Montreal electronic artificial urinary sphincters: Our futuristic alternatives to the AMS800™
- PMID: 29384472
- PMCID: PMC5963454
- DOI: 10.5489/cuaj.4493
Montreal electronic artificial urinary sphincters: Our futuristic alternatives to the AMS800™
Abstract
Introduction: We aimed to present three novel remotely controlled hydromechanical artificial urinary sphincters (AUSs) and report their in-vitro and ex-vivo results.
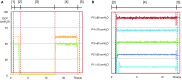
Methods: We successively developed three distinct hydromechanical AUSs on the basis of the existing AMS800™ device by incorporating an electronic pump. No changes were made to the cuff and balloon. The AUS#1 was designed as an electromagnetically controlled device. The AUS#2 and AUS#3 were conceived as Bluetooth 2.1 remotely controlled and Bluetooth 4.0 remotely-controlled, adaptive devices, respectively. In-vitro experiments profiled occlusive cuff pressure (OCP) during a complete device cycle, with different predetermined OCP. Ex-vivo experiments were performed on a fresh pig bladder with 4 cm cuff placed around the urethra. Leak point pressure with different predetermined OCP values was successively measured during cystometry via a catheter at the bladder dome.
Results: Our in-vitro and ex-vivo experiments demonstrated that these three novel AUSs provided stable and predetermined OCP - within the physiological range - and completely deflated the cuff, when required, in a limited time compatible with physiological voiding cycles.
Conclusions: Our three novel, remotely controlled AUSs showed promising results that should be confirmed by in-vivo experiments focusing on efficacy and safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Artificial Urinary Sphincter: Report of the 2015 Consensus Conference.Neurourol Urodyn. 2016 Apr;35 Suppl 2:S8-24. doi: 10.1002/nau.22989. Neurourol Urodyn. 2016. PMID: 27064055
-
Urethral atrophy after implantation of an artificial urinary sphincter: fact or fiction?BJU Int. 2016 Apr;117(4):669-76. doi: 10.1111/bju.13324. Epub 2015 Oct 12. BJU Int. 2016. PMID: 26384584
-
Newer and novel artificial urinary sphincters (AUS): the development of alternatives to the current AUS device.BJU Int. 2012 Dec;110 Suppl 4:5-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11614.x. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 23194117 Review.
-
Success of the narrow-backed cuff design of the AMS800 artificial urinary sphincter: analysis of 144 patients.J Urol. 1993 Nov;150(5 Pt 1):1412-4. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35793-2. J Urol. 1993. PMID: 8411412 Review.
-
Overview of the 2015 ICS Consensus Conference.Neurourol Urodyn. 2016 Apr;35(4):437-43. doi: 10.1002/nau.22999. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Neurourol Urodyn. 2016. PMID: 26998767
Cited by
-
Prosthetics in urology: Current status and future directions.Indian J Urol. 2023 Jan-Mar;39(1):12-20. doi: 10.4103/iju.iju_90_22. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Indian J Urol. 2023. PMID: 36824106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-generation Solutions: Are Patients Ready for Electronic Artificial Urinary Sphincters for Male Incontinence?Eur Urol Open Sci. 2025 Feb 21;74:21-27. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2025.02.004. eCollection 2025 Apr. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2025. PMID: 40066191 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Assistive Electronic Device Solutions for Urology.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Mar 30;13(4):551. doi: 10.3390/mi13040551. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35457855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advancements in penile prosthetics.F1000Res. 2019 Feb 18;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-193. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.17407.1. eCollection 2019. F1000Res. 2019. PMID: 30828431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial urinary sphincter and female stress urinary incontinence over the past 50 years: a narrative review.Transl Androl Urol. 2024 Aug 31;13(8):1674-1686. doi: 10.21037/tau-23-58. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Transl Androl Urol. 2024. PMID: 39280667 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thüroff JW, Abrams P, Andersson KE, et al. EAU guidelines on urinary incontinence. Eur Urol. 2011;59:387–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2010.11.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Foley FE. An artificial sphincter; a new device and operation for control of enuresis and urinary incontinence. J Urol. 1947;58:250–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)69552-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Islah M, Cho SY, Son H. The current role of the artificial urinary sphincter in male and female urinary incontinence. World J Mens Health. 2013;31:21–30. https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2013.31.1.21. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elliott DS, Barrett DM. Mayo Clinic long-term analysis of the functional durability of the AMS 800 artificial urinary sphincter: A review of 323 cases. J Urol. 1998;159:1206–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(01)63557-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Müller B, Deyhle H, Mushkolaj S, et al. The challenges in artificial muscle research to treat incontinence. Swiss Med Wkly. 2009;139:591–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
