An elevated expression of serum exosomal microRNA-191, - 21, -451a of pancreatic neoplasm is considered to be efficient diagnostic marker
- PMID: 29385987
- PMCID: PMC5793347
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4006-5
An elevated expression of serum exosomal microRNA-191, - 21, -451a of pancreatic neoplasm is considered to be efficient diagnostic marker
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer is associated with an extremely poor prognosis, so new biomarkers that can detect the initial stages are urgently needed. The significance of serum microRNA (miR) levels in pancreatic neoplasm such as pancreatic cancer and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) diagnosis remains unclear. We herein evaluated the usefulness of miRs enclosed in serum exosomes (ExmiRs) as diagnostic markers.
Methods: The ExmiRs from patients with pancreatic cancer (n = 32) or IPMN (n = 29), and patients without neoplasms (controls; n = 22) were enriched using ExoQuick-TC™. The expression of ExmiRs was evaluated using a next-generation sequencing analysis, and the selected three miRs through this analysis were confirmed by a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
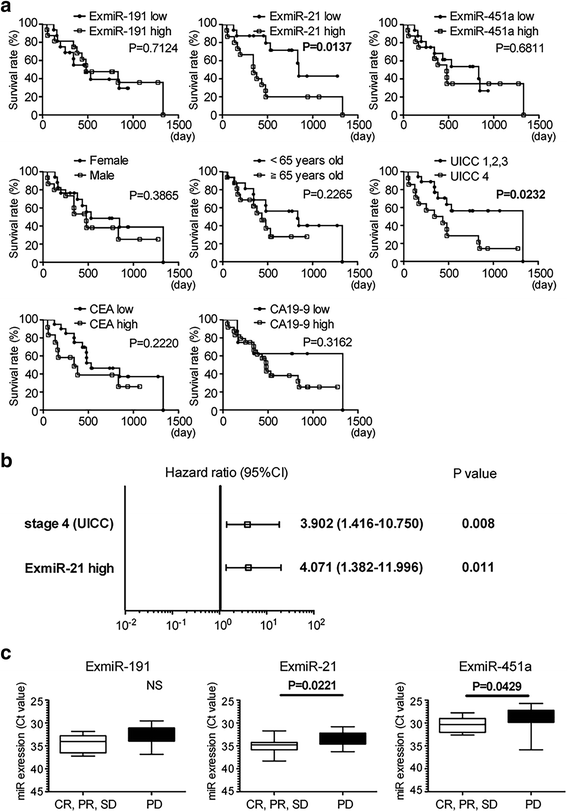
Results: The expression of ExmiR-191, ExmiR-21 and ExmiR-451a was significantly up-regulated in patients with pancreatic cancer and IPMN compared to the controls (p < 0.05). A receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that the area under the curve and the diagnostic accuracy of ExmiRs were 5-20% superior to those of three serum bulky circulating miRs (e.g.; ExmiR-21: AUC 0.826, accuracy 80.8%. Circulating miR-21: AUC 0.653, accuracy 62.3%). In addition, high ExmiR-451a was associated with mural nodules in IPMN (p = 0.010), and high ExmiR-21 was identified as a candidate prognostic factor for the overall survival (p = 0.011, HR 4.071, median OS of high-ExmiR-21: 344 days, median OS of low-ExmiR-21: 846 days) and chemo-resistant markers (p = 0.022).
Conclusions: The level of three ExmiRs can thus serve as early diagnostic and progression markers of pancreatic cancer and IPMN, and considered more useful markers than the circulating miRs (limited to these three miRs).
Keywords: Exosome; Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; Pancreatic cancer; Tumor marker; microRNA-21; microRNA-451a.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This retrospective study was conducted in accordance with the standards of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Asahikawa Medical University. (Number: 1303). All patients have provided written informed consent for their information to be stored and used in the hospital database.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors have read the journal’s policy on conflicts of interest and the journal’s authorship agreement. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Usefulness of exosome-encapsulated microRNA-451a as a minimally invasive biomarker for prediction of recurrence and prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2018 Feb;25(2):155-161. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.524. Epub 2018 Jan 16. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2018. PMID: 29130611
-
Exosome-encapsulated microRNA-4525, microRNA-451a and microRNA-21 in portal vein blood is a high-sensitive liquid biomarker for the selection of high-risk pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2019 Feb;26(2):63-72. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.601. Epub 2019 Jan 18. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2019. PMID: 30561106
-
Serum-derived exosomal miR-7977 combined with miR-451a as a potential biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 19;25(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13659-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39972247 Free PMC article.
-
Updates and Critical Evaluation on Novel Biomarkers for the Malignant Progression of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas.Anticancer Res. 2017 May;37(5):2185-2194. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11553. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28476781 Review.
-
Thirty years of experience with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: from discovery to international consensus.Digestion. 2014;90(4):265-72. doi: 10.1159/000370111. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Digestion. 2014. PMID: 25591885 Review.
Cited by
-
Alternating exosomes and their mimetics as an emergent strategy for targeted cancer therapy.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Aug 10;9:939050. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.939050. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36032679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Exosomes in Pancreatic Cancer From Bench to Clinical Application: An Updated Review.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 26;11:644358. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.644358. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Potential Role of Liquid Biopsy as a Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Predictive Biomarker in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Cells. 2023 Dec 19;13(1):3. doi: 10.3390/cells13010003. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38201207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating exosomal microRNAs as novel potential detection biomarkers in pancreatic cancer.Oncol Lett. 2020 Aug;20(2):1432-1440. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11691. Epub 2020 May 30. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32724386 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic cancer cell-derived exosomal microRNA-27a promotes angiogenesis of human microvascular endothelial cells in pancreatic cancer via BTG2.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jan;24(1):588-604. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14766. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31724333 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

