Structural Studies of Predicted Ligand Binding Sites and Molecular Docking Analysis of Slc2a4 as a Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Cancer
- PMID: 29382080
- PMCID: PMC5855608
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19020386
Structural Studies of Predicted Ligand Binding Sites and Molecular Docking Analysis of Slc2a4 as a Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Cancer
Abstract
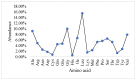
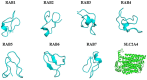
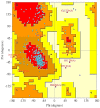
Presently, many studies have focused on exploring in silico approaches in the identification and development of alternative therapy for the treatment and management of cancer. Solute carrier family-2-member-4-gene (Slc2a4) which encodes glucose transporter 4 protein (GLUT4), has been identified as a promising therapeutic target for cancer. Though Slc2a4 is known to play a major regulatory role in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes, emerging evidence suggests that successful pharmacological inhibition of this protein may lead to the development of a novel drug candidate for the treatment of cancer. In this study, Slc2a4 protein sequence was retrieved and analysed using in silico approaches, and we identified seven putative antimicrobial peptides (AMPs; RAB1-RAB7) as anti-cancer. The structures of the protein and AMPs were modelled using I-TASSER server, and the overall quality of the Slc2a4 model was validated using PROCHECK. Subsequently, the probable motifs and active site of the protein were forecasted. Also, the molecular interaction between the AMPs and Slc2a4 was ascertained using PatchDock. The result revealed that, all the AMPs are good Slc2a4 inhibitors with RAB1 having the highest binding affinity of 12,392 and binding energy of -39.13 kcal/mol. Hence, this study reveals that all the generated AMPs can serve as therapeutic drug in treating cancer by inhibiting Slc2a4 which is responsible for the production of energy for cancer cells during angiogenesis. This is the first report on AMPs as inhibitors of Slc2a4 for the treatment of cancer.
Keywords: Slc2a4; antimicrobial peptides; cancer; docking; homology modelling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural and Molecular Docking Analytical Studies of the Predicted Ligand Binding Sites of Cadherin-1 in Cancer Prognostics.Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2020 Jul 28;13:1-9. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S253851. eCollection 2020. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2020. PMID: 32821128 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Based Docking Studies of GLUT4 Towards Exploring Selected Phytochemicals from Solanum xanthocarpum as a Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Cancer.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2019;16(4):406-416. doi: 10.2174/1570163815666180801152110. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2019. PMID: 30068281
-
Insulin acutely triggers transcription of Slc2a4 gene: participation of the AT-rich, E-box and NFKB-binding sites.Life Sci. 2014 Sep 26;114(1):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.07.040. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25123536
-
Antimicrobial Peptides: An Introduction.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1548:3-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6737-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28013493 Review.
-
Antimicrobial peptides with selective antitumor mechanisms: prospect for anticancer applications.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(28):46635-46651. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16743. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28422728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Computational Approach to Elucidate the Interactions of Chemicals From Artemisia annua Targeted Toward SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibition for COVID-19 Treatment.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 15;9:907583. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.907583. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35783612 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Molecular Docking Analytical Studies of the Predicted Ligand Binding Sites of Cadherin-1 in Cancer Prognostics.Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2020 Jul 28;13:1-9. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S253851. eCollection 2020. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2020. PMID: 32821128 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of quantitative phosphoproteomics and transcriptomics revealed phosphorylation-mediated molecular events as useful tools for a potential patient stratification and personalized treatment of human nonfunctional pituitary adenomas.EPMA J. 2020 Aug 13;11(3):419-467. doi: 10.1007/s13167-020-00215-0. eCollection 2020 Sep. EPMA J. 2020. PMID: 32849927 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Dynamics of Cobalt Protoporphyrin Antagonism of the Cancer Suppressor REV-ERBβ.Molecules. 2021 May 28;26(11):3251. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113251. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34071361 Free PMC article.
-
PZQ Therapy: How Close are we in the Development of Effective Alternative Anti-schistosomal Drugs?Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2019;19(4):337-349. doi: 10.2174/1871526519666181231153139. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30599112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Batra S., Adekola K.U., Rosen S.T., Shanmugam M. Cancer metabolism as a therapeutic target. Oncology. 2013;27:460–467. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

