Expansion of Sphingosine Kinase and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor Function in Normal and Cancer Cells: From Membrane Restructuring to Mediation of Estrogen Signaling and Stem Cell Programming
- PMID: 29385066
- PMCID: PMC5855642
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19020420
Expansion of Sphingosine Kinase and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor Function in Normal and Cancer Cells: From Membrane Restructuring to Mediation of Estrogen Signaling and Stem Cell Programming
Abstract
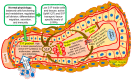
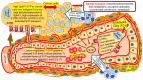
Sphingolipids, sphingolipid metabolizing enzymes, and their receptors network are being recognized as part of the signaling mechanisms, which govern breast cancer cell growth, migration, and survival during chemotherapy treatment. Approximately 70% of breast cancers are estrogen receptor (ER) positive and, thus, rely on estrogen signaling. Estrogen activates an intracellular network composed of many cytoplasmic and nuclear mediators. Some estrogen effects can be mediated by sphingolipids. Estrogen activates sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) and amplifies the intracellular concentration of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) in breast cancer cells during stimulation of proliferation and survival. Specifically, Estrogen activates S1P receptors (S1PR) and induces growth factor receptor transactivation. SphK, S1P, and S1PR expression are causally associated with endocrine resistance and progression to advanced tumor stages in ER-positive breast cancers in vivo. Recently, the network of SphK/S1PR was shown to promote the development of ER-negative cancers and breast cancer stem cells, as well as stimulating angiogenesis. Novel findings confirm and broaden our knowledge about the cross-talk between sphingolipids and estrogen network in normal and malignant cells. Current S1PRs therapeutic inhibition was indicated as a promising chemotherapy approach in non-responsive and advanced malignancies. Considering that sphingolipid signaling has a prominent role in terminally differentiated cells, the impact should be considered when designing specific SphK/S1PR inhibitors. This study analyzes the dynamic of the transformation of sphingolipid axis during a transition from normal to pathological condition on the level of the whole organism. The sphingolipid-based mediation and facilitation of global effects of estrogen were critically accented as a bridging mechanism that should be explored in cancer prevention.
Keywords: breast cancer; cancer stem cells; estrogen receptor; inflammation; sphingolipids; sphingosine kinase; sphingosine-1-phosphate; vasculature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sphingosine kinase and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling pathway in inflammatory gastrointestinal disease and cancers: A novel therapeutic target.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Mar;207:107464. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107464. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31863815 Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate and estrogen signaling in breast cancer.Adv Biol Regul. 2016 Jan;60:160-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Adv Biol Regul. 2016. PMID: 26601898 Review.
-
Identification of novel functional and spatial associations between sphingosine kinase 1, sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors and other signaling proteins that affect prognostic outcome in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.Int J Cancer. 2013 Feb 1;132(3):605-16. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27692. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 22733311
-
Divergence of Intracellular Trafficking of Sphingosine Kinase 1 and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 3 in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells and MCF-7-Derived Stem Cell-Enriched Mammospheres.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4314. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094314. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919234 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of released sphingosine 1-phosphate/sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor axis in skeletal muscle atrophy.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Dec;1864(12):3598-3614. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.08.040. Epub 2018 Sep 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 30279138
Cited by
-
Interaction of microRNAs with sphingosine kinases, sphingosine-1 phosphate, and sphingosine-1 phosphate receptors in cancer.Discov Oncol. 2021 Sep 20;12(1):33. doi: 10.1007/s12672-021-00430-9. Discov Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35201458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Microenvironment: Key Players in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Immunomodulation.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 4;13(13):3357. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133357. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34283088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triptolide Inhibits the Biological Processes of HUVECs and HepG2 Cells via the Serine Palmitoyltransferase Long Chain Base Subunit 2/Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling Pathway.Dis Markers. 2022 Nov 18;2022:9119423. doi: 10.1155/2022/9119423. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36438896 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of Ceramide- and Sphingosine-Metabolizing Enzymes as Sensitizers in Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 26;12(8):2062. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082062. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32722626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S1PR1 as a Novel Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer Therapy.Mol Diagn Ther. 2019 Aug;23(4):467-487. doi: 10.1007/s40291-019-00401-5. Mol Diagn Ther. 2019. PMID: 31115798 Review.
References
-
- Katzenellenbogen B.S., Choi I., Delage-Mourroux R., Ediger T.R., Martini P.G., Montano M., Sun J., Weis K., Katzenellenbogen J.A. Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: Selective ligands and receptor pharmacology. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000;74:279–2785. doi: 10.1016/S0960-0760(00)00104-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Osborne C.K., Schiff R., Fuqua S.A., Shou J. Estrogen receptor: Current understanding of its activation and modulation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001;7:4338–4342. - PubMed
-
- Schiff R., Massarweh S., Shou J., Osborne C.K. Breast cancer endocrine resistance: How growth factor signaling and estrogen receptor coregulators modulate response. Pt 2Clin. Cancer Res. 2003;9:447S–454S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

