An Evaluation of the Cost-effectiveness of Comprehensive MTM Integrated with Point-of-Care Phenotypic and Genetic Testing for U.S. Elderly Patients After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- PMID: 29384027
- PMCID: PMC10397765
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2018.24.2.142
An Evaluation of the Cost-effectiveness of Comprehensive MTM Integrated with Point-of-Care Phenotypic and Genetic Testing for U.S. Elderly Patients After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Abstract
Background: Poor health outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in elderly patients is an area of concern among policymakers and administrators. In an effort to determine the best strategy to improve outcomes among elderly patients who underwent PCI, several studies have evaluated the cost-effectiveness of genotype-guided antiplatelet therapy compared with universal use of any one of the antiplatelet drugs indicated for patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who underwent PCI. The results have either been in favor of genotype-guided antiplatelet therapy or universal use of ticagrelor. However, no study has yet evaluated the cost-effectiveness of pharmacist-provided face-to-face medication therapy management (MTM) combined with point-of-care genotype-guided antiplatelet therapy (POCP) when compared with universal use of ticagrelor or clopidogrel for the elderly after PCI.
Objective: To evaluate the cost-effectiveness of a pharmacist integration of MTM with POCP (MTM-POCP) when compared with universal use of ticagrelor or clopidogrel combined with MTM (MTM-ticagrelor or MTM-clopidogrel).
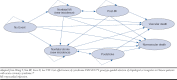
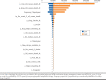
Methods: We conducted a cost-effectiveness analysis from the perspective of the U.S. health care system. A hybrid model, consisting of a 1-year decision tree and a 20-year Markov model, was used to simulate a cohort of elderly patients (aged at least 65 years) with ACS who underwent PCI. Treatment strategies available to patients were POCP, POCP-MTM, MTM-clopidogrel, or MTM-ticagrelor. Data used to populate the model were obtained from the PLATO trial and other published studies. Outcome measures were costs, quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) and incremental cost per QALY gained. A deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analysis was conducted to account for the joint uncertainty around the key parameters of the model. Finally, a benchmark willingness to pay of $50,000-200,000 was considered.
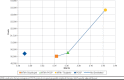
Results: The use of PCOP (with dual antiplatelet therapy) resulted in 5.29 QALYs, at a cost of $50,207. MTM-clopidogrel resulted in 5.34 QALYs, at a cost of $50,011. The use of POCP-MTM resulted in 5.36 QALYs, at a cost of $50,270. Finally, MTM-ticagrelor resulted in 5.42 QALYs, at a cost of $53,346. MTM-ticagrelor was found to be cost-effective compared with MTM-clopidogrel or MTM-POCP, irrespective of the willingness to pay. The deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses confirmed the robustness of the base-case analysis.
Conclusions: The combination of MTM-ticagrelor was cost-effective when compared with MTM-POCP or MTM-clopidogrel. The transitional probabilities, however, were mostly based on published studies. Analysis based on a prospective randomized clinical study, comparing all the treatment strategies included in this study, is warranted to confirm our findings.
Disclosures: No outside funding supported this study. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Study concept and design were contributed by Okere and Diaby. Ezendu took the lead in data collection, along with Okere. Data interpretation was performed by all the authors. The manuscript was written by Okere, Diaby, and Berthe and revised by Okere and Diaby.
Conflict of interest statement
No outside funding supported this study. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Study concept and design were contributed by Okere and Diaby. Ezendu took the lead in data collection, along with Okere. Data interpretation was performed by all the authors. The manuscript was written by Okere, Diaby, and Berthe and revised by Okere and Diaby.
Figures
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al. .; American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;131(4):e29-322. - PubMed
-
- Engstrøm T, Kelbæk H, Helqvist S, et al. . Complete revascularisation versus treatment of the culprit lesion only in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and multivessel disease (DANAMI-3—PRIMULTI): an open-label randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;386(9994):665-71. - PubMed
-
- Pilgrim T, Vranckx P, Valgimigli M, et al. . Risk and timing of recurrent ischemic events among patients with stable ischemic heart disease, non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome, and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 2016;175:56-65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous