miRNA-23a/CXCR4 regulates neuropathic pain via directly targeting TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome axis
- PMID: 29386025
- PMCID: PMC5791181
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-018-1073-0
miRNA-23a/CXCR4 regulates neuropathic pain via directly targeting TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome axis
Abstract
Background: Chemokine CXC receptor 4 (CXCR4) in spinal glial cells has been implicated in neuropathic pain. However, the regulatory cascades of CXCR4 in neuropathic pain remain elusive. Here, we investigated the functional regulatory role of miRNAs in the pain process and its interplay with CXCR4 and its downstream signaling.
Methods: miRNAs and CXCR4 and its downstream signaling molecules were measured in the spinal cords of mice with sciatic nerve injury via partial sciatic nerve ligation (pSNL). Immunoblotting, immunofluorescence, immunoprecipitation, and mammal two-hybrid and behavioral tests were used to explore the downstream CXCR4-dependent signaling pathway.
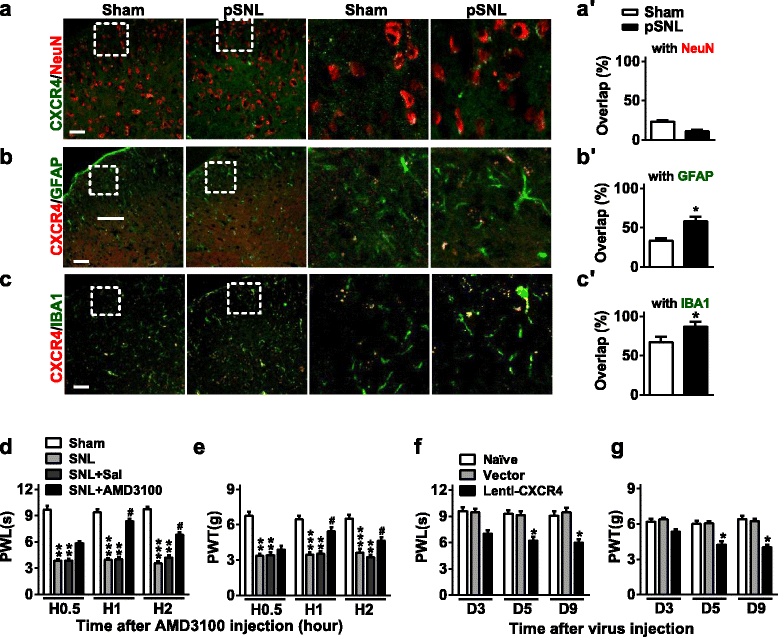
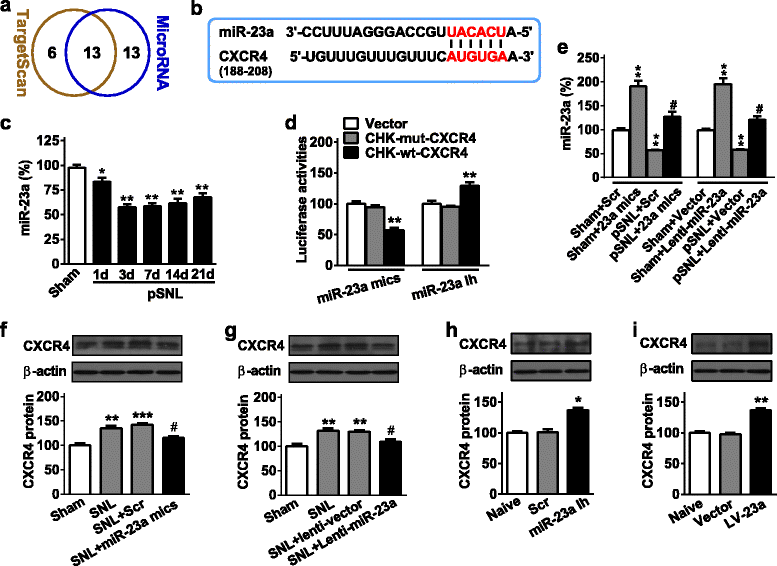
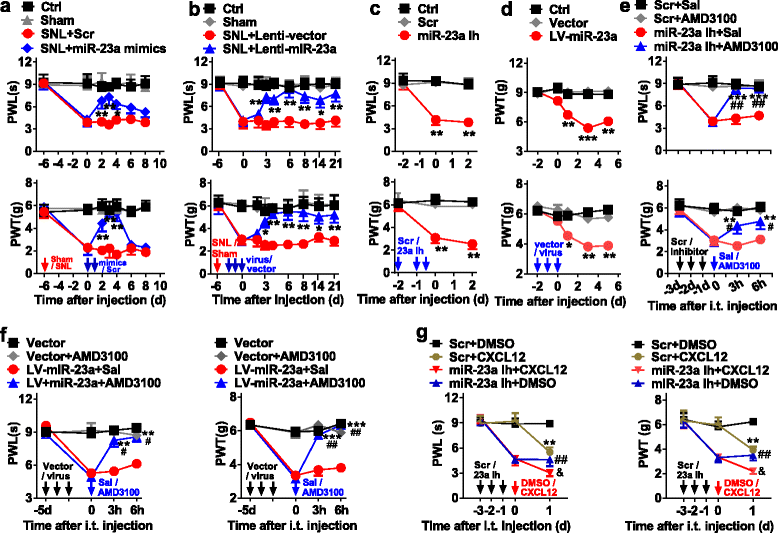
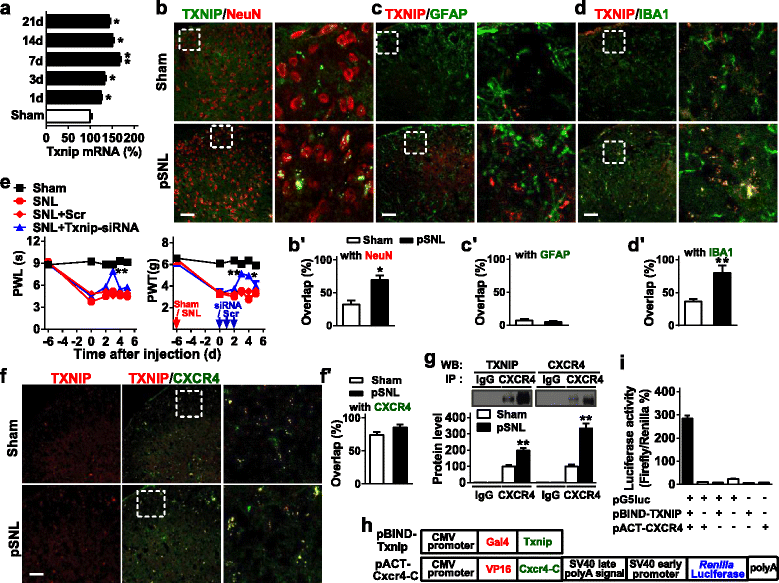
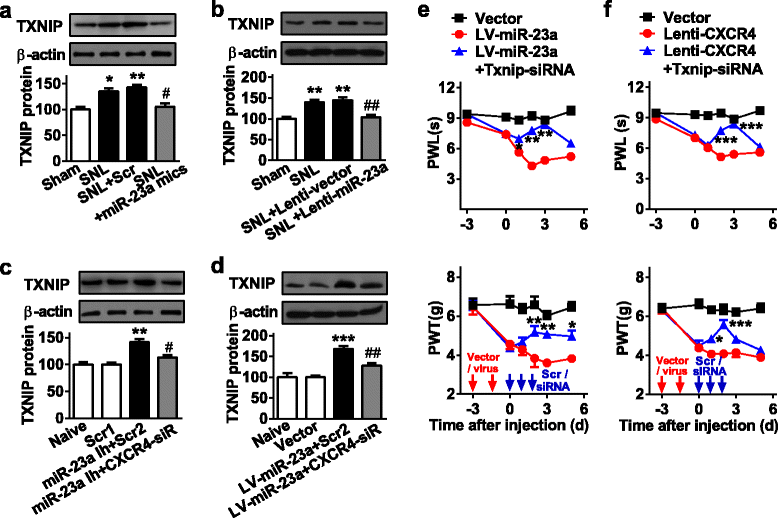
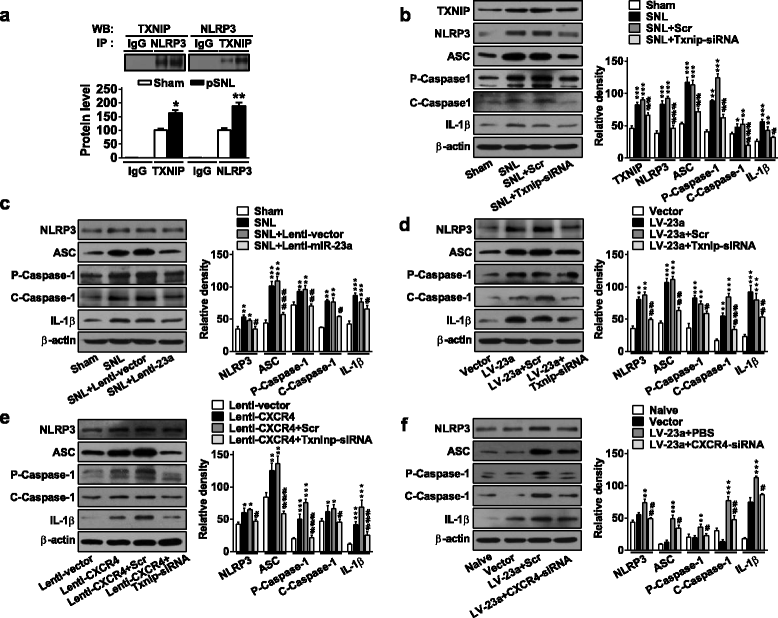
Results: CXCR4 expression increased in spinal glial cells of mice with pSNL-induced neuropathic pain. Blocking CXCR4 alleviated the pain behavior; contrarily, overexpressing CXCR4 induced pain hypersensitivity. MicroRNA-23a-3p (miR-23a) directly bounds to 3' UTR of CXCR4 mRNA. pSNL-induced neuropathic pain significantly reduced mRNA expression of miR-23a. Overexpression of miR-23a by intrathecal injection of miR-23a mimics or lentivirus reduced spinal CXCR4 and prevented pSNL-induced neuropathic pain. In contrast, knockdown of miR-23a by intrathecal injection of miR-23a inhibitor or lentivirus induced pain-like behavior, which was reduced by CXCR4 inhibition. Additionally, miR-23a knockdown or CXCR4 overexpression in naïve mice could increase the thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP), which was associated with induction of NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. Indeed, CXCR4 and TXNIP were co-expressed. The mammal two-hybrid assay revealed the direct interaction between CXCR4 and TXNIP, which was increased in the spinal cord of pSNL mice. In particular, inhibition of TXNIP reversed pain behavior elicited by pSNL, miR-23a knockdown, or CXCR4 overexpression. Moreover, miR-23a overexpression or CXCR4 knockdown inhibited the increase of TXNIP and NLRP3 inflammasome in pSNL mice.
