Enteral Nutrition in Pediatric Patients
- PMID: 29383300
- PMCID: PMC5788946
- DOI: 10.5223/pghn.2018.21.1.12
Enteral Nutrition in Pediatric Patients
Abstract
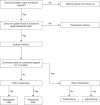
Pediatric patients require specialized attention and have diverse demands for proper growth and development, and thus need a different approach and interest in nutritional assessment and supply. Enteral nutrition is the most basic and important method of nutritional intervention, and its indications should be identified. Also, the sites, modes, types, and timing of nutritional intervention according to the patient's condition should be determined. In addition, various complications associated with enteral nutrition supply should be identified, and prevention and treatment are required. This approach to enteral nutrition and proper administration can help in the proper growth and recovery of pediatric patients with nutritional imbalances or nutritional needs.
Keywords: Child; Enteral nutrition; Malnutrition.
Figures
References
-
- Druml C, Ballmer PE, Druml W, Oehmichen F, Shenkin A, Singer P, et al. ESPEN guideline on ethical aspects of artificial nutrition and hydration. Clin Nutr. 2016;35:545–556. - PubMed
-
- Cederholm T, Barazzoni R, Austin P, Ballmer P, Biolo G, Bischoff SC, et al. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition. Clin Nutr. 2017;36:49–64. - PubMed
-
- American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.) Board of Directors. Clinical guidelines for the use of parenteral and enteral nutrition in adult and pediatric patients, 2009. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2009;33:255–259. - PubMed
-
- Jonkers CF, Prins F, Van Kempen A, Tepaske R, Sauerwein HP. Towards implementation of optimum nutrition and better clinical nutrition support. Clin Nutr. 2001;20:361–366. - PubMed
-
- Planas M, Camilo ME. Artificial nutrition: dilemmas in decision-making. Clin Nutr. 2002;21:355–361. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources