Factors influencing the virological testing of cornea donors
- PMID: 29381929
- PMCID: PMC5708928
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008561
Factors influencing the virological testing of cornea donors
Abstract
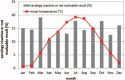
To assess the influence of donor, environment, and logistical factors on the results of virological testing of blood samples from cornea donors.Data from 670 consecutive cornea donors were analyzed retrospectively. Logistic regression analysis was used to assess the influence of different factors on the results of virological testing of blood samples from cornea donors.The mean annual rate of donors with serology-reactive or not evaluable result was 14.8% (99 of 670) (range 11.9%-16.9%). The cause of donor death by cancer increased the risk of serology-reactive or not evaluable result (P = .0300). Prolonged time between death and post mortem blood removal was associated with a higher rate of serology-reactive or not evaluable result (P < .0001). Mean monthly temperature including warmer months, differentiating between septic and aseptic donors, sex, and donor age had no significant impact on the results of virological testing of blood samples from cornea donors.The cause of donor death by cancer and a prolonged time between death and post mortem blood removal seem to be mainly responsible for serology-reactive or not evaluable result of blood samples from cornea donors. The percentage of discarded corneas caused by serology-reactive or not evaluable result may be reduced by shortening the period of time between death and post mortem blood removal.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Factors influencing the contamination rate of human organ-cultured corneas.Acta Ophthalmol. 2017 Dec;95(8):e706-e712. doi: 10.1111/aos.13375. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28321999
-
Factors that influence the suitability of human organ-cultured corneas.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016 Jan;254(1):135-41. doi: 10.1007/s00417-015-3119-7. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 26287265
-
[Analysis of Factors Influencing the Suitability of Donor Corneas in the LIONS Cornea Bank Saar-Lor-Lux, Trier/Westpfalz from 2006 to 2016].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2020 Nov;237(11):1334-1342. doi: 10.1055/a-1141-3703. Epub 2020 May 20. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2020. PMID: 32434230 German.
-
Factors affecting the serological testing of cadaveric donor cornea.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2018 Jan;66(1):61-65. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_656_17. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29283125 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative infectious serology testing of pre- and post-mortem blood samples from cornea donors.Cell Tissue Bank. 2012 Aug;13(3):447-52. doi: 10.1007/s10561-012-9326-0. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Cell Tissue Bank. 2012. PMID: 22802139
Cited by
-
Factors influencing the contamination rates of the conjunctival swabs and organ culture media of human donor eyes.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Sep;97(38):e11879. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011879. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30235655 Free PMC article.
-
Donor-Dependent Factors Influencing Contamination Rates of Conjunctival Swabs of Human Donor Eyes.Ann Transplant. 2019 Apr 10;24:191-198. doi: 10.12659/AOT.912266. Ann Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30967524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zirm E. Eine Erfolgreiche totale Keratoplastik. Graefes Arch Ophthalmol 1906;64:580–93.
-
- Moffatt SL, Cartwright VA, Stumpf TH. Centennial review of corneal transplantation. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2005;33:642–57. - PubMed
-
- Gain P, Jullienne R, He Z, et al. Global survey of corneal transplantation and eye banking. JAMA Ophthalmol 2016;134:167–73. - PubMed
-
- Yoeruek E, Bartz Schmidt KU. Current approaches to combat the shortage of corneal tissues: split-DMEK and double-split keratoplasty. Cornea 2015;34:e6–9. - PubMed
-
- Heindl LM, Riss S, Bachmann BO, et al. Split cornea transplantation for 2 recipients: a new strategy to reduce corneal tissue cost and shortage. Ophthalmology 2011;118:294–301. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

