Generation of a biotinylatable Sox2 mouse model to identify Sox2 complexes in vivo
- PMID: 29383478
- PMCID: PMC5847153
- DOI: 10.1007/s11248-018-0058-1
Generation of a biotinylatable Sox2 mouse model to identify Sox2 complexes in vivo
Abstract
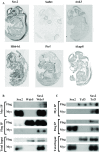
Sox2 is a Sry-box containing family member of related transcription factors sharing homology in their DNA binding domain. Sox2 is important during different stages of development, and previously we showed that Sox2 plays an important role in branching morphogenesis and epithelial cell differentiation in lung development. The transcriptional activity of Sox2 depends on its interaction with other proteins, leading to 'complex-specific' DNA binding and transcriptional regulation. In this study, we generated a mouse model containing a biotinylatable-tag targeted at the translational start site of the endogenous Sox2 gene (bioSox2). This tag was biotinylated by the bacterial birA protein and the resulting bioSox2 protein was used to identify associating partners of Sox2 at different phases of lung development in vivo (the Sox2 interactome). Homozygous bioSox2 mice are viable and fertile irrespective of the biotinylation of the bio tag, indicating that the bioSox2 gene is normally expressed and the protein is functional in all tissues. This suggests that partners of Sox2 are most likely able to associate with the bioSox2 protein. BioSox2 complexes were isolated with high affinity using streptavidin beads and analysed by MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry analysis. Several of the identified binding partners are already shown to have a respiratory phenotype. Two of these partners, Wdr5 and Tcf3, were validated to confirm their association in Sox2 complexes. This bioSox2 mouse model will be a valuable tool for isolating in vivo Sox2 complexes from different tissues.
Keywords: Biotinylatable tag; In vivo protein complexes; Knock-in; Sox2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sox2 uses multiple domains to associate with proteins present in Sox2-protein complexes.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 12;5(11):e15486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015486. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21103394 Free PMC article.
-
Sox2 is important for two crucial processes in lung development: branching morphogenesis and epithelial cell differentiation.Dev Biol. 2008 May 1;317(1):296-309. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.02.035. Epub 2008 Feb 29. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18374910
-
Sox2 regulates the emergence of lung basal cells by directly activating the transcription of Trp63.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014 Aug;51(2):311-22. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0419OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24669837
-
Sox2 regulation of hair cell development: incoherence makes sense.Hear Res. 2013 Mar;297:20-9. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.11.003. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Hear Res. 2013. PMID: 23154195 Review.
-
Isolation and characterization of hematopoietic transcription factor complexes by in vivo biotinylation tagging and mass spectrometry.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1054:55-67. doi: 10.1196/annals.1345.008. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16339652 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of SOX2 Interacting Proteins in the Developing Mouse Lung With Potential Implications for Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia.Front Pediatr. 2022 May 9;10:881287. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.881287. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35615634 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles for SOX2 and SOX21 in differentiation, distribution and maturation of pulmonary neuroendocrine cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Mar 3;80(3):79. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04731-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36867267 Free PMC article.
-
SOX2 and SOX21 in Lung Epithelial Differentiation and Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13064. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113064. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361852 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

