Urachal borderline mucinous cystadenoma: A rare case report and literature review
- PMID: 29381965
- PMCID: PMC5708964
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008740
Urachal borderline mucinous cystadenoma: A rare case report and literature review
Abstract
Rationale: Urachal borderline mucinous cystadenoma is very rare and has only 9 cases in the current literature with the biological behavior between adenoma and adenocarcinoma.
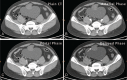
Patient concerns: We reported a 41-year-old man with moderate lower abdominal pain, and the imaging examination found an irregular cystic lesion extending from umbilicus to the dome of urinary bladder with significant separations and calcifications.
Diagnoses: The diagnosis was confirmed according to the specific anatomical location and pathological examination which was proved as mucinous cystadenoma with low malignant potential.
Interventions: The patient undertook radical excision and partial cystectomy.
Outcomes: His postoperative condition was good.
Lessons: Urachal borderline mucinous cystadenoma can be located by image examination, which may also offer several diagnostic tips according to separation, calcification, and enhancement in computed tomography scan. When combined with pathological findings, qualitative diagnosis can be determined. Surgical resection should be chosen as an optimal treatment. Our present study reviewed the clinical and biological information of all previous cases which were diagnosed as urachal borderline mucinous cystadenoma and we supplemented more data for further study.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cystic mucinous tumors of the urachus: carcinoma in situ or adenoma of unknown malignant potential?Can J Urol. 2012 Jun;19(3):6310-3. Can J Urol. 2012. PMID: 22704322 Review.
-
Complex mucinous cystadenoma of undetermined malignant potential of the urachus: a rare case with review of the literature.Malays J Pathol. 2014 Aug;36(2):145-8. Malays J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25194538 Review.
-
Mucinous Cystadenoma of the Urachus and Review of Current Classification of Urachal Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2019 Feb;143(2):258-263. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0319-RS. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 30398914 Review.
-
Urachal mucinous adenocarcinoma with pseudomyxoma peritonei: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Sep;96(35):e7548. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007548. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28858081 Free PMC article.
-
Metastatic urachal carcinoma of the ovary.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2011 Dec;37(12):1833-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.2011.01615.x. Epub 2011 Jul 27. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2011. PMID: 21794003
Cited by
-
Urachal Mucinous Cystic Tumor of Low Malignant Potential with Concurrent Sigmoid Colon Adenocarcinoma.Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2019 Jun 25;2019:1434838. doi: 10.1155/2019/1434838. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2019. PMID: 31341685 Free PMC article.
-
Urachal mucinous cystic tumor of low malignant potential in a polymorbid female: a case report and review of the literature.Int Cancer Conf J. 2022 Jan 15;11(2):104-108. doi: 10.1007/s13691-021-00530-x. eCollection 2022 Apr. Int Cancer Conf J. 2022. PMID: 35402128 Free PMC article.
-
Rare urachal mucinous cystic tumor of low malignant potential with peritoneal pseudomyxoma: A case report.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Oct 17;26(6):555. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12254. eCollection 2023 Dec. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37941591 Free PMC article.
-
Mucinous Cystadenoma of the Urachal Remnant Successfully Resected by Laparoscopic Surgery: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Jul 18;16(7):e64790. doi: 10.7759/cureus.64790. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39156387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nguyen M, Addicott B, Chu J, et al. Congenital cyst of the umbilical cord. Fetal Pediatr Pathol 2016;1–4. - PubMed
-
- Young S, McGeechan A, Davidson P, et al. Management of the giant umbilical cord: challenging the need for investigations in the newborn. Archives of disease in childhood Fetal and neonatal edition 2016. - PubMed
-
- Naiditch JA, Radhakrishnan J, Chin AC. Current diagnosis and management of urachal remnants. J Pediatr Surg 2013;48:2148–52. - PubMed
-
- Paner GP, Lopez-Beltran A, Sirohi D, et al. Updates in the pathologic diagnosis and classification of epithelial neoplasms of urachal origin. Adv Anat Pathol 2016;23:71–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

