Binding kinetics of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles with proteins
- PMID: 29383361
- PMCID: PMC5842697
- DOI: 10.1039/c7nr06810g
Binding kinetics of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles with proteins
Abstract
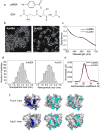
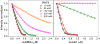
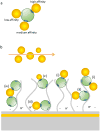
Synthetic ultrasmall nanoparticles (NPs) can be designed to interact with biologically active proteins in a controlled manner. However, the rational design of NPs requires a clear understanding of their interactions with proteins and the precise molecular mechanisms that lead to association/dissociation in biological media. Although much effort has been devoted to the study of the kinetics mechanism of protein corona formation on large NPs, the nature of NP-protein interactions in the ultrasmall regime is radically different and poorly understood. Using a combination of experimental and computational approaches, we studied the interactions of a model protein, CrataBL, with ultrasmall gold NPs passivated with p-mercaptobenzoic acid (AuMBA) and glutathione (AuGSH). We have identified this system as an ideal in vitro platform to understand the dependence of binding affinity and kinetics on NP surface chemistry. We found that the structural and chemical complexity of the passivating NP layer leads to quite different association kinetics, from slow and reaction-limited (AuGSH) to fast and diffusion-limited (AuMBA). We also found that the otherwise weak and slow AuGSH-protein interactions measured in buffer solution are enhanced in macromolecular crowded solutions. These findings advance our mechanistic understanding of biomimetic NP-protein interactions in the ultrasmall regime and have implications for the design and use of NPs in the crowded conditions common to all biological media.
Figures
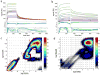

Similar articles
-
A nanoinformatics decision support tool for the virtual screening of gold nanoparticle cellular association using protein corona fingerprints.Nanotoxicology. 2018 Dec;12(10):1148-1165. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2018.1504998. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Nanotoxicology. 2018. PMID: 30182778
-
Biointeractions of ultrasmall glutathione-coated gold nanoparticles: effect of small size variations.Nanoscale. 2016 Mar 28;8(12):6577-88. doi: 10.1039/c5nr07642k. Nanoscale. 2016. PMID: 26934984 Free PMC article.
-
A model beyond protein corona: thermodynamics and binding stoichiometries of the interactions between ultrasmall gold nanoclusters and proteins.Nanoscale. 2020 Feb 21;12(7):4573-4585. doi: 10.1039/c9nr09170j. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Nanoscale. 2020. PMID: 32043104
-
Protein corona, understanding the nanoparticle-protein interactions and future perspectives: A critical review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Feb 1;169:290-301. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.108. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33340622 Review.
-
Protein-Nanoparticle Interaction: Corona Formation and Conformational Changes in Proteins on Nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Aug 6;15:5783-5802. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S254808. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32821101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Realizing active targeting in cancer nanomedicine with ultrasmall nanoparticles.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2024 Sep 30;15:1208-1226. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.15.98. eCollection 2024. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39376728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strong dependence of the nano-bio interactions on core morphology and layer composition of ultrasmall nanostructures.J Chem Phys. 2019 Sep 14;151(10):105102. doi: 10.1063/1.5115192. J Chem Phys. 2019. PMID: 31521088 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial neural networks for the inverse design of nanoparticles with preferential nano-bio behaviors.J Chem Phys. 2020 Aug 7;153(5):054102. doi: 10.1063/5.0013990. J Chem Phys. 2020. PMID: 32770917 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Ionic Strength in the Formation of Stable Supramolecular Nanoparticle-Protein Conjugates for Biosensing.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 21;23(4):2368. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042368. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216496 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric inhibition of α-thrombin enzymatic activity with ultrasmall gold nanoparticles.Nanoscale Adv. 2019 Jan 1;1(1):378-388. doi: 10.1039/c8na00081f. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Nanoscale Adv. 2019. PMID: 30931428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De M, You CC, Srivastava S, Rotello VM. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:10747–10753. - PubMed
-
- Kotov NA. Science. 2010;330:188–189. - PubMed
-
- Kopp M, Kollenda S, Epple M. Acc Chem Res. 2017;50:1383–1390. - PubMed
-
- Nel AE, Mädler L, Velegol D, Xia T, Hoek EM, Somasundaran P, Klaessig F, Castranova V, Thompson M. Nat Mat. 2009;8:543–557. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

