VEGF Triggers the Activation of Cofilin and the Arp2/3 Complex within the Growth Cone
- PMID: 29382077
- PMCID: PMC5855606
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19020384
VEGF Triggers the Activation of Cofilin and the Arp2/3 Complex within the Growth Cone
Abstract
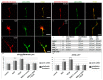
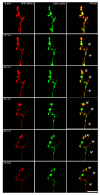
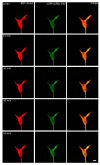
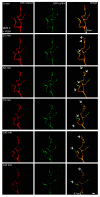
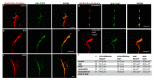
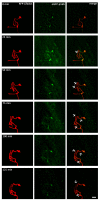
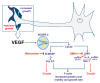
A crucial neuronal structure for the development and regeneration of neuronal networks is the axonal growth cone. Affected by different guidance cues, it grows in a predetermined direction to reach its final destination. One of those cues is the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which was identified as a positive effector for growth cone movement. These positive effects are mainly mediated by a reorganization of the actin network. This study shows that VEGF triggers a tight colocalization of cofilin and the Arp2/3 complex to the actin cytoskeleton within chicken dorsal root ganglia (DRG). Live cell imaging after microinjection of GFP (green fluorescent protein)-cofilin and RFP (red fluorescent protein)-LifeAct revealed that both labeled proteins rapidly redistributed within growth cones, and showed a congruent distribution pattern after VEGF supplementation. Disruption of signaling upstream of cofilin via blocking LIM-kinase (LIMK) activity resulted in growth cones displaying regressive growth behavior. Microinjection of GFP-p16b (a subunit of the Arp2/3 complex) and RFP-LifeAct revealed that both proteins redistributed into lamellipodia of the growth cone within minutes after VEGF stimulation. Disruption of the signaling to the Arp2/3 complex in the presence of VEGF by inhibition of N-WASP (neuronal Wiskott-Aldrich-Scott protein) caused retraction of growth cones. Hence, cofilin and the Arp2/3 complex appear to be downstream effector proteins of VEGF signaling to the actin cytoskeleton of DRG growth cones. Our data suggest that VEGF simultaneously affects different pathways for signaling to the actin cytoskeleton, since activation of cofilin occurs via inhibition of LIMK, whereas activation of Arp2/3 is achieved by stimulation of N-WASP.
Keywords: Arp2/3; LIMK; N-WASP; VEGF; actin; cofilin; cytoskeleton; growth cone; time-lapse imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
VEGF Signaling Regulates Cofilin and the Arp2/3-complex within the Axonal Growth Cone.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2015;12(3):293-307. doi: 10.2174/1567202612666150603141144. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 26036972 Review.
-
Control of growth cone motility and morphology by LIM kinase and Slingshot via phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of cofilin.J Neurosci. 2003 Apr 1;23(7):2527-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02527.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12684437 Free PMC article.
-
Fast rearrangement of the neuronal growth cone's actin cytoskeleton following VEGF stimulation.Histochem Cell Biol. 2013 Mar;139(3):431-45. doi: 10.1007/s00418-012-1036-y. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23052841
-
Arp2/3 complex is essential for actin network treadmilling as well as for targeting of capping protein and cofilin.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Sep;24(18):2861-75. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-12-0857. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23885122 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of growth cone actin dynamics by ADF/cofilin.J Histochem Cytochem. 2003 Apr;51(4):411-20. doi: 10.1177/002215540305100402. J Histochem Cytochem. 2003. PMID: 12642619 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression Pattern of T-Type Ca2+ Channels in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells after VEGF Treatment.Cells. 2021 Sep 1;10(9):2277. doi: 10.3390/cells10092277. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571926 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Profiling of the Substantia Nigra to Identify Determinants of Lewy Body Pathology and Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss.J Proteome Res. 2021 May 7;20(5):2266-2282. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00747. Epub 2021 Apr 26. J Proteome Res. 2021. PMID: 33900085 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Human Spinal Cord Injury: The Effect on Individual Values of pNF-H, GFAP, S100 Proteins and Selected Growth Factors, Cytokines and Chemokines.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Jan 24;44(2):578-596. doi: 10.3390/cimb44020040. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35723326 Free PMC article.
-
Cofilin Acts as a Booster for Progression of Malignant Tumors Represented by Glioma.Cancer Manag Res. 2022 Nov 24;14:3245-3269. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S389825. eCollection 2022. Cancer Manag Res. 2022. PMID: 36452435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nociception-Dependent CCL21 Induces Dorsal Root Ganglia Axonal Growth via CCR7-ERK Activation.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 14;13:880647. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.880647. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911704 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

