Helicobacter pylori eradication improves the quality of life regardless of the treatment outcome: A multicenter prospective cohort study
- PMID: 29384953
- PMCID: PMC6392891
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009507
Helicobacter pylori eradication improves the quality of life regardless of the treatment outcome: A multicenter prospective cohort study
Abstract
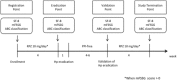
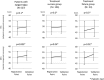
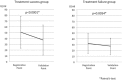
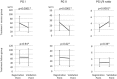
Helicobacter pylori (Hp) eradication is recommended for improving the quality of life (QOL) of patients with epigastric symptoms, especially reflux and dyspepsia. However, no reports have investigated the improvement of QOL after the eradication of Hp irrespective of epigastric symptoms. The aim of this study was to investigate the improvement in the QOL after the eradication of Hp irrespective of epigastric symptoms, and evaluate the factors associated with an improved QOL after the eradication of Hp.This prospective cohort study was performed at 15 referral institutions from September 2013 to December 2014. The patients' QOL and epigastric symptoms were evaluated before and after the eradication of Hp using the 8-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-8) and the modified Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, respectively.One hundred sixty-five of 184 Hp-infected patients underwent Hp eradication treatment. The treatment was successful in 82.4% (136/165) of the cases. One hundred sixty of the 165 Hp-infected patients were eligible for inclusion in the QOL analysis. In the indices of QOL on the SF-8, the scores on both the mental component summary (MCS) and the physical component summary (PCS) were found to have significantly improved after the eradication of Hp. However, the epigastric symptoms before the eradication of Hp were not correlated with either the MCS or PCS. A low QOL value before the eradication of Hp was the factor what was most strongly associated with the improvement in the QOL.The eradication of Hp improved the QOL, regardless of the outcome of the treatment, especially in patients who had an impaired QOL before the eradication.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori eradication ameliorates symptoms and improves quality of life in patients on long-term acid suppression. A large prospective study in primary care.Dig Dis Sci. 2002 Jul;47(7):1567-74. doi: 10.1023/a:1015823320831. Dig Dis Sci. 2002. PMID: 12141818
-
Characteristics and Predictive Factor of Helicobacter pylori-Associated Functional Dyspepsia in Japanese Patients.Digestion. 2019;100(4):277-285. doi: 10.1159/000496101. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Digestion. 2019. PMID: 30630185
-
Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy Ameliorates Latent Digestive Symptoms in Chronic Atrophic Gastritis.Digestion. 2018;97(4):333-339. doi: 10.1159/000486618. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Digestion. 2018. PMID: 29587295
-
Chemoprevention of gastric cancer by Helicobacter pylori eradication and its underlying mechanism.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Aug;34(8):1287-1295. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14646. Epub 2019 Mar 27. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30828872 Review.
-
Is there an increased risk of GERD after Helicobacter pylori eradication?: a meta-analysis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 May;105(5):1007-13; quiz 1006, 1014. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.734. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20087334 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolving Concepts in Helicobacter pylori Management.Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):267-283. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.09.047. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Gastroenterology. 2024. PMID: 37806461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Personalized Approach in Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Dec 21;12(1):7. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010007. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36671208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Different Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapies on Gastrointestinal Symptoms.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Aug 5;57(8):803. doi: 10.3390/medicina57080803. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34441009 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023 Apr 20;9(1):19. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00431-8. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023. PMID: 37081005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pepsinogen and Serum IgG Detection Is a Valuable Diagnostic Method for Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Low-Prevalence Country: A Report from Sri Lanka.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jul 29;11(8):1364. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11081364. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34441303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warren JR, Marshall BJ. Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1983;1:1273–5. - PubMed
-
- Herrero R, Park JY, Forman D. The fight against gastric cancer: the IARC Working Group report. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:1107–14. - PubMed
-
- Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med 2001;345:784–9. - PubMed
-
- Marshall BJ, Goodwin CS, Warren JR, et al. Prospective double-blind trial of duodenal ulcer relapse after eradication of Campylobacter pylori. Lancet 1988;2:1437–42. - PubMed
-
- Franchini M, Cruciani M, Mengoli C, et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on platelet count in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Antimicrob Chemother 2007;60:237–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

