C omparative Evaluation of the Intranasal Spray Formulation of Midazolam and Dexmedetomidine in Patients Undergoing Surgical Removal of Impacted Mandibular Third Molars: A Split Mouth Prospective Study
- PMID: 29382993
- PMCID: PMC5772022
- DOI: 10.1007/s12663-016-0992-5
C omparative Evaluation of the Intranasal Spray Formulation of Midazolam and Dexmedetomidine in Patients Undergoing Surgical Removal of Impacted Mandibular Third Molars: A Split Mouth Prospective Study
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this prospective randomized single blinded split mouth study was to conduct a comparative evaluation of the efficacy of intranasal atomised spray formulation of Dexmedetomidine with Midazolam in patients undergoing surgical removal of bilaterally impacted mandibular third molars.
Methods: This prospective study was conducted in twenty volunteers. Each volunteer underwent the surgical removal of an impacted mandibular third molar at two separate appointments at an interval of two weeks. The first third molar surgery was conducted using either intranasal Midazolam (Group M) or intranasal Dexmedetomidine (Group D). At the second appointment the surgical procedure was performed using the sedative agent not used at the first appointment. The primary testing outcome variables were Plasma oxygen saturation (SpO2), pulse and blood pressure and Modified Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation (OAA/S) scale. These were recorded at predetermined intervals starting 10 min before the administration of local anaesthesia and continued up to 10 min after completion of the procedure. In addition surgeon's opinion regarding the patient cooperation, event amnesia, post operative nausea & vomiting were obtained.
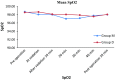
Results: The sample composed of twenty patients (M = 9 and F = 11). There was statistically no significant difference between Group M and Group D with respect to mean SpO2. Minor differences were however noted at 20 and 30 min after sedation. There was no significant difference between the groups with respect to mean pulse rate, blood pressure, OAA/S, event amnesia, post operative nausea and vomiting and patient cooperation.
Conclusion: We conclude that Midazolam and Dexmedetomidine are equivalent and can be used in minor oral surgery with minimal complications. These drugs can be used intranasally using nasal atomization device in routine outpatient basis in otherwise normal healthy but anxious patients. All procedures must however be performed in the presence of an anaesthesiologist and with ready availability of emergency drugs and equipment.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; Intranasal spray formulation; Midazolam; Nasal atomization device.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with Ethical StandardsNo conflict of interest is present.The study was approved by Research and Ethical committee of Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed University, Pune.All the patients included in the study were provided with subject information sheet. Patients signed the informed consent of the institute proforma as well as structured proforma of the study.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Intranasal Atomized Dexmedetomidine for Sedation in Surgical Removal of Impacted Mandibular Third Molars: A Prospective Study.Cureus. 2023 Mar 26;15(3):e36721. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36721. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37123751 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Intranasal Dexmedetomidine for Conscious Sedation in Patients Undergoing Surgical Removal of Impacted Third Molar: A Double-Blind Split Mouth Study.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2016 Dec;15(4):512-516. doi: 10.1007/s12663-016-0889-3. Epub 2016 Apr 21. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2016. PMID: 27833345 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal atomized dexmedetomidine for sedation during third molar extraction.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013 Jul;42(7):857-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013. PMID: 23497981 Clinical Trial.
-
Dexmedetomidine versus midazolam in outpatient third molar surgery.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006 Sep;64(9):1353-8. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2006.05.020. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006. PMID: 16916668 Clinical Trial.
-
[Efficacy and safety of intranasal dexmedetomidine premedication for children undergoing CT or magnetic resonance imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Apr 2;58(4):314-318. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20191224-00830. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32234139 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effects of dexmedetomidine in non-operating room anesthesia in adults: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Braz J Anesthesiol. 2023 Sep-Oct;73(5):641-664. doi: 10.1016/j.bjane.2021.12.002. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 34933035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Dexmedetomidine with or without Midazolam during procedural dental sedation in children: a randomized controlled clinical trial.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Oct 26;24(1):1298. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04992-2. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39462365 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Intranasal Dexmedetomidine Spray Versus Intranasal Normal Saline Spray in Patients Undergoing Transalveolar Extractions for Anxiety Reduction: A Randomized Control Study.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2023 Jun 4;22(3):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s12663-023-01933-4. Online ahead of print. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2023. PMID: 37362875 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of dexmedetomidine with midazolam for dental surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 23;99(43):e22288. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022288. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33120732 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
