Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for radiation-induced lung injury
- PMID: 29386045
- PMCID: PMC5793340
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-018-0776-6
Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for radiation-induced lung injury
Abstract
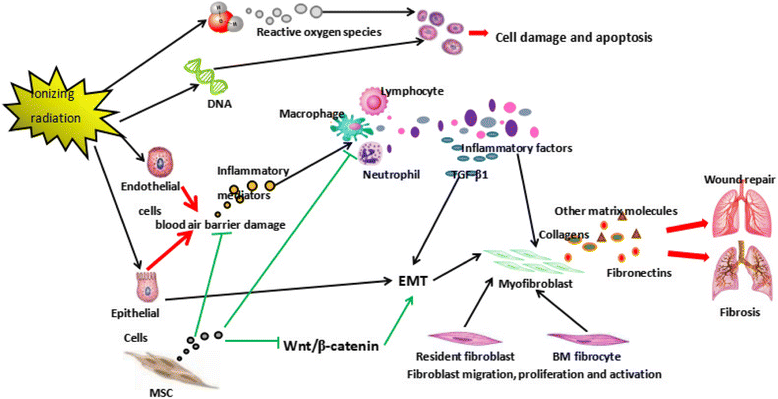
Since radiotherapy is widely used in managing thoracic tumors, physicians have begun to realize that radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) seriously limits the effects of radiotherapy. Unfortunately, there are still no effective methods for controlling RILI. Over the last few decades numerous studies have reported the beneficial effects of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) on tissue repair and regeneration. MSCs can not only differentiate into lung alveolar epithelial cells and secrete anti-inflammatory factors, but they also deliver some vehicles for gene therapy in repairing the injured lung, which provides new ideas for managing RILI. Thus, many scientists have attempted to manage RILI using MSC-based therapy. However, as a novel therapy MSCs still face various limitations. Herein, we shed light on the current understanding of MSC-based therapy for RILI, including the feasibility, molecular mechanisms, animal studies, and clinical research of MSC-based therapy for RILI. We also present an overview of RILI and MSCs.
Keywords: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs); Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI); Stem cell therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Not applicable.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-Induced Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Exhibit an Enhanced Therapeutic Effect on Radiation-Induced Lung Injury in Mice due to an Increased Proliferation Potential and Enhanced Antioxidant Ability.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(4):1295-1310. doi: 10.1159/000485490. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29183009
-
Applications and therapeutic mechanisms of action of mesenchymal stem cells in radiation-induced lung injury.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Mar 25;12(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02279-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33766127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intravenous delivery of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuates acute radiation-induced lung injury in rats.Cytotherapy. 2015 May;17(5):560-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2015.02.011. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Cytotherapy. 2015. PMID: 25791071
-
Concise Review: Therapeutic Potential of the Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Secretome and Extracellular Vesicles for Radiation-Induced Lung Injury: Progress and Hypotheses.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019 Apr;8(4):344-354. doi: 10.1002/sctm.18-0038. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30618085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Radiation-Induced Lung Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 8;20(16):3876. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163876. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31398940 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-466f-3p reverses EMT process through inhibiting AKT/GSK3β pathway via c-MET in radiation-induced lung injury.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Apr 7;41(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02351-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35392967 Free PMC article.
-
NVP-AUY922 alleviates radiation-induced lung injury via inhibition of autophagy-dependent ferroptosis.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Feb 26;8(1):86. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00887-9. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35220409 Free PMC article.
-
[Normal mouse serum alleviates radiation pneumonitis in mice by inhibiting the focal adhesion signaling pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 May 20;44(5):801-809. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.01. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38862437 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the protein kinase B/nuclear factor kappa B pathway.World J Stem Cells. 2025 Jun 26;17(6):106488. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488. World J Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40585959 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviation of pulmonary fibrosis by the dual PPAR agonist saroglitazar and breast milk mesenchymal stem cells via modulating TGFß/SMAD pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Aug;397(8):5953-5974. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03004-y. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38376539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mouiseddine M, Francois S, Semont A, Sache A, Allenet B, Mathieu N, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells home specifically to radiation-injured tissues in a non-obese diabetes/severe combined immunodeficiency mouse model. Br J Radiol. 2007;80(Spec No 1):S49–55 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources