Applying GRADE-CERQual to qualitative evidence synthesis findings-paper 2: how to make an overall CERQual assessment of confidence and create a Summary of Qualitative Findings table
- PMID: 29384082
- PMCID: PMC5791047
- DOI: 10.1186/s13012-017-0689-2
Applying GRADE-CERQual to qualitative evidence synthesis findings-paper 2: how to make an overall CERQual assessment of confidence and create a Summary of Qualitative Findings table
Abstract
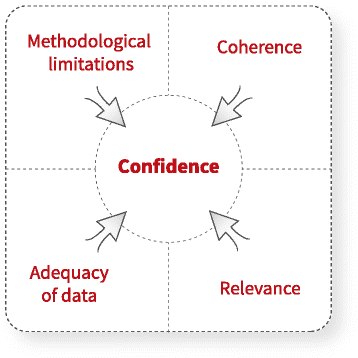
Background: The GRADE-CERQual (Confidence in Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative research) approach has been developed by the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation) Working Group. The approach has been developed to support the use of findings from qualitative evidence syntheses in decision making, including guideline development and policy formulation. CERQual includes four components for assessing how much confidence to place in findings from reviews of qualitative research (also referred to as qualitative evidence syntheses): (1) methodological limitations, (2) coherence, (3) adequacy of data and (4) relevance. This paper is part of a series providing guidance on how to apply CERQual and focuses on making an overall assessment of confidence in a review finding and creating a CERQual Evidence Profile and a CERQual Summary of Qualitative Findings table.
Methods: We developed this guidance by examining the methods used by other GRADE approaches, gathering feedback from relevant research communities and developing consensus through project group meetings. We then piloted the guidance on several qualitative evidence syntheses before agreeing on the approach.
Results: Confidence in the evidence is an assessment of the extent to which a review finding is a reasonable representation of the phenomenon of interest. Creating a summary of each review finding and deciding whether or not CERQual should be used are important steps prior to assessing confidence. Confidence should be assessed for each review finding individually, based on the judgements made for each of the four CERQual components. Four levels are used to describe the overall assessment of confidence: high, moderate, low or very low. The overall CERQual assessment for each review finding should be explained in a CERQual Evidence Profile and Summary of Qualitative Findings table.
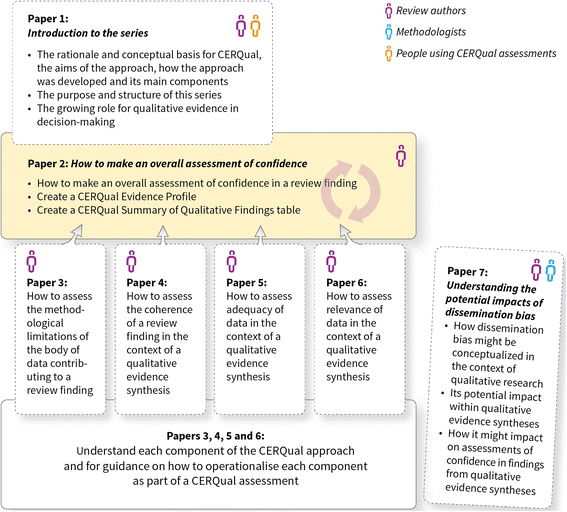
Conclusions: Structuring and summarising review findings, assessing confidence in those findings using CERQual and creating a CERQual Evidence Profile and Summary of Qualitative Findings table should be essential components of undertaking qualitative evidence syntheses. This paper describes the end point of a CERQual assessment and should be read in conjunction with the other papers in the series that provide information on assessing individual CERQual components.
Keywords: Confidence; Evidence-based practice; GRADE; Guidance; Methodology; Qualitative evidence synthesis; Qualitative research; Research design; Systematic review methodology.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable. This study did not undertake any formal data collection involving any humans or animals.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lewin S, Glenton C, Munthe-Kaas H, Carlsen B, Colvin CJ, Gulmezoglu M, Noyes J, Booth A, Garside R, Rashidian A. Using qualitative evidence in decision making for health and social interventions: an approach to assess confidence in findings from qualitative evidence syntheses (GRADE-CERQual) PLoS Med. 2015;12(10):e1001895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001895. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Munthe-Kaas HM, Bohren M, Carlsen B, Glenton C, Lewin S, Colvin CJ, Tuncalp Ö, Noyes J, Booth A, Garside R, et al. Applying GRADE-CERQual to qualitative evidence synthesis findings—paper 3: how to assess methodological limitations. Implement Sci. 2018;13(Suppl 1): 10.1186/s13012-017-0690-9. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources