The scaffolding protein JADE1 physically links the acetyltransferase subunit HBO1 with its histone H3-H4 substrate
- PMID: 29382722
- PMCID: PMC5868276
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000677
The scaffolding protein JADE1 physically links the acetyltransferase subunit HBO1 with its histone H3-H4 substrate
Abstract
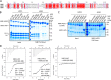
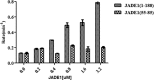
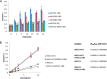
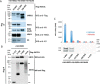
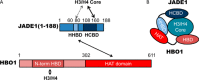
The human enzyme histone acetyltransferase binding to ORC1 (HBO1) regulates DNA replication, cell proliferation, and development. HBO1 is part of a multiprotein histone acetyltransferase (HAT) complex that also contains inhibitor of growth family member (ING) 4/5, MYST/Esa1-associated factor (MEAF) 6, and the scaffolding proteins Jade family PHD finger (JADE) 1/2/3 or bromodomain and PHD finger-containing protein (BRPF) 2/3 to acetylate histone H4 H4K5/8/12 or H3K14, respectively. Within this four-protein complex, JADE1 determines histone H4 substrate specificity of the HBO1-HAT complex. However, the mechanism by which JADE1 controls the H4-specific acetyltransferase activity of HBO1 is unknown. Here we used recombinant proteins in vitro to dissect the specific regions and activities of HBO1 and JADE1 that mediate histone H3-H4 acetylation via the HBO1-HAT domain. We found that JADE1 increases the catalytic efficiency of HBO1 acetylation of an H3-H4 substrate by about 5-fold through an N-terminal, 21-residue HBO1- and histone-binding domain and a nearby second histone core-binding domain. We also demonstrate that HBO1 contains an N-terminal histone-binding domain (HBD) that makes additional contacts with H3-H4 independent of JADE1 interactions with histones and that the HBO1 HBD does not significantly contribute to HBO1's overall HAT activity. Experiments with JADE1 deletions in vivo recapitulated these in vitro interactions and their roles in HBO1 histone acetylation activity. Together, these results indicate that the N-terminal region of JADE1 functions as a platform that brings together the catalytic HBO1 subunit with its cognate H3-H4 substrate for histone acetylation.
Keywords: acetyltransferase; chromatin regulation; epigenetics; histone acetylation; protein complex.
© 2018 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural and mechanistic insights into regulation of HBO1 histone acetyltransferase activity by BRPF2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 2;45(10):5707-5719. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx142. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28334966 Free PMC article.
-
Exchange of associated factors directs a switch in HBO1 acetyltransferase histone tail specificity.Genes Dev. 2013 Sep 15;27(18):2009-24. doi: 10.1101/gad.223396.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 24065767 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Jade-1 in the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) HBO1 complex.J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 24;283(43):28817-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801407200. Epub 2008 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18684714 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering structure, function and mechanism of lysine acetyltransferase HBO1 in protein acetylation, transcription regulation, DNA replication and its oncogenic properties in cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Feb;77(4):637-649. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03296-x. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31535175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional acyltransferase HBO1: a key regulatory factor for cellular functions.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Nov 14;29(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00661-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39543485 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NCAPG2 facilitates glioblastoma cells' malignancy and xenograft tumor growth via HBO1 activation by phosphorylation.Cell Tissue Res. 2021 Feb;383(2):693-706. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03281-y. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Cell Tissue Res. 2021. PMID: 32897418
-
An Analysis of JADE2 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 19;11(9):2576. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092576. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37761019 Free PMC article.
-
Functions and mechanisms of protein lysine butyrylation (Kbu): Therapeutic implications in human diseases.Genes Dis. 2022 Nov 29;10(6):2479-2490. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.10.025. eCollection 2023 Nov. Genes Dis. 2022. PMID: 37554202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitor of Growth 4 (ING4) is a positive regulator of rRNA synthesis.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 21;9(1):17235. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53767-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31754246 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of lncRNAs in the Dependent Regulation of Cancer and Their Potential Therapeutic Use.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 11;23(2):764. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020764. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054945 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