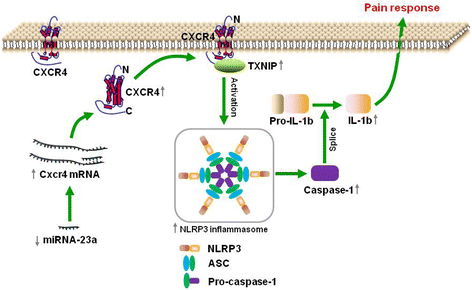
Conclusions: miR-23a, by directly targeting CXCR4, regulates neuropathic pain via TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome axis in spinal glial cells. Epigenetic interventions against miR-23a, CXCR4, or TXNIP may potentially serve as novel therapeutic avenues in treating peripheral nerve injury-induced nociceptive hypersensitivity.
Keywords: CXCR4; NLRP3 inflammasome; Sciatic nerve injury; Spinal glia cell; TXNIP; miRNA-23a.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All procedures were approved by the Committee on the Use of Live Animals in Teaching and Research and performed according to the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals as established by the Laboratory Animal Unit at the University of Hong Kong.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Attenuation of mechanical pain hypersensitivity by treatment with Peptide5, a connexin-43 mimetic peptide, involves inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome in nerve-injured mice.Exp Neurol. 2018 Feb;300:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.10.016. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Exp Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29055716
-
MicroRNA-152 attenuates neuroinflammation in intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP)-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Mar;80:106141. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106141. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31982825
-
IRE1α inhibition decreased TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation through miR-17-5p after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Feb 2;15(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1077-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29394934 Free PMC article.
-
NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasomes and peripheral neuropathic pain - Emphasis on microRNAs (miRNAs) as important regulators.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 15;955:175901. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175901. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37451423 Review.
-
