Ticagrelor attenuates myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury possibly through downregulating galectin-3 expression in the infarct area of rats
- PMID: 29381821
- PMCID: PMC5980592
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13536
Ticagrelor attenuates myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury possibly through downregulating galectin-3 expression in the infarct area of rats
Abstract
Aims: The full benefits of myocardial revascularization strategies applied to acute myocardial infarction patients might be reduced by myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion (I/R) injury. It is known that inflammation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of I/R injury and galectin-3, a known inflammatory factor, is actively involved in ischaemia-induced inflammation and fibrosis of various organs. Previous studies demonstrated that anti-platelets therapy with ticagrelor, a new P2Y12 receptor antagonist, could effectively attenuate myocardial I/R injury and I/R injury-related inflammatory responses. It remains unknown whether the cardioprotective effects of ticagrelor are also mediated by modulating myocardial galectin-3 expression.
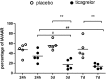
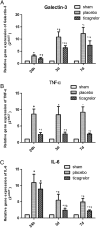
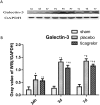
Methods: We determined the ratio of infarct area (IA)/area at risk (AAR), expression of galectin-3, TNF-α and IL-6 in infarct area of rats treated with placebo (equal volume saline per gastric gavage immediately after LAD ligation, then once daily till study end) or ticagrelor (150 mg kg-1 dissolved in saline per gastric gavage immediately after LAD ligation, then once daily till study end) at 24 h, 3 and 7 days post I (45 min)/R injury. Sham-operated rats served as control.
Results: Our results showed that ticagrelor treatment significantly reduced IA/AAR ratio at 3 and 7 days post I/R, downregulated mRNA and protein expression of galectin-3, as well as mRNA expression of TNF-α and IL-6 in infarct area at 24 h, 3 and 7 days post I/R.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the cardioprotective effects of ticagrelor might partly be mediated by downregulating galectin-3 expression in infarct area in this rat model of myocardial I/R injury.
Keywords: galectin-3; inflammation; ischaemia-reperfusion injury; ticagrelor.
© 2018 The Authors. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Berger PB, Ellis SG, Holmes DR Jr, Granger CB, Criger DA, Betriu A, et al Relationship between delay in performing direct coronary angioplasty and early clinical outcome in patients with acute myocardial infarction: results from the global use of strategies to open occluded arteries in Acute Coronary Syndromes (GUSTO‐IIb) trial. Circulation 1999; 100: 14–20. - PubMed
-
- Benhabbouche S, Crola da Silva C, Abrial M, Ferrera R. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim 2011). [The basis of ischemia‐reperfusion and myocardial protection]; 30 (Suppl 1): S2–S16. - PubMed
-
- Sanada S, Komuro I, Kitakaze M. Pathophysiology of myocardial reperfusion injury: preconditioning, postconditioning, and translational aspects of protective measures. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2011; 301: H1723–H1741. - PubMed
-
- Frangogiannis NG, Smith CW, Entman ML. The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res 2002; 53: 31–47. - PubMed
-
- Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ. Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 1121–1135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

