Protective effects of hydrogen sulfide on chronic kidney disease by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis
- PMID: 29383015
- PMCID: PMC5780625
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2017-711
Protective effects of hydrogen sulfide on chronic kidney disease by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis
Abstract
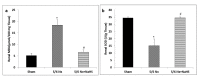
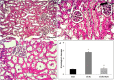
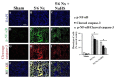
The current study aimed to examine the renoprotective effects of long-term treatment with sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS), a prominent hydrogen sulfide donor, in 5/6 nephrectomy animal model. Twenty-four rats were randomly divided into 3 groups including sham-operated group (Sham), 5/6-nephrectomized group (5/6 Nx), and NaHS-treated group (5/6Nx+NaHS). NaHS (30 micromol/l) was added twice daily into the drinking water and renal failure was induced by 5/6 nephrectomy. Twelve weeks after surgical procedure, blood pressure, creatinine clearance (CCr), urine concentration of neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) and tissue concentration of malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), as well as renal morphological changes, apoptosis (cleaved caspase-3) and inflammation (p-NF-κB) were measured. Five-sixth nephrectomy induced severe renal damage as indicated by renal dysfunction, hypertension and significant histopathological injury which were associated with increased NGAL and MDA levels, oxidant/antioxidant imbalance, decreased SOD activity and CCr and also overexpression of p-NF-κB and cleaved caspase-3 proteins. Instead, NaHS treatment attenuated renal dysfunction through reduction of NGAL concentration, hypertension, CCr, oxidant/antioxidant imbalance, inflammation and apoptosis. These findings suggest that long term NaHS treatment can be useful in preventing the progression of CKD by improving oxidant/antioxidant balance and reducing inflammation and apoptosis in the kidney.
Keywords: apoptosis; blood pressure; chronic kidney disease; creatinine clearance; hydrogen sulfide; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of nitric oxide signaling in renoprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide against chronic kidney disease in rats: Involvement of oxidative stress, autophagy and apoptosis.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jul;234(7):11411-11423. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27797. Epub 2018 Nov 27. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30478901
-
Ameliorative effects of hydrogen sulfide (NaHS) on chronic kidney disease-induced brain dysfunction in rats: implication on role of nitric oxide (NO) signaling.Metab Brain Dis. 2018 Dec;33(6):1945-1954. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0301-8. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Metab Brain Dis. 2018. PMID: 30090953
-
Effects of hydrogen sulfide on acetaminophen-induced acute renal toxicity in rats.Int Urol Nephrol. 2019 Apr;51(4):745-754. doi: 10.1007/s11255-018-2053-0. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30604234
-
[Protective effect of hydrogen sulfide on kidneys of type 1 diabetic rats].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Feb 8;32(2):181-184. doi: 10.13459/j.cnki.cjap.2016.02.023. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 29931873 Chinese.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Two Derivative Prescriptions of Rokumijiogan, Hachimijiogan and Bakumijiogan against Renal Damage in Nephrectomized Rats.Medicines (Basel). 2023 Mar 21;10(3):24. doi: 10.3390/medicines10030024. Medicines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36976313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dissolving sodium hydrosulfide in drinking water is not a good source of hydrogen sulfide for animal studies.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 9;13(1):21839. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49437-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38071388 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-lipoic acid ameliorates tauopathy-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis, and behavioral deficits through the balance of DIAP1/DrICE ratio and redox homeostasis: Age is a determinant factor.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Apr;36(4):669-683. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00679-7. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 33547995
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide donors in cancer development and progression.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jan 1;17(1):73-88. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.47850. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33390834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen sulfide regulation of renal and mesenteric blood flow.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):H1157-H1165. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00303.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31625777 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin accelerates myelin recovery and ameliorates behavioral deficits in the animal model of multiple sclerosis via adjustment of AMPK/Nrf2/mTOR signaling and maintenance of endogenous oligodendrogenesis during brain self-repairing period.Pharmacol Rep. 2020 Jun;72(3):641-658. doi: 10.1007/s43440-019-00019-8. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Pharmacol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32048246
References
-
- Abboud H, Henrich WL. Stage IV Chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:56–65. - PubMed
-
- Akchurin OM, Kaskel F. Update on Inflammation in Chronic Kidney Disease. Blood Purif. 2015;39:84–92. - PubMed
-
- Aminzadeh MA, Vaziri ND. Downregulation of the renal and hepatic hydrogen sulfide (H2S)-producing enzymes and capacity in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27:498–504. - PubMed
-
- Avci Cicek, E, Rota S, Dursun B, Kavalci E. Evaluation of serum NGAL and hepcidin levels in chronic kidney disease patients. Ren Fail. 2016;38:35–39. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
