SozRank: A new approach for localizing the epileptic seizure onset zone
- PMID: 29381703
- PMCID: PMC5806930
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005953
SozRank: A new approach for localizing the epileptic seizure onset zone
Abstract
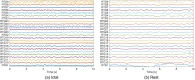
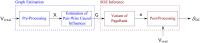
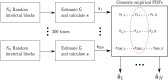
Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders affecting about 1% of the world population. For patients with focal seizures that cannot be treated with antiepileptic drugs, the common treatment is a surgical procedure for removal of the seizure onset zone (SOZ). In this work we introduce an algorithm for automatic localization of the seizure onset zone (SOZ) in epileptic patients based on electrocorticography (ECoG) recordings. The proposed algorithm builds upon the hypothesis that the abnormal excessive (or synchronous) neuronal activity in the brain leading to seizures starts in the SOZ and then spreads to other areas in the brain. Thus, when this abnormal activity starts, signals recorded at electrodes close to the SOZ should have a relatively large causal influence on the rest of the recorded signals. The SOZ localization is executed in two steps. First, the algorithm represents the set of electrodes using a directed graph in which nodes correspond to recording electrodes and the edges' weights quantify the pair-wise causal influence between the recorded signals. Then, the algorithm infers the SOZ from the estimated graph using a variant of the PageRank algorithm followed by a novel post-processing phase. Inference results for 19 patients show a close match between the SOZ inferred by the proposed approach and the SOZ estimated by expert neurologists (success rate of 17 out of 19).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





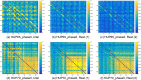
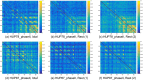
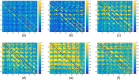
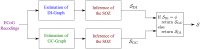
References
-
- Fisher RS, v Emde Boas W, Blume W, Elger C, Genton P, Lee P, et al. Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: definitions proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia. 2005;46(4):470–472. doi: 10.1111/j.0013-9580.2005.66104.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Mierlo P, Papadopoulou M, Carrette E, Boon P, Vandenberghe S, Vonck K, et al. Functional brain connectivity from EEG in epilepsy: Seizure prediction and epileptogenic focus localization. Progress in Neurobiology. 2014;121:19–35. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.06.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yaffe RB, Borger P, Megevand P, Groppe AM, Kramer MA, Chu CJ, et al. Physiology of functional and effective networks in epilepsy. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2015;126:227–236. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.09.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duncan JS, Sander JW, Sisodiya SM, Walker MC. Adult epilepsy. The Lancet. 2007;367(9516):1087–1100. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68477-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosenow F, Luders H. Presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Brain. 2001; p. 1683–1700. doi: 10.1093/brain/124.9.1683 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

