Evaluation of alveolar bone support around incisors in patients with unilateral cleft lip, alveolus, and palate in late mixed dentition using cone beam computed tomography
- PMID: 29384701
- PMCID: PMC8288317
- DOI: 10.2319/071517-472.1
Evaluation of alveolar bone support around incisors in patients with unilateral cleft lip, alveolus, and palate in late mixed dentition using cone beam computed tomography
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate alveolar bone support around cleft-adjacent maxillary central incisors (U1) in patients with unilateral cleft lip, alveolus and palate (UCLAP) in the late mixed dentition and to investigate the correlation between the alveolar bone thickness (ABT) and tooth inclination.
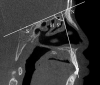
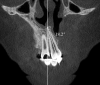
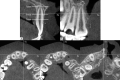
Materials and methods: Cone beam computed tomography scans of 45 subjects with UCLAP (29 boys, 16 girls; mean age = 10.74 ± 1.08 years) were assessed. The distance between the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) and alveolar bone crest (AC), and the ABTs at 3 mm, 6 mm, and the apex were measured on the labial, lingual and distal surfaces of U1. The cleft and normal sides were compared using a paired t-test and Pearson's χ2 test. Pearson's correlation was used to explore the association between the ABT and tooth inclination of cleft-adjacent U1 in the labiolingual and mesiodistal dimensions.
Results: The CEJ-AC distances were significantly greater in cleft-adjacent U1 ( P < .01), with more bone height reduction observed labially and distally ( P < .001). The labial, lingual, and apico-distal ABTs were decreased on the cleft side ( P < .01). A positive correlation was found between the apico-labial ABT and the labiolingual inclination ( r = 0.568, P < .01).
Conclusions: Patients with UCLAP have reduced alveolar bone support around the cleft-adjacent U1, and the apico-labial ABT tends to decrease with increasing lingual tooth inclination; however, the correlation was weak.
Keywords: Alveolar bone; Cone beam computed tomography; Tooth inclination; Unilateral cleft lip, alveolus, and palate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship Between Crown to Root Ratio and Alveolar Bone Support in Patients With Unilateral Cleft Lip and Alveolus.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2021 Feb;58(2):215-221. doi: 10.1177/1055665620950155. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2021. PMID: 32808559
-
Correlation between Cleft Width and Adjacent Teeth Inclination in Patients with Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Using CBCT: A Retrospective Study.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2025 Jun;62(6):1032-1038. doi: 10.1177/10556656241236532. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2025. PMID: 38419460
-
Alveolar bone morphology in patients with bilateral complete cleft lip and palate in the mixed dentition: cone beam computed tomography evaluation.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2012 Mar;49(2):208-14. doi: 10.1597/10-198. Epub 2011 Jul 8. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2012. PMID: 21740185
-
Facial alveolar bone thickness and modifying factors of anterior maxillary teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cone-beam computed tomography studies.BMC Oral Health. 2021 Mar 22;21(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01495-2. BMC Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 33752651 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Remodeling during Orthodontic Movement of Lower Incisors-Narrative Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 15;19(22):15002. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192215002. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36429721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Frontal and Axial Evaluation of Craniofacial Morphology in Repaired Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patients Utilizing Cone Beam Computed Tomography; An Observational Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Oct 24;17(21):7786. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17217786. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33114340 Free PMC article.
-
Canine pillar bone bearing traction method of skull external fixator combined with nickel-titanium memory alloy spring for unilateral cleft lip and palate with severe facial skeletal hypoplasia.Afr Health Sci. 2024 Sep;24(3):345-352. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v24i3.38. Afr Health Sci. 2024. PMID: 40777948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu R, Lu D, Wamalwa P, Li C, Hu H, Zou S. Craniofacial morphology characteristics of operated unilateral complete cleft lip and palate patients in mixed dentition. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112:e16–e25. - PubMed
-
- Stec M, Szczepanska J, Pypec J, Hirschfelder U. Periodontal status and oral hygiene in two populations of cleft patients. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2007;44:73–78. - PubMed
-
- Perdikogianni H, Papaioannou W, Nakou M, Oulis C, Papagiannoulis L. Periodontal and microbiological parameters in children and adolescents with cleft lip and/or palate. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2009;19:455–467. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

