Effects of treatment with chemotherapy and/or tamoxifen on the biomarkers of cardiac injury and oxidative stress in women with breast cancer
- PMID: 29381962
- PMCID: PMC5708961
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008723
Effects of treatment with chemotherapy and/or tamoxifen on the biomarkers of cardiac injury and oxidative stress in women with breast cancer
Abstract
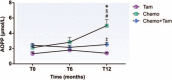
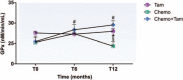
There has been an increase in deaths from cardiovascular diseases following breast cancer therapy. Evidence has shown that this outcome is, in part, associated with cardiotoxicity induced by the chemotherapeutic drugs and the increase in oxidative stress. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of chemotherapy and hormone therapy with tamoxifen on the biomarkers of cardiac injury and oxidative stress in women with breast cancer.Thirty women were followed-up for 1 year and were divided into 3 groups according to the treatment protocol: women treated only with tamoxifen and clinical follow up for 12 months (Tam, n = 10); women treated only with chemotherapy for 6 months with clinical follow up for an additional 6-month period (Chemo, n = 10); and women who received chemotherapy for 6 months followed by a 6-month period only with tamoxifen therapy and clinical follow up (Chemo + Tam, n = 10). Analysis of the blood levels of cardiac troponin I (cTnI), advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP) and the activity of the plasmatic isoform of the antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase (GPx) was performed before treatment (T0) and at 6 (T6) and 12 (T12) months after treatment.The Chemo group showed higher levels of cTnI (0.065 ± 0.006 ng/mL, P < .05) and AOPP (4.99 ± 0.84 μmol/L, P < .05) and reduced GPx activity (24.4 ± 1.1 nM/min/mL, P < .05) at T12 than the Tam group (cTnI: 0.031 ± 0.001 ng/mL; AOPP: 1.40 ± 0.10 μmol/L; GPx: 28.0 ± 0.7 nM/min/mL) and Chemo + Tam group (cTnI: 0.037 ± 0.002 ng/mL; AOPP: 2.53 ± 0.30 μmol/L; GPx: 29.5 ± 1.0 nM/min/mL).These data support the hypothesis that long-term oxidative stress after chemotherapy may have an impact on cardiovascular diseases and that tamoxifen has cardioprotective effects.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hormone therapy with tamoxifen reduces plasma levels of NT-B-type natriuretic peptide but does not change ventricular ejection fraction after chemotherapy in women with breast cancer.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015 Feb;48(2):154-60. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20144189. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015. PMID: 25424369 Free PMC article.
-
Tamoxifen alone versus tamoxifen plus 1-(2-tetrahydrofuryl)-5-fluorouracil in the treatment of advanced breast cancer: a sequential trial.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1981;1(1):53-8. doi: 10.1007/BF01807892. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1981. PMID: 6816315 Clinical Trial.
-
Augmented antioxidant status in Tamoxifen treated postmenopausal women with breast cancer on co-administration with Coenzyme Q10, Niacin and Riboflavin.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008 May;61(6):933-41. doi: 10.1007/s00280-007-0547-z. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17668211
-
Current status of post-chemotherapy tamoxifen in early breast cancer.Oncology (Williston Park). 1994 Nov;8(11):39-43; discussion 47-9. Oncology (Williston Park). 1994. PMID: 7826838 Review.
-
Levonorgestrel intrauterine system for endometrial protection in women with breast cancer on adjuvant tamoxifen.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 21;12(12):CD007245. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007245.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33348436 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
New Insights in the Era of Clinical Biomarkers as Potential Predictors of Systemic Therapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Women with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 22;15(13):3290. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133290. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Preliminary Evaluation of Advanced Oxidation Protein Products (AOPPs) as a Potential Approach to Evaluating Prognosis in Early-Stage Breast Cancer Patients and Its Implication in Tumour Angiogenesis: A 7-Year Single-Centre Study.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 6;16(5):1068. doi: 10.3390/cancers16051068. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473424 Free PMC article.
-
Randomised controlled trial of intermittent vs continuous energy restriction during chemotherapy for early breast cancer.Br J Cancer. 2022 May;126(8):1157-1167. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01650-0. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Br J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34912072 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Aromatase inhibitors use and risk for cardiovascular disease in breast cancer patients: A population-based cohort study.Breast. 2021 Oct;59:157-164. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2021.07.004. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Breast. 2021. PMID: 34265496 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Cachexia: Unaddressed Aspect in Cancer Patients.Cells. 2022 Mar 14;11(6):990. doi: 10.3390/cells11060990. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35326441 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Raj S, Franco VI, Lipshultz SE. Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: a review of pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 2014;16:314–28. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

