Case report: remarkable remission of SAPHO syndrome in response to Tripterygium wilfordii hook f treatment
- PMID: 29382023
- PMCID: PMC5709022
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008903
Case report: remarkable remission of SAPHO syndrome in response to Tripterygium wilfordii hook f treatment
Abstract
Rationale: SAPHO (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis) syndrome is an autoinflammatory disease with no standardized treatment. Tripterygium wilfordii hook f (TwHF) is a Chinese herb with immunosuppressive effects and has been used to treat some chronic inflammatory diseases. However, it has not been reported as a therapeutic option in SAPHO syndrome. Here we present the first report in which a remarkable remission of SAPHO syndrome was achieved in response to TwHF.
Patient concerns: A 57-year-old female patient noted swelling and pain at the anterior chest wall and scattered rashes like psoriasis vulgaris. Bone scintigraphy demonstrated the classic "bull's head" sign and magnetic resonance images indicated bone marrow edema on T5.
Diagnoses: The diagnosis was made by dermatological and osteoarticular manifestations and classical "bull's head" sign in bone scintigraphy.
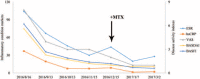
Interventions: TwHF with a priming dose of 20 mg 3 times per day and a gradual dose reduction of 20 mg per day in every 3 months. Four months later, methotrexate was added with 10 mg per week.
Outcomes: Osteoarticular symptoms and radiological abnormalities were improved dramatically.
Lessons: This case illustrates a promising strategy to treat SAPHO syndrome.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Successful treatment of synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis and paradoxical skin lesions by Tripterygium wilfordii hook f: a case report.J Int Med Res. 2020 Sep;48(9):300060520949100. doi: 10.1177/0300060520949100. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32962502 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights in the Treatment of SAPHO Syndrome and Medication Recommendations.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Apr 13;15:2365-2380. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S353539. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35444448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid induction of clinical remission in SAPHO syndrome using high-dose Tripterygium glycosides: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jul 2;99(27):e21102. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021102. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32629743 Free PMC article.
-
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. in the treatment of synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis syndrome: a clinical trial.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Jun;40(6):2427-2438. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05562-x. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33389313 Clinical Trial.
-
Imaging for Synovitis, Acne, Pustulosis, Hyperostosis, and Osteitis (SAPHO) Syndrome.Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2016 Nov;42(4):695-710. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2016.07.011. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2016. PMID: 27742022 Review.
Cited by
-
Successful treatment of synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis and paradoxical skin lesions by Tripterygium wilfordii hook f: a case report.J Int Med Res. 2020 Sep;48(9):300060520949100. doi: 10.1177/0300060520949100. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32962502 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of treatments for patients with SAPHO syndrome: a follow-up study of 24 cases from a single center and review of literature.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Mar;40(3):1131-1139. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05322-x. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32789818 Review.
-
New Insights in the Treatment of SAPHO Syndrome and Medication Recommendations.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Apr 13;15:2365-2380. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S353539. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35444448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid induction of clinical remission in SAPHO syndrome using high-dose Tripterygium glycosides: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jul 2;99(27):e21102. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021102. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32629743 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of lncRNA and circRNA Expression in Mouse Testes after Exposure to Triptolide.Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(8):665-673. doi: 10.2174/1389200220666190729130020. Curr Drug Metab. 2019. PMID: 31362668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Firinu D, Garcia-Larsen V, Manconi PE, et al. SAPHO syndrome: current developments and approaches to clinical treatment. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2016;18:35. - PubMed
-
- Kao PN, Qiu D. Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of triptolide, the principal active diterpenoid from the Chinese medicinal herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. Drugs R D 2003;4:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Benhamou CL, Chamot AM, Kahn MF, et al. Synovitis-acne-pustulosis hyperostosis-osteomyelitis syndrome (SAPHO). A new syndrome among the spondyloarthropathies? Clin Exp Rheumatol 1988;6:109–12. - PubMed
-
- Wong KF, Yuan Y, Luk JM. Tripterygium wilfordii bioactive compounds as anticancer and anti-inflammatory agents. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2012;39:311–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

