In silico analysis of structural modifications in and around the integrin αIIb genu caused by ITGA2B variants in human platelets with emphasis on Glanzmann thrombasthenia
- PMID: 29385657
- PMCID: PMC5902390
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.365
In silico analysis of structural modifications in and around the integrin αIIb genu caused by ITGA2B variants in human platelets with emphasis on Glanzmann thrombasthenia
Abstract
Background: Studies on the inherited bleeding disorder, Glanzmann thrombasthenia (GT), have helped define the role of the αIIbβ3 integrin in platelet aggregation. Stable bent αIIbβ3 undergoes conformation changes on activation allowing fibrinogen binding and its taking an extended form. The αIIb genu assures the fulcrum of the bent state. Our goal was to determine how structural changes induced by missense mutations in the αIIb genu define GT phenotype.
Methods: Sanger sequencing of ITGA2B and ITGB3 in the index case followed by in silico modeling of all known GT-causing missense mutations extending from the lower part of the β-propeller, and through the thigh and upper calf-1 domains.
Results: A homozygous c.1772A>C transversion in exon 18 of ITGA2B coding for a p.Asp591Ala substitution in an interconnecting loop of the lower thigh domain of αIIb in a patient with platelets lacking αIIbβ3 led us to extend our in silico modeling to all 16 published disease-causing missense variants potentially affecting the αIIb genu. Modifications of structuring H-bonding were the major cause in the thigh domain although one mutation gave mRNA decay. In contrast, short-range changes induced in calf-1 appeared minor suggesting long-range effects. All result in severe to total loss of αIIbβ3 in platelets. The absence of mutations within a key Ca2+-binding loop in the genu led us to scan public databases; three potential single allele variants giving major structural changes were identiffied suggesting that this key region is not protected from genetic variation.
Conclusions: It appears that the αIIb genu is the object of stringent quality control to prevent platelets from circulating with activated and extended integrin.
Keywords: ITGA2B; Glanzmann thrombasthenia; genetic variants; in silico analysis; αIIb genu.
© 2018 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
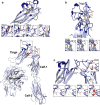
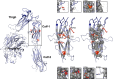
References
-
- Adair, B. D. , & Yeager, M. (2002). Three‐dimensional model of the human platelet integrin αIIbβ3 based on electron cryomicroscopy and x‐ray crystallography. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99, 14059–14064. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.212498199 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ballut, L. , Sapay, N. , Chautard, E. , Imberty, A. , & Ricard‐Blum, S. (2013). Mapping of heparin/heparin sulfate binding sites on αvβ3 integrin by molecular docking. Journal of Molecular Recognition, 26, 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmr.2250 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blue, R. , Li, J. , Steinberger, J. , Murcia, M. , Filizola, M. , & Coller, B. S. (2010). Effects of limiting extension at the alphaIIb genu on ligand binding to integrin alphaIIbbeta3. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 17604–17613. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.107763 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buitrago, C. L. , Rendon, A. , Liang, Y. , Simeoni, I. , Negri, A. , Consortium, T. , Filizola, M. , Ouwehand, W. H. , & Coller, B. S. (2015). 4151 αIIbβ3 variants defined by next‐generation sequencing: Predicting variants likely to cause Glanzmann thrombasthenia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112, E1898–E1907. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1422238112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carrell, N. A. , Fitzgerald, L. A. , Steiner, B. , Erickson, H. P. , & Phillips, D. R. (1985). Structure of human platelet membrane glycoproteins IIb and IIIa as determined by electron microscopy. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 260, 1743–1749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

