On the Design of an Efficient Cardiac Health Monitoring System Through Combined Analysis of ECG and SCG Signals
- PMID: 29382098
- PMCID: PMC5856087
- DOI: 10.3390/s18020379
On the Design of an Efficient Cardiac Health Monitoring System Through Combined Analysis of ECG and SCG Signals
Abstract
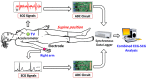
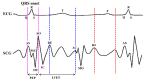
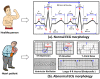
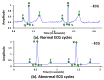
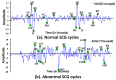
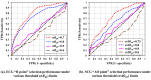
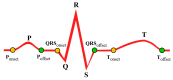
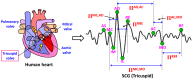
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a major public concern and socioeconomic problem across the globe. The popular high-end cardiac health monitoring systems such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computerized tomography scan (CT scan), and echocardiography (Echo) are highly expensive and do not support long-term continuous monitoring of patients without disrupting their activities of daily living (ADL). In this paper, the continuous and non-invasive cardiac health monitoring using unobtrusive sensors is explored aiming to provide a feasible and low-cost alternative to foresee possible cardiac anomalies in an early stage. It is learned that cardiac health monitoring based on sole usage of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals may not provide powerful insights as ECG provides shallow information on various cardiac activities in the form of electrical impulses only. Hence, a novel low-cost, non-invasive seismocardiogram (SCG) signal along with ECG signals are jointly investigated for the robust cardiac health monitoring. For this purpose, the in-laboratory data collection model is designed for simultaneous acquisition of ECG and SCG signals followed by mechanisms for the automatic delineation of relevant feature points in acquired ECG and SCG signals. In addition, separate feature points based novel approach is adopted to distinguish between normal and abnormal morphology in each ECG and SCG cardiac cycle. Finally, a combined analysis of ECG and SCG is carried out by designing a Naïve Bayes conditional probability model. Experiments on Institutional Review Board (IRB) approved licensed ECG/SCG signals acquired from real subjects containing 12,000 cardiac cycles show that the proposed feature point delineation mechanisms and abnormal morphology detection methods consistently perform well and give promising results. In addition, experimental results show that the combined analysis of ECG and SCG signals provide more reliable cardiac health monitoring compared to the standalone use of ECG and SCG.
Keywords: cardiac anomalies; cardiovascular disease (CVD); electrocardiogram (ECG); seismocardiogram (SCG).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Automatic and Robust Delineation of the Fiducial Points of the Seismocardiogram Signal for Non-invasive Estimation of Cardiac Time Intervals.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2017 Aug;64(8):1701-1710. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2016.2616382. Epub 2016 Oct 12. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2017. PMID: 28113202
-
ECG-Free Heartbeat Detection in Seismocardiography and Gyrocardiography Signals Provides Acceptable Heart Rate Variability Indices in Healthy and Pathological Subjects.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;23(19):8114. doi: 10.3390/s23198114. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37836942 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic Identification of Systolic Time Intervals in Seismocardiogram.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 22;6:37524. doi: 10.1038/srep37524. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27874050 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Research for Unobtrusive Atrial Fibrillation Detection Methods Based on Cardiac Dynamics Signals: A Survey.Sensors (Basel). 2021 May 31;21(11):3814. doi: 10.3390/s21113814. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complementary role of cardiovascular imaging and laboratory indices in early detection of cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus.Lupus. 2017 Mar;26(3):227-236. doi: 10.1177/0961203316671810. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Lupus. 2017. PMID: 27687024 Review.
Cited by
-
Heart rate informed detection of cardiac events using the Kalman filter.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Sep;195:110480. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.110480. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40541072
-
A Unified Framework for Quality Indexing and Classification of Seismocardiogram Signals.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2020 Apr;24(4):1080-1092. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2019.2931348. Epub 2019 Jul 26. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2020. PMID: 31369387 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Seismocardiography.Vibration. 2019 Mar;2(1):64-86. doi: 10.3390/vibration2010005. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Vibration. 2019. PMID: 34113791 Free PMC article.
-
A Flexible 12-Lead/Holter Device with Compression Capabilities for Low-Bandwidth Mobile-ECG Telemedicine Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Nov 5;18(11):3773. doi: 10.3390/s18113773. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30400587 Free PMC article.
-
High-Resolution Seismocardiogram Acquisition and Analysis System.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Oct 13;18(10):3441. doi: 10.3390/s18103441. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30322147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yeh K.H. A secure IoT-based healthcare system with body sensor networks. IEEE Access. 2016;4:10288–10299. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2638038. - DOI
-
- Ma Y., Wang Y., Yang J., Miao Y., Li W. Big health application system based on health internet of things and big data. IEEE Access. 2016;5:7885–7897. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2638449. - DOI
-
- Alwan A., Armstrong T., Bettcher D., Branca F., Chisholm D., Ezzati M., Garfield R., MacLean D., Mathers C., Mendis S., et al. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010: Description of the Global Burden of NCDs, Their Risk Factors and Determinants. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2011.
-
- Mozaffarian D., Benjamin E.J., Go A.S., Arnett D.K., Blaha M.J., Cushman M., Das S.R., de Ferranti S., Després J.P., Fullerton H.J., et al. Executive summary: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the american heart association. Circulation. 2016;133:447–454. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000366. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

