Study of the Anti-Staphylococcal Potential of Honeys Produced in Northern Poland
- PMID: 29382105
- PMCID: PMC6017226
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23020260
Study of the Anti-Staphylococcal Potential of Honeys Produced in Northern Poland
Abstract
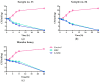
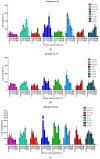
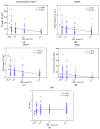
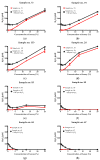
The antimicrobial activity of 144 samples of honeys including 95 products from apiaries located in Northern Poland was evaluated. The antibacterial activity of those natural products, their thermal stability, and activity in the presence of catalase was investigated by microdilution assays in titration plates. The MTT assay was performed for the determination of anti-biofilm activity. Spectrophotometric assays were used for the determination of antioxidant potential, total phenolic content, and ability to generate hydrogen peroxide. Some of the investigated honeys exhibited surprisingly high antimicrobial, especially anti-staphylococcal, potential, with Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) values of only 1.56% (v/v). Much higher resistance was observed in the case of staphylococci growing as biofilms. Lower concentrations of the product, up to 12.5% (v/v) stimulated its growth and effective eradication of biofilm required concentration of at least 25% (v/v). Hydrogen peroxide has been identified as a crucial contributor to the antimicrobial activity of honeys supplied by Polish beekeepers. However, some of the results suggest that phytochemicals, especially polyphenols, play an important role depending on botanical source (both positive, e.g., in the case of buckwheat honeys as well as negative, e.g., in the case of some rapeseed honeys) in their antimicrobial potential.
Keywords: MIC; Staphylococcus; antibacterial activity; antioxidants; biofilm; correlations; honey; phenolics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activity of Polish unifloral honeys against pathogenic bacteria and its correlation with colour, phenolic content, antioxidant capacity and other parameters.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016 Mar;62(3):269-76. doi: 10.1111/lam.12541. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26693829
-
Antimicrobial activity of heat-treated Polish honeys.Food Chem. 2021 May 1;343:128561. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128561. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33267984
-
Identification of components in Kazakhstan honeys that correlate with antimicrobial activity against wound and skin infecting microorganisms.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Dec 20;21(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03466-0. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 34930218 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid combinations containing natural products and antimicrobial drugs that interfere with bacterial and fungal biofilms.Phytomedicine. 2017 Dec 15;37:14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.10.021. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Phytomedicine. 2017. PMID: 29174600 Review.
-
[Characteristics and pro-health benefits of herbhoneys].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2019 Jun 28;46(276):263-267. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2019. PMID: 31260436 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
The Anti-Staphylococcal Potential of Ethanolic Polish Propolis Extracts.Molecules. 2019 May 3;24(9):1732. doi: 10.3390/molecules24091732. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31058881 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a model to understand the synergies underlying the antibacterial mechanism of H2O2-producing honeys.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 19;10(1):17692. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74937-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33077785 Free PMC article.
-
Antidotal or protective effects of honey and one of its major polyphenols, chrysin, against natural and chemical toxicities.Acta Biomed. 2019 Dec 23;90(4):533-550. doi: 10.23750/abm.v90i4.7534. Acta Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31910181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral and Antibacterial Effect of Honey Enriched with Rubus spp. as a Functional Food with Enhanced Antioxidant Properties.Molecules. 2022 Jul 29;27(15):4859. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154859. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956811 Free PMC article.
-
Bee Pollen and Bee Bread as a Source of Bacteria Producing Antimicrobials.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jun 13;10(6):713. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10060713. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34199247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hołderna-Kędzia E., Kędzia B. Miody odmianowe i ich Znaczenie Lecznicze. 1st ed. WDR; Włocławek, Poland: 2002. p. 112.
-
- Kwakman P.H., Van den Akker J.P., Guclu A., Aslami H., Binnekade J.M., de Boer L., Boszhard L., Paulus F., Middelhoek P., te Velde A.A., et al. Medical-grade honey kills antibiotic-resistant bacteria in vitro and eradicates skin colonization. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008;46:1677–1682. doi: 10.1086/587892. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

