Upregulation of transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 predicts poor prognosis in invasive breast cancer: A STROBE-compliant article
- PMID: 29384939
- PMCID: PMC6392956
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009476
Upregulation of transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 predicts poor prognosis in invasive breast cancer: A STROBE-compliant article
Abstract
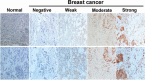
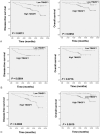
Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 (TM4SF1) belongs to the 4-transmembrane-domain family and functions as an oncogene in multiple human cancers. In this work, we aim to determine TM4SF1 expression and its prognostic impact on patients with invasive breast cancer.Overall, we enrolled 209 invasive breast cancer patients and immunohistochemically examined the expression of TM4SF1 in tumor specimens. The relationship between TM4SF1 expression and clinicopathological parameter and patient survival of breast cancer patients was analyzed.Among the 209 cases, 137 (65.6%) exhibited high expression of TM4SF1. High TM4SF1 expression was significantly associated with advanced histological grade and negative estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) tumors were more likely to express high levels of TM4SF1 than non-TNBC cases. Patients with high tumoral expression of TM4SF1 had a significantly shorter disease-free survival (DFS; P = .00) and overall survival (OS; P = .01) than those with low expression of TM4SF1. When survival analysis was restricted to the 167 patients (79.9%) receiving adjuvant chemotherapy, TM4SF1 expression was also correlated with poorer DFS and OS (P = .00). In multiple Cox regression analysis TM4SF1 expression remained an independent prognostic indicator for OS and DFS.TM4SF1 is upregulated and serves as an independent poor prognostic indicator in invasive breast cancer.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poor prognosis of single hormone receptor- positive breast cancer: similar outcome as triple-negative breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2015 Mar 18;15:138. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1121-4. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25880075 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen receptor expression predicts decreased survival in early stage triple-negative breast cancer.Ann Surg Oncol. 2015 Jan;22(1):82-9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-3984-z. Epub 2014 Aug 22. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25145503
-
Clinicopathological characteristics of triple negative breast cancer at a tertiary care hospital in India.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(24):10577-83. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.24.10577. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25605142
-
An overview of triple-negative breast cancer.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016 Feb;293(2):247-69. doi: 10.1007/s00404-015-3859-y. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016. PMID: 26341644 Review.
-
Three Members of Transmembrane-4-Superfamily, TM4SF1, TM4SF4, and TM4SF5, as Emerging Anticancer Molecular Targets against Cancer Phenotypes and Chemoresistance.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;16(1):110. doi: 10.3390/ph16010110. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-30 Family Reduction Maintains Self-Renewal and Promotes Tumorigenesis in NSCLC-Initiating Cells by Targeting Oncogene TM4SF1.Mol Ther. 2018 Dec 5;26(12):2751-2765. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30301667 Free PMC article.
-
TM4SF1, a binding protein of DVL2 in hepatocellular carcinoma, positively regulates beta-catenin/TCF signalling.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Mar;25(5):2356-2364. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14787. Epub 2019 Dec 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 31876386 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction Proteomics Identifies ERbeta Association with Chromatin Repressive Complexes to Inhibit Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Exert An Oncosuppressive Role in Triple-negative Breast Cancer.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Feb;19(2):245-260. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001817. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31792072 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omic lineage tracing predicts the transcriptional, epigenetic and genetic determinants of cancer evolution.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 1;15(1):7609. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51424-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39218912 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of TM4SF1 and DDR1 expression in epithelial ovarian cancer.Oncol Lett. 2023 Aug 30;26(4):448. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.14035. eCollection 2023 Oct. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37720676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

