GLCCI1 rs37973: A potential genetic predictor of therapeutic response to inhaled corticosteroids in Chinese asthma patients
- PMID: 29384926
- PMCID: PMC6392942
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009442
GLCCI1 rs37973: A potential genetic predictor of therapeutic response to inhaled corticosteroids in Chinese asthma patients
Abstract
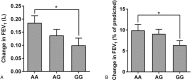
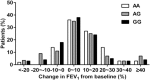
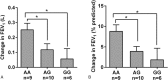
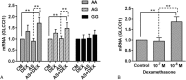
Glucocorticoids are the primary anti-inflammatory therapy for asthma, but their effects are characterized by some interindividual variability that might have a genetic basis.We aimed to determine the relationship between pulmonary function change and the variant of the glucocorticoid-induced transcript 1 (GLCCI1) gene in patients with asthma receiving long-term ICS treatment, the association of GLCCI1 genotypes and the level of GLCCI1 expression and cytokines production.A total of 418 patients with asthma, including 25 individuals from 11 families with a history of asthma, were enrolled. The effects of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in GLCCI1 on changes in lung function in response to inhaled glucocorticoids were assessed. The expression levels of GLCCI1 mRNA and cytokines were also measured.The SNP rs37973 in GLCCI1 was independently associated with changes in forced expiratory volume at one second (FEV1) and FEV1%pred. Individuals homozygous for the wild-type allele who had a percent FEV1 change greater than 5% were more common than individuals homozygous for the rare allele. When patients were stratified according to genotype, GLCCI1 expression was enhanced upon administration of low-dose dexamethasone among patients with the rs37973 A allele; however, GG homozygotes required high-dose dexamethasone to achieve enhanced GLCCI1 expression. Furthermore, the levels of some cytokines were significantly reduced after glucocorticoid treatment in individuals with the AA and AG genotypes.The genetic variant rs37973 in GLCCI1 is associated with poorer clinical therapeutic response to inhaled glucocorticoids in a Chinese asthma population.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The GLCCI1 rs37973 variant and the efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in the treatment of asthma: A meta-analysis.Clin Respir J. 2023 Jun;17(6):568-579. doi: 10.1111/crj.13627. Epub 2023 May 8. Clin Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37157161 Free PMC article.
-
Genomewide association between GLCCI1 and response to glucocorticoid therapy in asthma.N Engl J Med. 2011 Sep 29;365(13):1173-83. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0911353. Epub 2011 Sep 26. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21991891 Free PMC article.
-
GLCCI1 variant accelerates pulmonary function decline in patients with asthma receiving inhaled corticosteroids.Allergy. 2014 May;69(5):668-73. doi: 10.1111/all.12400. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Allergy. 2014. PMID: 24673601
-
Effects of genetic factors to inhaled corticosteroid response in children with asthma: a literature review.J Int Med Res. 2017 Dec;45(6):1818-1830. doi: 10.1177/0300060516683877. Epub 2017 Jan 25. J Int Med Res. 2017. PMID: 29251255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The analysis of the factors influencing the development of glucocorticoid resistance in the etiopathogenesis of severe bronchial asthma].Postepy Biochem. 2010;56(4):373-82. Postepy Biochem. 2010. PMID: 21473041 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Genetic Determinants of Poor Response to Treatment in Severe Asthma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 20;22(8):4251. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084251. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33923891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacogenetic Factors Affecting Asthma Treatment Response. Potential Implications for Drug Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2019 May 21;10:520. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00520. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31178722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Glucocorticoid-Induced Transcript 1 Gene Deficiency on Glucocorticoid Activation in Asthmatic Mice.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Dec 5;131(23):2817-2826. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.246061. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 30511684 Free PMC article.
-
The GLCCI1 rs37973 variant and the efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in the treatment of asthma: A meta-analysis.Clin Respir J. 2023 Jun;17(6):568-579. doi: 10.1111/crj.13627. Epub 2023 May 8. Clin Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37157161 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of STIP1 and GLCCI1 polymorphisms on the risk of childhood asthma and inhaled corticosteroid response in Chinese asthmatic children.BMC Pulm Med. 2020 Nov 18;20(1):303. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-01332-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2020. PMID: 33208131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- London SJ, Romieu I. Gene by environment interaction in asthma. Ann Rev Public Health 2009;30:55–80. - PubMed
-
- Drazen JM, Silverman EK, Lee TH. Heterogeneity of therapeutic responses in asthma. Br Med Bull 2000;56:1054–70. - PubMed
-
- Szefler SJ, Martin RJ, King TS, et al. Significant variability in response to inhaled corticosteroids for persistent asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002;109:410–8. - PubMed
-
- Weiss ST. New approaches to personalized medicine for asthma: where are we? J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;129:327–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

