocorticoid treatment; IgG4; Inflammation; Riedel.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of retrospective study formal consent was not required.
Figures
References
-
- Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, Chan JK, Heathcote JG, Aalberse R, Azumi A, Bloch DB, Brugge WR, Carruthers MN, Cheuk W, Cornell L, Castillo CF, Ferry JA, Forcione D, Klöppel G, Hamilos DL, Kamisawa T, Kasashima S, Kawa S, Kawano M, Masaki Y, Notohara K, Okazaki K, Ryu JK, Saeki T, Sahani D, Sato Y, Smyrk T, Stone JR, Takahira M, Umehara H, Webster G, Yamamoto M, Yi E, Yoshino T, Zamboni G, Zen Y, Chari S. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(10):3061–3067. doi: 10.1002/art.34593. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, Matsui S, Sumida T, Mimori T, Tanaka Y, Tsubota K, Yoshino T, Kawa S, Suzuki R, Takegami T, Tomosugi N, Kurose N, Ishigaki Y, Azumi A, Kojima M, Nakamura S, Inoue D. Research Program for Intractable Disease by Ministry of Health, L., Welfare Japan, G.t., A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod. Rheumatol. 2012;22(1):1–14. doi: 10.3109/s10165-011-0508-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

