Corylin Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via the Inhibition of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Mediated by Long Noncoding RNA GAS5
- PMID: 29382035
- PMCID: PMC5855602
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19020380
Corylin Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via the Inhibition of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Mediated by Long Noncoding RNA GAS5
Abstract
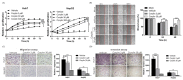
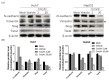
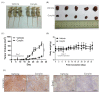
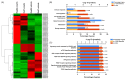
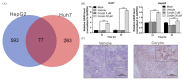
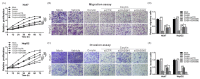
Corylin is a flavonoid extracted from the nuts of Psoralea corylifolia L. (Fabaceae), which is a widely used anti-inflammatory and anticancer herb in China. Recent studies revealed antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and bone differentiation-promoting effects of corylin. However, there are no studies examining the anticancer activity of corylin. In this study, we used cells and animal models to examine the antitumor effects of corylin on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and then studied its downstream regulatory mechanisms. The results showed that corylin significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasiveness of HCC cells and suppressed epithelial-mesenchymal transition. We found that the anti-HCC mechanism of corylin's action lies in the upregulation of tumor suppressor long noncoding RNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5) and the activation of its downstream anticancer pathways. In animal experiments, we also found that corylin can significantly inhibit tumor growth without significant physiological toxicity. The above results suggest that corylin has anti-HCC effects and good potential as a clinical treatment.
Keywords: corylin; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; hepatocellular carcinoma; lncRNA GAS5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Corylin increases the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to chemotherapy through long noncoding RNA RAD51-AS1-mediated inhibition of DNA repair.Cell Death Dis. 2018 May 1;9(5):543. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0575-0. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29749376 Free PMC article.
-
Mannose-mediated inhibitory effects of PA-MSHA on invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via EGFR/Akt/IκBβ/NF-κB pathway.Liver Int. 2015 Apr;35(4):1416-29. doi: 10.1111/liv.12644. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25066210
-
I131 reinforces antitumor activity of metuximab by reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via VEGFR-2 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.Genes Cells. 2018 Jan;23(1):35-45. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12545. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Genes Cells. 2018. PMID: 29210217
-
Can small nucleolar RNA be a novel molecular target for hepatocellular carcinoma?Gene. 2020 Apr 5;733:144384. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144384. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Gene. 2020. PMID: 31978508 Review.
-
Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Chinese Herbal Compounds against Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Molecules. 2016 Jan 27;21(2):142. doi: 10.3390/molecules21020142. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 26828466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA GAS5 overexpression inhibits M2-like polarization of tumour-associated macrophages in SMCC-7721 cells by promoting PTEN expression.Int J Exp Pathol. 2020 Dec;101(6):215-222. doi: 10.1111/iep.12374. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Int J Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 33146930 Free PMC article.
-
A review of Psoralea corylifolia L.: a valuable plant with profound biological significance.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 20;15:1521040. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1521040. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39902075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive Production of a New Highly Soluble Glucoside, Corylin-7-O-β-Glucoside with Potent Anti-inflammatory and Anti-melanoma Activities.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Feb;197(2):1174-1191. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-05071-6. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39377873
-
Hydroxygenkwanin Inhibits Class I HDAC Expression and Synergistically Enhances the Antitumor Activity of Sorafenib in Liver Cancer Cells.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 25;10:216. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00216. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32158695 Free PMC article.
-
3',4'-Dihydroxyflavonol Modulates the Cell Cycle in Cancer Cells: Implication as a Potential Combination Drug in Osteosarcoma.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Jul 3;14(7):640. doi: 10.3390/ph14070640. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34358066 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

