Discovery of Potent and Selective MRCK Inhibitors with Therapeutic Effect on Skin Cancer
- PMID: 29382705
- PMCID: PMC5901721
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2870
Discovery of Potent and Selective MRCK Inhibitors with Therapeutic Effect on Skin Cancer
Abstract
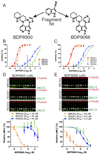
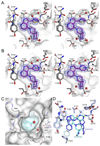
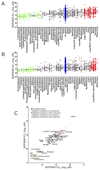
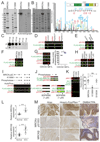
The myotonic dystrophy-related Cdc42-binding kinases MRCKα and MRCKβ contribute to the regulation of actin-myosin cytoskeleton organization and dynamics, acting in concert with the Rho-associated coiled-coil kinases ROCK1 and ROCK2. The absence of highly potent and selective MRCK inhibitors has resulted in relatively little knowledge of the potential roles of these kinases in cancer. Here, we report the discovery of the azaindole compounds BDP8900 and BDP9066 as potent and selective MRCK inhibitors that reduce substrate phosphorylation, leading to morphologic changes in cancer cells along with inhibition of their motility and invasive character. In over 750 human cancer cell lines tested, BDP8900 and BDP9066 displayed consistent antiproliferative effects with greatest activity in hematologic cancer cells. Mass spectrometry identified MRCKα S1003 as an autophosphorylation site, enabling development of a phosphorylation-sensitive antibody tool to report on MRCKα status in tumor specimens. In a two-stage chemical carcinogenesis model of murine squamous cell carcinoma, topical treatments reduced MRCKα S1003 autophosphorylation and skin papilloma outgrowth. In parallel work, we validated a phospho-selective antibody with the capability to monitor drug pharmacodynamics. Taken together, our findings establish an important oncogenic role for MRCK in cancer, and they offer an initial preclinical proof of concept for MRCK inhibition as a valid therapeutic strategy.Significance: The development of selective small-molecule inhibitors of the Cdc42-binding MRCK kinases reveals their essential roles in cancer cell viability, migration, and invasive character. Cancer Res; 78(8); 2096-114. ©2018 AACR.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel small-molecule MRCK inhibitor blocks cancer cell invasion.Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Oct 5;12:54. doi: 10.1186/s12964-014-0054-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2014. PMID: 25288205 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and Challenges for the Development of MRCK Kinases Inhibitors as Potential Cancer Chemotherapeutics.Cells. 2023 Feb 7;12(4):534. doi: 10.3390/cells12040534. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-crystal structures of inhibitors with MRCKβ, a key regulator of tumor cell invasion.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24825. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024825. Epub 2011 Sep 20. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21949762 Free PMC article.
-
The CDC42 effector protein MRCKβ autophosphorylates on Threonine 1108.Small GTPases. 2020 Nov;11(6):451-460. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2018.1564472. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Small GTPases. 2020. PMID: 30667325 Free PMC article.
-
Myotonic dystrophy kinase-related Cdc42-binding kinases (MRCK), the ROCK-like effectors of Cdc42 and Rac1.Small GTPases. 2015;6(2):81-8. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2014.1000699. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Small GTPases. 2015. PMID: 26090570 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor-intrinsic CDC42BPB confers resistance to anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade in breast cancer.Mol Ther. 2024 Oct 2;32(10):3669-3682. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.07.021. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39086134
-
The Na+, K+-ATPase β1 subunit regulates epithelial tight junctions via MRCKα.JCI Insight. 2021 Feb 22;6(4):e134881. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.134881. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33507884 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting and extending the eukaryotic druggable genome with natural products: cytoskeletal targets of natural products.Nat Prod Rep. 2020 May 1;37(5):634-652. doi: 10.1039/c9np00053d. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Nat Prod Rep. 2020. PMID: 31764930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MRCKβ links Dasm1 to actin rearrangements to promote dendrite development.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100730. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100730. Epub 2021 Apr 30. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33933448 Free PMC article.
-
MRCK as a Potential Target for Claudin-Low Subtype of Breast Cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jan 1;20(1):1-14. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.88285. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38164185 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

