Long noncoding RNA BC005927 upregulates EPHB4 and promotes gastric cancer metastasis under hypoxia
- PMID: 29383777
- PMCID: PMC5891181
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13519
Long noncoding RNA BC005927 upregulates EPHB4 and promotes gastric cancer metastasis under hypoxia
Abstract
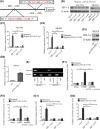
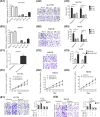
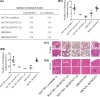
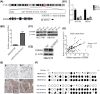
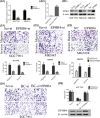
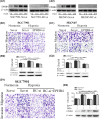
Hypoxia plays a critical role in the metastasis of gastric cancer (GC), yet the underlying mechanism remains largely unclear. It is also not known whether long, noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in the contribution of hypoxia to GC metastasis. In the present study, we found that lncRNA BC005927 can be induced by hypoxia in GC cells and mediates hypoxia-induced GC cell metastasis. Furthermore, BC005927 is frequently upregulated in GC samples and increased BC005927 expression was correlated with a higher tumor-node-metastasis stage. GC patients with higher BC005927 expression had poorer prognoses than those with lower expression. Additional experiments showed that BC005927 expression is induced by hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α); ChIP assay and luciferase reporter assays confirmed that this lncRNA is a direct transcriptional target of HIF-1α. Next, we found that EPHB4, a metastasis-related gene, is regulated by BC005927 and that the expression of EPHB4 was positively correlated with that of BC005927 in the clinical GC samples assessed. Intriguingly, EPHB4 expression was also increased under hypoxia, and its upregulation by BC005927 resulted in hypoxia-induced GC cell metastasis. These results advance the current understanding of the role of BC005927 in the regulation of hypoxia signaling and offer new avenues for the development of therapeutic interventions against cancer progression.
Keywords: EPHB4; gastric cancer; hypoxia; lncRNA; metastasis.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-inducible lncRNA-AK058003 promotes gastric cancer metastasis by targeting γ-synuclein.Neoplasia. 2014 Dec;16(12):1094-106. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.10.008. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 25499222 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-224 promotes the cell growth, migration and invasion by directly targeting RASSF8 in gastric cancer.Mol Cancer. 2017 Feb 7;16(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0603-1. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28173803 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA GMAN, Up-regulated in Gastric Cancer Tissues, Is Associated With Metastasis in Patients and Promotes Translation of Ephrin A1 by Competitively Binding GMAN-AS.Gastroenterology. 2019 Feb;156(3):676-691.e11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.10.054. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30445010
-
The role of hypoxia-induced long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in tumorigenesis and metastasis.Biomed J. 2021 Oct;44(5):521-533. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2021.03.005. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 34654684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hypoxia-Long Noncoding RNA Interaction in Solid Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 6;22(14):7261. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147261. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-622 Increases miR-30a Expression through Inhibition of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α to Improve Metastasis and Chemoresistance in Human Invasive Breast Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 3;16(3):657. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030657. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339408 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory roles and potential prognosis implications of long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer.Histol Histopathol. 2020 May;35(5):433-442. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-188. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Histol Histopathol. 2020. PMID: 31793657 Review.
-
The Roles of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and Non-Coding RNAs in Gastrointestinal Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2019 Dec 4;10(12):1008. doi: 10.3390/genes10121008. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31817259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIF in Gastric Cancer: Regulation and Therapeutic Target.Molecules. 2022 Jul 31;27(15):4893. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154893. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Hypoxia-Associated Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Chemo-Therapy Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 23;26(3):936. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030936. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940704 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277‐300. - PubMed
-
- Gupta GP, Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679‐695. - PubMed
-
- Wang JR, Gan WJ, Li XM, et al. Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by regulating MMP‐9 and E‐cadherin. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:2474‐2484. - PubMed
-
- Fu J, Chen Y, Cao J, et al. p28GANK overexpression accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness and metastasis via phosphoinositol 3‐kinase/AKT/hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1alpha pathways. Hepatology. 2011;53:181‐192. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

