Catheter ablation of symptomatic idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias : A five-year single-centre experience
- PMID: 29383491
- PMCID: PMC5876169
- DOI: 10.1007/s12471-018-1085-5
Catheter ablation of symptomatic idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias : A five-year single-centre experience
Abstract
Aims: This study was designed to gain insight into the patient characteristics, results and possible complications of ablation procedures for symptomatic idiopathic premature ventricular complexes (PVC) and idiopathic ventricular tachycardia (VT).
Methods: Data were collected from all patients who underwent radiofrequency catheter ablation for symptomatic PVCs and idiopathic VT in the Catharina Hospital between 1 January 2011 and 31 December 2015. The procedural endpoint was elimination or non-inducibility of the clinical arrhythmia. Successful sustained ablation was defined as the persistent elimination of at least 80% of the PVCs or the absence of VTs at follow-up. In case of suspected PVC-induced cardiomyopathy, the systolic left ventricular function was reassessed 3 months post procedure.
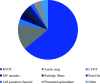
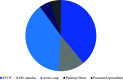
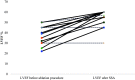
Results: Our cohort consisted of 131 patients who underwent one or more ablation procedures; 99 because of symptomatic premature ventricular complexes, 32 because of idiopathic VT. In total 147 procedures were performed. The procedural ablation success rate was 89%. Successful sustained ablation rate was 82%. Eighteen (13.2%) patients had suspected PVC-induced cardiomyopathy. In 15 of them (83%), successful sustained ablation was achieved and the left ventricular ejection fraction improved from a mean of 39% (±8.8) to 55.4% (±8.1). Most arrhythmias originated from the right ventricular outflow tract (60%) or aortic cusps (13%). Complications included three tamponades.
Conclusion: Catheter ablation therapy for idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias is very effective with a sustained success rate of 82%. In patients with PVC-induced cardiomyopathy, it leads to improvement of systolic left ventricular function. However, risk for complications is not negligible, even in experienced hands.
Keywords: Ablation; Catheter; Idiopathic; Premature; Tachycardia; Ventricular.
Conflict of interest statement
A.W.G.J. Oomen, L.R.C. Dekker and A. Meijer declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Outcomes of single-procedure radiofrequency catheter ablation for idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias: a single-centre retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2024 Feb 20;14(2):e081815. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-081815. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38382956 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter Outcomes for Catheter Ablation of Idiopathic Premature Ventricular Complexes.JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2015 Jun;1(3):116-123. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2015.04.005. Epub 2015 Apr 27. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2015. PMID: 29759353
-
Pre-procedural arrhythmia burden and the outcome of catheter ablation of idiopathic premature ventricular complexes.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2021 Apr;44(4):703-710. doi: 10.1111/pace.14211. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33675240
-
Are antiarrhythmic agents indicated in premature ventricular complex-induced cardiomyopathy and when?J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2024 Mar;35(3):574-582. doi: 10.1111/jce.16055. Epub 2023 Sep 7. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2024. PMID: 37676022 Review.
-
Mechanism, diagnosis, and treatment of outflow tract tachycardia.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015 Oct;12(10):597-608. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.121. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26283265 Review.
Cited by
-
Ablation of idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias.Neth Heart J. 2018 Apr;26(4):173-174. doi: 10.1007/s12471-018-1095-3. Neth Heart J. 2018. PMID: 29484566 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Outcomes of single-procedure radiofrequency catheter ablation for idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias: a single-centre retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2024 Feb 20;14(2):e081815. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-081815. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38382956 Free PMC article.
-
The R-S difference index: A new electrocardiographic method for differentiating idiopathic premature ventricular contractions originating from the left and right ventricular outflow tracts presenting a left bundle branch block pattern.Front Physiol. 2022 Sep 19;13:1002926. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1002926. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36200051 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of idiopathic premature ventricular complexes on left ventricular ejection fraction.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2020 Mar;25(2):e12702. doi: 10.1111/anec.12702. Epub 2019 Sep 22. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2020. PMID: 31542896 Free PMC article.
-
Ventricular tachycardia ablation in children.Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2023 Jul-Aug;23(4):99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.ipej.2023.03.002. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2023. PMID: 36906176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Huls van Taxis CF, Piers SR, de Riva SM. Fatigue as presenting symptom and a high burden of premature ventricular contractions are independently associated with increased ventricular wall stress in patients with normal left ventricular function. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2015;8:1452–1459. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

