WNT5A induces castration-resistant prostate cancer via CCL2 and tumour-infiltrating macrophages
- PMID: 29381686
- PMCID: PMC5846063
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2017.451
WNT5A induces castration-resistant prostate cancer via CCL2 and tumour-infiltrating macrophages
Abstract
Background: Although the standard treatment for the patients with recurrent and metastatic prostate cancer (CaP) is androgen deprivation therapy, castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) eventually emerges. Our previous report indicated that bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP6) induced CRPC via tumour-infiltrating macrophages. In a separate line of study, we have observed that the WNT5A/BMP6 loop in CaP bone metastasis mediates resistance to androgen deprivation in tissue culture. Simultaneously, we have reported that BMP6 induced castration resistance in CaP cells via tumour-infiltrating macrophages. Therefore, our present study aims to investigate the mechanism of WNT5A and its interaction with macrophages on CRPC.
Methods: Doxycycline inducible WNT5A overexpression prostate cancer cell line was used for detailed mechanical study.
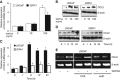
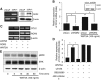
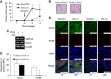
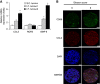
Results: WNT5A was associated with increased expression of chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) in the human CaP cell line, LNCaP. Mechanistically, this induction of CCL2 by WNT5A is likely to be mediated via the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signalling pathway. Our in vivo experiments demonstrated that the overexpression of WNT5A in LNCaP cells promoted castration resistance. Conversely, this resistance was inhibited with the removal of macrophages via clodronate liposomes. When patient-derived CaP LuCaP xenografts were analysed, high levels of WNT5A were correlated with increased levels of CCL2 and BMP6. In addition, higher levels of CCL2 and BMP6 were more commonly observed in intra-femoral transplanted tumours as compared to subcutaneous-transplanted tumours in the patient-derived PCSD1 bone-niche model.
Conclusions: These findings collectively suggest that WNT5A may be a key gene that induces CRPC in the bone niche by recruiting and regulating macrophages through CCL2 and BMP6, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prostate cancer bone metastases acquire resistance to androgen deprivation via WNT5A-mediated BMP-6 induction.Br J Cancer. 2014 Mar 18;110(6):1634-44. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.23. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24518599 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-6 induces castration resistance in prostate cancer cells through tumor infiltrating macrophages.Cancer Sci. 2013 Aug;104(8):1027-32. doi: 10.1111/cas.12206. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Cancer Sci. 2013. PMID: 23710822 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages induce neuroendocrine differentiation of prostate cancer cells via BMP6-IL6 Loop.Prostate. 2011 Oct 1;71(14):1525-37. doi: 10.1002/pros.21369. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Prostate. 2011. PMID: 21374653
-
Androgen deprivation therapy-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer through downregulating SPDEF and activating CCL2.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 May;1864(5 Pt A):1717-1727. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.02.016. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 29477409
-
Recent advances in prostate cancer: WNT signaling, chromatin regulation, and transcriptional coregulators.Asian J Androl. 2023 Mar-Apr;25(2):158-165. doi: 10.4103/aja2022109. Asian J Androl. 2023. PMID: 36695247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SFMBT2-Mediated Infiltration of Preadipocytes and TAMs in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 22;12(9):2718. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092718. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32971847 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Noncoding RNA in the Occurrence of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 9;24(2):1305. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021305. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Prostate Organogenesis and a Role for iPSC-Derived Prostate Organoids to Study Prostate Development and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 3;22(23):13097. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313097. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CC Chemokine Ligand-2: A Promising Target for Overcoming Anticancer Drug Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;14(17):4251. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174251. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt and β-Catenin Signaling in the Bone Metastasis of Prostate Cancer.Life (Basel). 2021 Oct 16;11(10):1099. doi: 10.3390/life11101099. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azenshtein E, Luboshits G, Shina S, Neumark E, Shahbazian D, Weil M, Wigler N, Keydar I, Ben-Baruch A (2002) The CC chemokine RANTES in breast carcinoma progression: regulation of expression and potential mechanisms of promalignant activity. Cancer Res 62(4): 1093–2102. - PubMed
-
- Baron R, Kneissel M (2013) WNT signalling in bone homeostasis and disease: from human mutations to treatments. Nat Med 19(2): 179–192. - PubMed
-
- Blanc E, Roux GL, Benard J, Raguenez G (2005) Low expression of Wnt-5a gene is associated with high-risk neuroblastoma. Oncogene 24(7): 1277–1283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