Physiological and Pathophysiological Roles of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein: A Perspective on Redox Inflammation and Metabolism.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Feb;38(4-6):442-460. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0022. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 35754346 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human PMSCs-derived small extracellular vesicles alleviate neuropathic pain through miR-26a-5p/Wnt5a in SNI mice model.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Sep 7;19(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02578-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 36071475 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs in neuropathic pain.Neuronal Signal. 2020 Apr;4(1):NS20190099. doi: 10.1042/NS20190099. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Neuronal Signal. 2020. PMID: 32587755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduction of SIRT1 epigenetically upregulates NALP1 expression and contributes to neuropathic pain induced by chemotherapeutic drug bortezomib.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Oct 20;15(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1327-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30342528 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA SMEK1 promotes neuropathic pain in rats through targeting microRNA-216a-5p to mediate Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP) expression.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):5540-5551. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1965811. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34517790 Free PMC article.
-
Maresin 1 Attenuates Radicular Pain Through the Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome-Induced Pyroptosis via NF-κB Signaling.Front Neurosci. 2020 Aug 26;14:831. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00831. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32982664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knerlich-Lukoschus F, von der Ropp-Brenner B, Lucius R, Mehdorn HM, Held-Feindt J. Spatiotemporal CCR1, CCL3(MIP-1alpha), CXCR4, CXCL12(SDF-1alpha) expression patterns in a rat spinal cord injury model of posttraumatic neuropathic pain. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;14:583–597. doi: 10.3171/2010.12.SPINE10480. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

